中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (10): 1508-1520.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.10.020
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
脂肪干细胞分离、纯化和保存:研究进展与未来方向
陈犹白1,2,陈聪慧3,Qixu Zhang2,韩 岩1
- 1解放军总医院整形修复科,北京市 100853;2美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森肿瘤中心整形外科,美国休斯敦 77030;3美莱医疗美容医院口腔美容中心,北京市 100020
-
收稿日期:2016-01-16出版日期:2016-03-04发布日期:2016-03-04 -
通讯作者:韩岩,主任医师,教授,博士生导师,解放军总医院整形修复科,北京市 100853 并列通讯作者:Qixu Zhang,助理教授,美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森肿瘤中心整形外科,休斯敦 77030 -
作者简介:陈犹白,男,1986年生,黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市人,汉族,解放军医学院在读博士,美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森肿瘤中心联合培养博士,医师,主要从事脂肪干细胞和组织工程的研究。
Isolation, purification and preservation of adipose-derived stem cells: research progress and future development
Chen You-bai1, 2, Chen Cong-hui3, Qixu Zhang2, Han Yan1
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 2Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston 77030, Texas, USA; 3Dental Cosmetic Center, Mylike Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery Hospital, Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2016-01-16Online:2016-03-04Published:2016-03-04 -
Contact:Han Yan, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 1000853, China Corresponding author: Qixu Zhang, Assistant professor, Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston 77030, Texas, USA -
About author:Chen You-bai, Studying for doctorate, Physician, Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 1000853, China; Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston 77030, Texas, USA
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
结果与结论:脂肪组织分布广泛,给脂肪干细胞提供了充足的来源。利用吸脂术获得脂肪组织,患者痛苦小,供区损伤低。胶原酶消化法操作简单,产量高,仍然是基础实验中脂肪干细胞的主要分离方法,但是临床应用中一般不分离脂肪干细胞,或者利用临床级的无异种胶原酶甚至无酶的分离方法。脂肪干细胞的产量、表型、增殖和分化能力等生物学特性会受到取材和分离过程中多种因素的影响,因此目前需要制定标准化的脂肪干细胞分离准则。
ORCID: 0000-0002-6810-2957 (韩岩)
引用本文
陈犹白,陈聪慧,Qixu Zhang,韩 岩. 脂肪干细胞分离、纯化和保存:研究进展与未来方向[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(10): 1508-1520.
Chen You-bai, Chen Cong-hui, Qixu Zhang, Han Yan. Isolation, purification and preservation of adipose-derived stem cells: research progress and future development[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(10): 1508-1520.
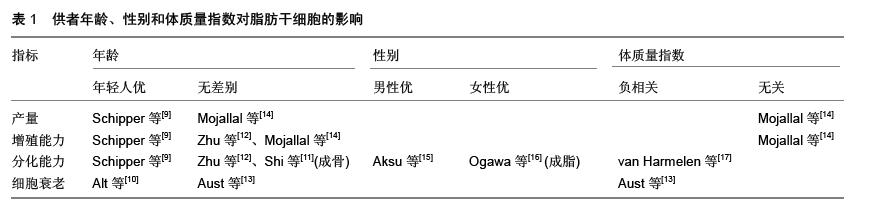

2.2.4 脂肪取材部位 Schipper等[9]认为人前臂脂肪组织中的干细胞含量最多,而腹部皮下浅层脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞的生命力和抗凋亡能力最强。Van Harmelen等[17]认为皮下脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞比内脏脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞增殖能力强。Oedayrajsingh-Varma等[20]认为腹部、臀部和乳房的脂肪干细胞产量无明显差异。Faustini等[21]则认为男性的腹部脂肪干细胞产量高于背部和膝盖。Macotela等[22]、Hauner等[23]认为皮下脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞分化成脂能力优于内脏和大腿脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞。Toyoda等[24]认为腹部皮下脂肪和腹腔大网膜脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞增殖能力没有明显差异,但是前者具有更强的分化能力。Cawthorn等[25]认为内脏脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞的成脂能力强于皮下脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞,但是增殖能力则较弱。Jurgens等[26]认为腹部脂肪提取的脂肪干细胞产量比侧腹、臀部、大腿等部位高,但其增殖能力和分化成骨和软骨能力没有差异。Fraser等[27]的研究显示侧腹的脂肪干细胞产量高于腹部。Prunet-Marcassus等[28]认为腹股沟脂肪组织分离的基质血管成分的分化和增殖能力较强。Jacob等认为皮下深层脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞可能更适合作为细胞疗法的脂肪供区。Sinno等[29]回顾分析了相关脂肪移植的相关文章,发现不同部位的脂肪活性无明显差异(循证等级Ⅳ)。
.jpg)
| [1] Zuk PA. The adipose-derived stem cell: looking back and looking ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11): 1783-1787.[2] Becker AJ, Mcculloch EA, Till JE. Cytological demonstration of the clonal nature of spleen colonies derived from transplanted mouse marrow cells. Nature. 1963;197:452-454.[3] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6(2):230-247.[4] Prindull G, Prindull B, Meulen N. Haematopoietic stem cells (CFUc) in human cord blood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978;67(4):413-416.[5] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052): 1707-1710.[6] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.[7] Shore EM, Ahn J, Jan de Beur S, et al. Paternally inherited inactivating mutations of the GNAS1 gene in progressive osseous heteroplasia. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(2):99-106.[8] 吴尉,梁芳,宋小琴,等.人脂肪干细胞的提取和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(28):4498-4502.[9] Schipper BM, Marra KG, Zhang W, et al. Regional anatomic and age effects on cell function of human adipose-derived stem cells. Ann Plast Surg. 2008; 60(5):538-544.[10] Alt EU, Senst C, Murthy SN, et al. Aging alters tissue resident mesenchymal stem cell properties.Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(2):215-225.[11] Shi Y, Niedzinski JR, Samaniego A, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells combined with a demineralized cancellous bone substrate for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(13-14): 1313-1321.[12] Zhu M, Kohan E, Bradley J, et al. The effect of age on osteogenic, adipogenic and proliferative potential of female adipose-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2009;3(4):290-301.[13] Aust L, Devlin B, Foster SJ, et al. Yield of human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(1):7-14. [14] Mojallal A, Lequeux C, Shipkov C, et al. Influence of age and body mass index on the yield and proliferation capacity of adipose-derived stem cells. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2011;35(6):1097-1105.[15] Aksu AE, Rubin JP, Dudas JR, et al. Role of gender and anatomical region on induction of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Ann Plast Surg. 2008;60(3):306-322.[16] Ogawa R, Mizuno H, Watanabe A, et al. Adipogenic differentiation by adipose-derived stem cells harvested from GFP transgenic mice-including relationship of sex differences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 319(2):511-517.[17] van Harmelen V, Skurk T, Röhrig K, et al. Effect of BMI and age on adipose tissue cellularity and differentiation capacity in women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003; 27(8):889-895.[18] Cianfarani F, Toietta G, Di Rocco G, et al. Diabetes impairs adipose tissue-derived stem cell function and efficiency in promoting wound healing.Wound Repair Regen. 2013;21(4):545-553.[19] Eterno V, Zambelli A, Pavesi L, et al. Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ASCs) may favour breast cancer recurrence via HGF/c-Met signaling. Oncotarget. 2014;5(3):613-633.[20] Oedayrajsingh-Varma MJ, van Ham SM, Knippenberg M, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell yield and growth characteristics are affected by the tissue-harvesting procedure. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(2): 166-177.[21] Faustini M, Bucco M, Chlapanidas T, et al. Nonexpanded mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine: yield in stromal vascular fraction from adipose tissues.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(6):1515-1521.[22] Macotela Y, Boucher J, Tran TT, et al. Sex and depot differences in adipocyte insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Diabetes. 2009;58(4):803-812.[23] Hauner H, Entenmann G. Regional variation of adipose differentiation in cultured stromal-vascular cells from the abdominal and femoral adipose tissue of obese women. Int J Obes. 1991;15(2):121-126.[24] Toyoda M, Matsubara Y, Lin K, et al. Characterization and comparison of adipose tissue-derived cells from human subcutaneous and omental adipose tissues. Cell Biochem Funct. 2009;27(7):440-447.[25] Cawthorn WP, Scheller EL, MacDougald OA. Adipose tissue stem cells meet preadipocyte commitment: going back to the future. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(2): 227-246.[26] Jurgens WJ, Oedayrajsingh-Varma MJ, Helder MN, et al. Effect of tissue-harvesting site on yield of stem cells derived from adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;332(3): 415-426.[27] Fraser J, Wulur I, Alfonso Z, et al. Differences in stem and progenitor cell yield in different subcutaneous adipose tissue depots. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(5): 459-467.[28] Prunet-Marcassus B, Cousin B, Caton D, et al. From heterogeneity to plasticity in adipose tissues: site-specific differences. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(6):727-736.[29] Sinno S, Wilson S, Brownstone N, et al. Current Thoughts on Fat Grafting: Using the Evidence to Determine Fact or Fiction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016; 137(3):818-824.[30] Iyyanki T, Hubenak J, Liu J, et al. Harvesting technique affects adipose-derived stem cell yield. Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35(4):467-476.[31] Vallée M, Côté JF, Fradette J. Adipose-tissue engineering: taking advantage of the properties of human adipose-derived stem/stromal cells. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2009;57(4):309-317.[32] Schreml S, Babilas P, Fruth S, et al. Harvesting human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: resection versus liposuction. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(7):947-957.[33] Pu LL, Coleman SR, Cui X, et al. Autologous fat grafts harvested and refined by the Coleman technique: a comparative study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122(3): 932-937.