中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (14): 2123-2128.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.14.022
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇
脐血间充质干细胞移植对心肌细胞凋亡的影响
王艳丽1,李金峰1,王艳萍2,高 明1
- 1唐山市开滦总医院心内科,河北省唐山市 063000;2唐山市遵化市人民医院,河北省唐山市 064200
Effect of umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on myocardial cell apoptosis
Wang Yan-li1, Li Jin-feng1, Wang Yan-ping2, Gao Ming1
- 1Department of Cardiology, Tangshan Kailuan General Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 2People’s Hospital of Zunhua, Tangshan 064200, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
心肌细胞:又称心肌纤维,受自主神经支配,属于有横纹的不随意肌,具有兴奋收缩的能力。各心肌纤维分支的末端可相互连接构成肌纤维网。根据它们的组织学特点、电生理特性以及功能上的区别,粗略地分为两大类型:一类是普通的心肌细胞,包括心房肌和心室肌,含有丰富的肌原纤维;另一类是一些特殊分化的心肌细胞,组成心脏的特殊传导系统,称为自律细胞,它们含肌原纤维甚小或完全缺乏,故收缩功能已基本丧失。
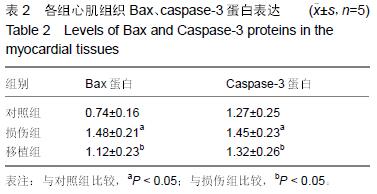
bax和caspase-3:bax基因属于bcl-2基因家族,编码的Bax蛋白可与Bcl-2形成异二聚体,对Bcl-2产生阻抑作用。研究发现Bax/Bcl-2两蛋白之间的比例关系是决定对细胞凋亡抑制作用强弱的关键因素,因此认为,bax是极重要的促细胞凋亡基因之一。caspase-3是凋亡过程中最关键的凋亡执行蛋白酶,一旦被信号途径激活,能将细胞内的蛋白质降解,使细胞不可逆的走向死亡。
背景:研究发现,脐血间充质干细胞移植可为减少心肌细胞凋亡、减轻心肌纤维化、改善心脏功能发挥作用。
目的:观察脐血间充质干细胞移植对大鼠心肌细胞凋亡的影响。
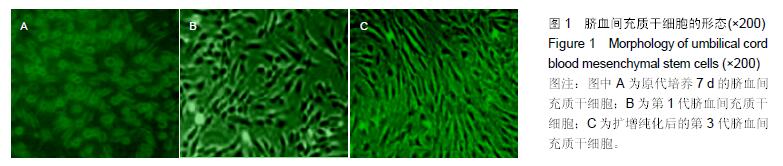
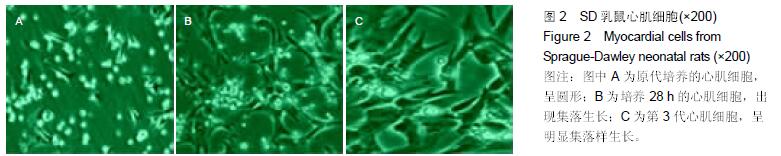
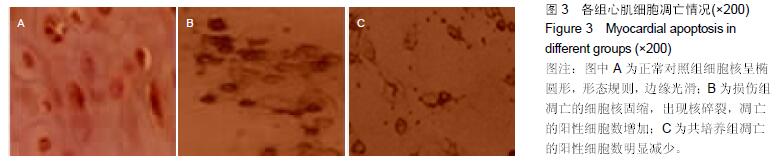
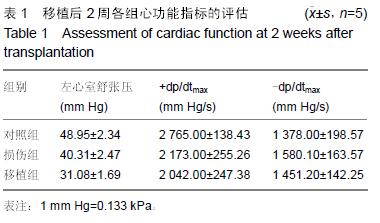
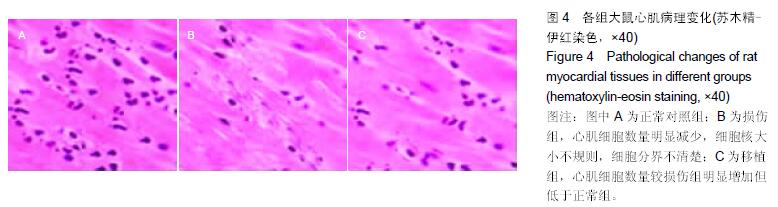
方法:①体外实验:将原代培养72 h的正常心肌细胞作为对照组,阿霉素损伤心肌细胞作为损伤组,阿霉素损伤心肌细胞与脐血间充质干细胞共培养作为共培养组,培养48 h采用TUNEL染色评估心肌细胞的凋亡情况;②体内实验:SD大鼠45只,随机分为正常对照组、阿霉素组、脐血间充质干细胞移植组,移植后2周采用Powerlab检查心功能,蛋白质免疫印迹法检测凋亡相关蛋白Bax、Caspase-3表达水平,组织学观察各组心肌病理变化。
结果与结论:①正常对照组的心肌细胞凋亡率较低,损伤组心肌细胞凋亡明显增加,共培养组凋亡率显著降低,各组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②与阿霉素组比较,脐血间充质干细胞移植组的心功能指标明显降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),但仍高于正常对照组(P < 0.05);③阿霉素组心肌细胞损伤后Bax、Caspase-3表达水平较高,脐血间充质干细胞移植组Bax、Caspase-3表达水平降低 (P < 0.05),但仍高于正常对照组(P < 0.05);④与阿霉素组比较,脐血间充质干细胞移植组心肌梗死面积显著减小(P < 0.05),但仍高于正常对照组(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,脐血间充质干细胞作用能够抑制阿霉素诱导的大鼠心肌细胞的凋亡,其发挥作用的途径可能与下调Bax、Caspase-3的表达水平有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-7125-4281(王艳丽)

.jpg)