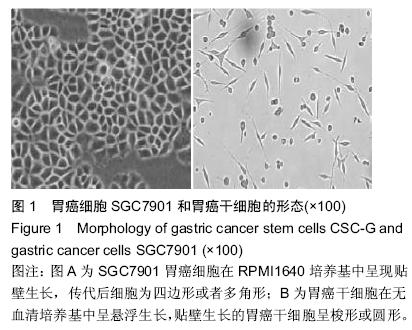
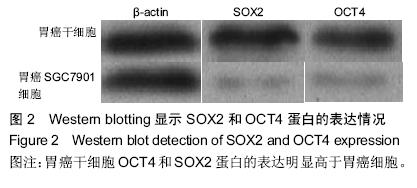
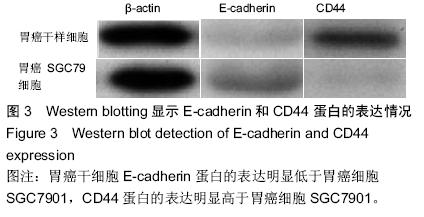
| [1] 郑朝旭,郑荣寿,陈万青.中国2009年胃癌发病与死亡分析中国肿瘤,2013,22(5):327-332.[2] 李子禹,季鑫,季加孚.新辅助化疗对胃癌手术并发症的影响[J].中国实用外科杂志,2013,(4):275-278.[3] 樊永丽,赵华,于津浦,等.胃癌患者术后化疗联合CIK免疫治疗的临床疗效[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2012,19(2): 168-174.[4] 吴楠蝶,魏嘉,刘宝瑞.胃癌分子靶向治疗的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2014,27(12):1318-1322.[5] 保秋萍,李惠民.肿瘤干细胞的耐药性与耐药机制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(1):116-119.[6] Cabezas-Wallscheid N, Trumpp A. Stem cells. Potency finds its niches. Science. 2016;351(6269):126-127. [7] 南今娘,胡续光,李洪秀.肿瘤干细胞研究国际发展态势:基于国际数据库的文献检索结果分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(6):1085-1094.[8] 侯萍,李剑平.肿瘤干细胞的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(14):2629-2632.[9] Bautista W, Klein J, Cuvelier S, et al. Cancer stem cell invasion of the hepatic microvasculature as a predictor of tumour recurrence following surgical resection in adult patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;29(8):409.[10] Papadopoulou A, Kaloyannidis P, Yannaki E, et al. Adoptive transfer of Aspergillus-specific T cells as a novel anti-fungal therapy for hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: progress and challenges. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015.[11] 王瑞海.肿瘤干细胞的分离培养及生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27):5087-5090.[12] 陈浩,许浪.信号通路对胃癌干细胞及胃癌发生的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(14):2532-2537.[13] 乐雄,杨德同,张洪海.胃癌干细胞对氟尿嘧啶敏感性及化疗药物耐受细胞的生物学机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(19):3022-3026.[14] Hayakawa Y, Ariyama H, Stancikova J, et al. Mist1 Expressing Gastric Stem Cells Maintain the Normal and Neoplastic Gastric Epithelium and Are Supported by a Perivascular Stem Cell Niche. Cancer Cell. 2015;28(6): 800-814. [15] Wen Z, Feng S, Wei L, et al. Evodiamine, a novel inhibitor of the Wnt pathway, inhibits the self-renewal of gastric cancer stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(6):1657-1663. [16] Brungs D, Aghmesheh M, Vine KL, et al.Gastric cancer stem cells: evidence, potential markers, and clinical implications. J Gastroenterol. 2015. [17] 宋东颖,王毅,孙岚,等.肿瘤干细胞理论及肿瘤干细胞分离和鉴定研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2012,26(5): 674-679.[18] 赵小琴,符立梧.肿瘤干细胞耐药机制研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2012,28(12):1637-1642.[19] Doherty MR, Smigiel JM, Junk DJ, et al. Cancer Stem Cell Plasticity Drives Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2016;8(1):8. [20] 张雁.肿瘤干细胞理论的演变[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2012,33(6):701-708.[21] 乔明曦,张晓君,巴爽,等.肿瘤干细胞靶向给药系统的研究进展[J].药学学报,2013,48(4):477-483.[22] Valizadeh A, Ahmadzadeh A, Saki G, et al. Role of tumor necrosis factor-producing mesenchymal stem cells on apoptosis of chronic b-lymphocytic tumor cells resistant to fludarabine-based chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(18):8533-8539.[23] 李姗姗,王丽,边育红.基于肿瘤干细胞的恶性肿瘤靶向治疗策略[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015,(2):309-314.[24] White PT, Subramanian C, Zhu Q, et al. Novel HSP90 inhibitors effectively target functions of thyroid cancer stem cell preventing migration and invasion. Surgery. 2016;159(1):142-151.[25] 王旗春,田艳萍.肿瘤干细胞的调控机制及其临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(43):8557-8560. [26] Gemenetzidis E, Gammon L, Biddle A, et al.Invasive oral cancer stem cells display resistance to ionising radiation. Oncotarget. 2015;6(41):43964-43977. [27] Zhu X, Niedermann G. Rapid and efficient transfer of the T cell aging marker CD57 from glioblastoma stem cells to CAR T cells. Oncoscience. 2015;2(5):476-482.[28] Younan PM, Peterson CW, Polacino P, et al. Lentivirus-mediated Gene Transfer in Hematopoietic Stem Cells Is Impaired in SHIV-infected, ART-treated Nonhuman Primates. Mol Ther. 2015;23(5):943-951. [29] 吕阳,许戈良.肿瘤干细胞与肿瘤转移的关系[J].中国普通外科杂志,2013,22(3):359-362.[30] 李士亭,陶文成.肿瘤干细胞表面标记物CD44在胃癌浸润和淋巴结转移中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(23):3669-3673.[31] Xu M, Gong A, Yang H, et al. Sonic hedgehog-glioma associated oncogene homolog 1 signaling enhances drug resistance in CD44(+)/Musashi-1(+) gastric cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2015;369(1):124-133. [32] Liang S, Li C, Zhang C, et al. CD44v6 monoclonal antibody-conjugated gold nanostars for targeted photoacoustic imaging and plasmonic photothermal therapy of gastric cancer stem-like cells. Theranostics. 2015;5(9):970-984. [33] 李阳,赵永福.胃癌干细胞的分离、鉴定及其特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5188-5192.[34] 何学彦,张超.胃癌干细胞对5-氟尿嘧啶的敏感性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(41):6606-6610.[35] Nishikawa S, Konno M, Hamabe A,et al.Surgically resected human tumors reveal the biological significance of the gastric cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD26. Oncol Lett. 2015;9(5):2361-2367. [36] Zhou L, Yu L, Feng ZZ, et al. Aberrant expression of markers of cancer stem cells in gastric adenocarcinoma and their relationship to vasculogenic mimicry. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(10):4177-4183.[37] Cheng J, Wang J, Peng Y, et al. Research on gastric cancer stem cells: current status, problems and future directions. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014;36(11): 801-804. [38] 李荣,李蓉,戴光荣.顺铂在大鼠体内富集胃癌干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(41):6611-6615.[39] Simmini S, Bialecka M, Huch M, et al. Transformation of intestinal stem cells into gastric stem cells on loss of transcription factor Cdx2. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5728. [40] Morisaki T, Yashiro M, Kakehashi A, et al. Comparative proteomics analysis of gastric cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e110736. |
.jpg)