[34] Keck M, Zeyda M, Gollinger K, et al. Local anesthetics have a major impact on viability of preadipocytes and their differentiation into adipocytes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(5):1500-1505.[35] Eom YW, Lee JE, Yang MS, et al. Rapid isolation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells by the storage of lipoaspirates. Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(6):999-1007.[36] 肖建红,张阳春,张常然,等. 人皮下脂肪干细胞的成骨、成脂分化诱导及鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(32):5155-5161.[37] Locke M, Windsor J, Dunbar PR. Human adipose- derived stem cells: isolation, characterization and applications in surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2009;79(4): 235-244.[38] Gimble JM, Bunnell BA, Frazier T, et al. Adipose- derived stromal/stem cells: a primer. Organogenesis. 2013;9(1):3-10.[39] 赵娜.脂肪干细胞诱导分化的现状及前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(6):969-974.[40] 刘琴,王丽平,喻晶,等.组织块贴壁法扩增兔脂肪干细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(1):88-93.[41] Priya N, Sarcar S, Majumdar AS, et al. Explant culture: a simple, reproducible, efficient and economic technique for isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from human adipose tissue and lipoaspirate. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(9):706-716.[42] Jing W, Xiao J, Xiong Z, et al. Explant culture: an efficient method to isolate adipose-derived stromal cells for tissue engineering. Artif Organs. 2011;35(2): 105-112.[43] Doi K, Kuno S, Kobayashi A, et al. Enrichment isolation of adipose-derived stem/stromal cells from the liquid portion of liposuction aspirates with the use of an adherent column. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(3):381-391.[44] Markarian CF, Frey GZ, Silveira MD, et al. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: a comparison among different methods. Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36(4): 693-702.[45] Zeng G, Lai K, Li J, et al. A rapid and efficient method for primary culture of human adipose-derived stem cells. Organogenesis. 2013;9(4):287-295.[46] Kurita M, Matsumoto D, Shigeura T, et al. Influences of centrifugation on cells and tissues in liposuction aspirates: optimized centrifugation for lipotransfer and cell isolation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121(3): 1033-1041.[47] Yoshimura K, Shigeura T, Matsumoto D, et al. Characterization of freshly isolated and cultured cells derived from the fatty and fluid portions of liposuction aspirates. J Cell Physiol. 2006;208(1):64-76.[48] 张鉴清,季佳霖,崔新明,等.小鼠附睾脂肪干细胞的分离培养及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(28):4535- 4541.[49] Krähenbühl SM, Grognuz A, Michetti M, et al. Enhancement of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Expansion and Stability for Clinical use. Int J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015.[50] 依里牙尔•依里哈木,王云海,王理,等.脂肪干细胞体外分离培养鉴定及免疫学性质[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(14):2167-2172.[51] Lee RH, Kim B, Choi I, et al. Characterization and expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004;14(4-6):311-324.[52] Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, et al. Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J Med. 2005;54(3):132-141.[53] Bunnell BA, Flaat M, Gagliardi C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods. 2008;45(2):115-120.[54] Chieregato K, Castegnaro S, Madeo D, et al. Epidermal growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor-bb can substitute for fetal bovine serum and compete with human platelet-rich plasma in the ex vivo expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from adipose tissue. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(8):933-943.[55] Tunaitis V, Borutinskait? V, Navakauskien? R, et al. Effects of different sera on adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(9):733-746.[56] Dromard C, Bourin P, André M, et al. Human adipose derived stroma/stem cells grow in serum-free medium as floating spheres. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317(6): 770-780.[57] Mischen BT, Follmar KE, Moyer KE, et al. Metabolic and functional characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells in tissue engineering. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122(3):725-738.[58] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12):4279-4295.[59] 侯晓琳,郁卫东,崔梅花,等.小鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的分离培养及肠道归巢[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(6): 854-860.