| [1] Zwierzchowski TJ, Stasikowska-Kanicka O, Danilewicz M, et al. Assessment of apoptosis and MMP-1, MMP-3 and TIMP-2 expression in tibial hyaline cartilage after viable medial meniscus transplantation in the rabbit. Arch Med Sci.2012;8(6):1108-1114. [2] Fukui T, Tenborg E, Yik JH, et al. In-vitro and in-vivo imaging of MMP activity in cartilage and joint injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2015;460(3): 741-746. [3] Sun S, Bay-Jensen AC, Karsdal MA, et al. The active form of MMP-3 is a marker of synovial inflammation and cartilage turnover in inflammatory joint diseases. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2014;20(15):93-96. [4] Gotoh M, Mitsui Y, Shibata H, et al. Increased matrix metalloprotease-3 gene expression in ruptured rotator cuff tendons is associated with postoperative tendon retear. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(8): 1807-1812. [5] Ni GX, Zhan LQ, Gao MQ, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 inhibitor retards treadmill running-induced cartilage degradation in rats.Arthritis Res Ther.2011;13(6):R192. [6] Hesek D, Toth M, Meroueh SO, et al.Design and characterization of a metalloproteinase inhibitor-tethered resin for the detection of active MMPs in biological samples. Chem Biol.2006; 13(4):379-386. [7] 房学迅,杨金刚,史秀娟.来源于天然产物的基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)抑制剂[J].化学进展,2007,19(12):1991-1998. [8] 宁志刚,杨柳,王富友,等.保留钙化层结构的猪股骨滑车全厚软骨缺损模型建立[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2012, 26(5):527-531. [9] Moran ME, Kim HK, Salter RB. Biological resurfacing of full-thickness defects in patellar articular cartilage of the rabbit. Investigation of autogenous periosteal grafts subjected to continuous passive motion.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1992;74(5):659-667. [10] Koskinen A,Vuolteenaho K,Moilanen T,et al.Resistin as a factor in osteoarthritis: synovial fluid resistin concentrations correlate positively with interleukin 6 and matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1 and MMP-3.Scand J Rheumatol.2014;43(3):249-253. [11] Bassiouni HM, El-Deeb M, Kenawy N, et al. Phonoarthrography, musculoskeletal ultrasonography, and biochemical biomarkers for the evaluation of knee cartilage in osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21(5): 500-508. [12] Wang YL, Li XJ, Qin RF, et al.Matrix metalloproteinase and its inhibitor in temporomandibular joint osteoarthrosis after indirect trauma in young goats[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2008;46(3):192-197. [13] Troeberg L,Lazenbatt C,Anower-E-Khuda MF, et al. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans control the extracellular trafficking and the activity of the metalloprotease inhibitor TIMP-3. Chem Biol. 2014; 21(10):1300-1309. [14] Tourville TW, Poynter ME, Desarno MJ, et al. Relationship between synovial fluid ARGS-aggrecan fragments, cytokines, MMPs, and TIMPs following acute ACL injury: A cross-sectional study. J Orthop Res.2015;33(12):1796-803. [15] Haller JM,Swearingen CA,Partridge D,et al. Intraarticular Matrix Metalloproteinases and Aggrecan Degradation Are Elevated After Articular Fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2015;22(10):132-136. [16] 方舒锴,史晨辉,董金波,等.关节腔注射强力霉素对兔膝骨关节炎模型的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2009,9(19): 3664-3666. [17] 陈操,秦超,刘维钢,等. 白介素18髓核内注射对兔椎间盘作用的实验研究[J]. 石河子大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 28(5):587-591. [18] 刘志翔,张柳,张楠.降钙素对兔骨关节炎软骨基质金属蛋白酶1的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(22): 1741-1743, 页4. [19] 詹荔琼,党娜,高美钦,等.大鼠膝关节软骨与不同强度跑台运动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(20): 3634- 3638. [20] Roos EM, Dahlberg L.Positive effects of moderate exercise on glycosaminoglycan content in knee cartilage: a four-month, randomized, controlled trial in patients at risk of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum.2005; 52(11):3507-3514. |
.jpg)
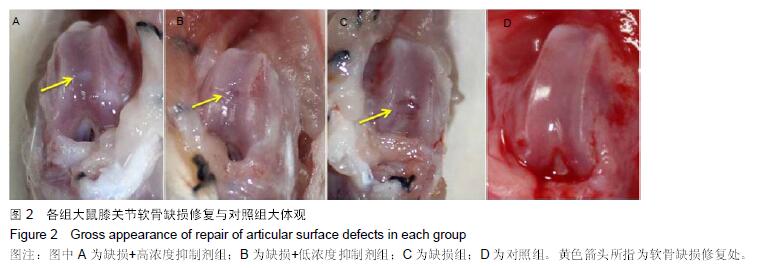
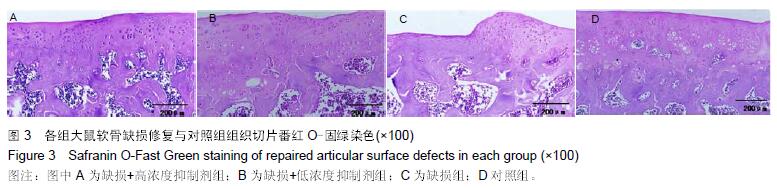
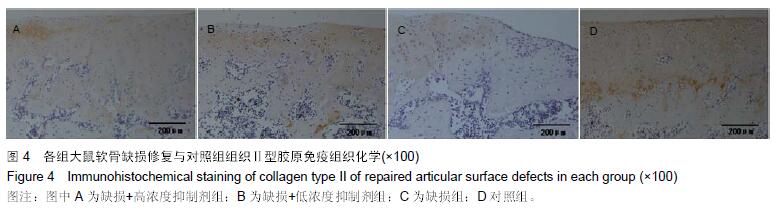
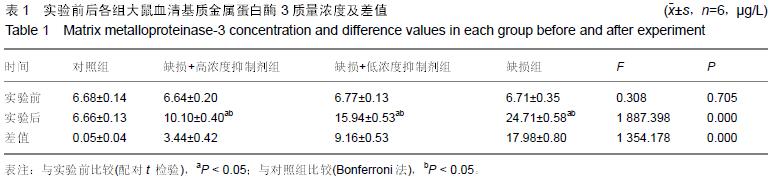
.jpg)
.jpg)