[60] 刘子琪,孙同文,万有栋,等 脂肪源性干细胞体外分离培养及向内皮祖细胞的诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(32):5182-5187.[61] Francis MP, Sachs PC, Elmore LW, et al. Isolating adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from lipoaspirate blood and saline fraction. Organogenesis. 2010;6(1):11-14.[62] Gierloff M, Petersen L, Oberg HH, et al. Adipogenic differentiation potential of rat adipose tissue-derived subpopulations of stromal cells. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67(10):1427-1435.[63] Jiang A, Li M, Duan W, et al. Improvement of the survival of human autologous fat transplantation by adipose-derived stem-cells-assisted lipotransfer combined with bFGF. ScientificWorldJournal. 2015; 2015:968057.[64] 曹菁,姜南,徐扬阳,等.人脂肪干细胞促进小鼠随意型皮瓣血管的新生[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(19):2993- 2998.[65] Yu G, Wu X, Dietrich MA, et al. Yield and characterization of subcutaneous human adipose-derived stem cells by flow cytometric and adipogenic mRNA analyzes. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(4):538-546.[66] Wan Safwani WK, Makpol S, Sathapan S, et al. The changes of stemness biomarkers expression in human adipose-derived stem cells during long-term manipulation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2011;58(4): 261-270.[67] Kocaoemer A, Kern S, Klüter H, et al. Human AB serum and thrombin-activated platelet-rich plasma are suitable alternatives to fetal calf serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2007;25(5):1270-1278.[68] Matsumoto D, Shigeura T, Sato K, et al. Influences of preservation at various temperatures on liposuction aspirates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120(6): 1510-1517.[69] Chaput B, Orio J, Garrido I, et al. A clinical scalable cryopreservation method of adipose tissue for reconstructive surgery assessed by stromal vascular fraction and mice studies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 133(4):815-826.[70] Choudhery MS, Badowski M, Muise A, et al. Cryopreservation of whole adipose tissue for future use in regenerative medicine. J Surg Res. 2014;187(1): 24-35.[71] Erol OO, Agaoglu G. Facial rejuvenation with staged injections of cryopreserved fat and tissue cocktail: clinical outcomes in the past 10 years. Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33(5):639-653.[72] Atik B, Oztürk G, Erdo?an E, et al. Comparison of techniques for long-term storage of fat grafts: an experimental study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118(7): 1533-1537.[73] 刘玉平,刘涛,王明明,等.人髌下脂肪垫来源脂肪间充质干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(41):6566-6571.[74] 曹娜,裴路,张微.脂肪干细胞和生物支架应用于牙槽骨修复[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(1):137-142.[75] Gonda K, Shigeura T, Sato T, et al. Preserved proliferative capacity and multipotency of human adipose-derived stem cells after long-term cryopreservation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121(2): 401-410.[76] Dariolli R, Bassaneze V, Nakamuta JS, et al. Porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells retain their proliferative characteristics, senescence, karyotype and plasticity after long-term cryopreservation. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e67939.[77] 戴兵,徐海艇,金海东,等.低氧对脂肪干细胞和关节软骨细胞三维共培养成软骨能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(29):4630-4635.[78] 张慧,郑红光,张德伟,等.雌激素影响冻存肾脂肪囊来源脂肪间充质干细胞的成脂分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(27):4998-5004.[79] 马洪斌,李运祥,王铭伦.腺病毒携带骨形态发生蛋白14基因转染脂肪干细胞修复损伤关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(1):54-60.[80] 黄成龙,肖金刚.脂肪干细胞成骨分化及与复合支架结合:在修复骨质疏松症骨缺损中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(41):6696-6702.[81] Mizuno H. Adipose-derived stem cells for tissue repair and regeneration: ten years of research and a literature review. J Nippon Med Sch. 2009;76(2):56-66. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 张同同, 王中华, 文 杰, 宋玉鑫, 刘 林. 3D打印模型在颈椎肿瘤手术切除与重建中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [6] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [8] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [9] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [10] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [11] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [12] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [13] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [14] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
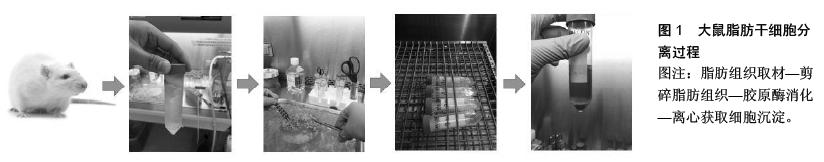
文献筛选流程:按照图1的步骤进行。
.jpg)
文献筛选的标准:通过标题及摘要判断其主要内容与脂肪干细胞的分离、纯化、传代培养和冻存相关,根据被引次数,文献作者和所在期刊进行初选。
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||