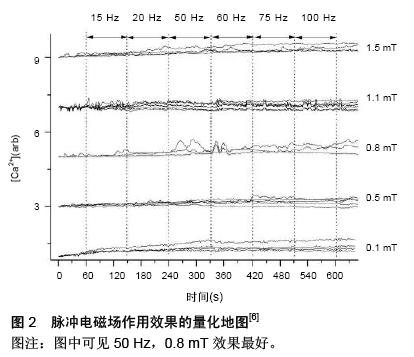
| [1] Sollazzo V, Palmieri A, Pezzetti F,et al.Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on human osteoblastlike cells (MG-63): a pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(8):2260-2277.[2] Ongaro A, Pellati A, Bagheri L,et al.Pulsed electromagnetic fields stimulate osteogenic differentiation in human bone marrow and adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2014;35(6):426-436.[3] 黄晶晶,杨福军,赵吉,等.脉冲电磁场对大鼠成骨细胞作用的研究[J].天津医药,2012,40(7):685-687.[4] 周建,陈克明,葛宝丰,等.50 Hz正弦交变电磁场促进体外培养成骨细胞分化成熟的双“强度窗”效应[J].生理物理学报,2011,27(6):507-516.[5] Selvamurugan N, Kwok S, Vasilov A,et al.Effects of BMP-2 and pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) on rat primary osteoblastic cell proliferation and gene expression.J Orthop Res. 2007;25(9):1213-1220.[6] Zhang X, Liu X, Pan L,et al.Magnetic fields at extremely low-frequency (50 Hz, 0.8 mT) can induce the uptake of intracellular calcium levels in osteoblasts.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;396(3):662-666.[7] Jansen JH, van der Jagt OP, Punt BJ,et al.Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation in human osteoprogenitor cells by pulsed electromagnetic fields: an in vitro study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:188.[8] 李志锋,程国政,陈克明,等.不同强度脉冲电磁场对大鼠颅骨成骨细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].西北国防医学杂志, 2010, 31(3):179-181.[9] 谢肇,李起鸿,许建中,等.脉冲电磁场对去卵巢骨质疏松症大鼠成骨细胞和破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2007,29(1):8-12.[10] Chang K, Chang WH, Tsai MT,et al.Pulsed electromagnetic fields accelerate apoptotic rate in osteoclasts.Connect Tissue Res. 2006;47(4):222-228.[11] Shankar VS, Simon BJ, Bax CM,et al.Effects of electromagnetic stimulation on the functional responsiveness of isolated rat osteoclasts.J Cell Physiol. 1998;176(3):537-544.[12] Chen J, He HC, Xia QJ,et al.Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on the mRNA expression of RANK and CAII in ovariectomized rat osteoclast-like cell.Connect Tissue Res. 2010;51(1):1-7.[13] Zhou J, He H, Yang L,et al.Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone mass and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats.Arch Med Res. 2012;43(4):274-282. [14] 沈伟伟,赵建华脉冲电磁场对废用性骨质疏松大鼠骨密度和血清转化生长因子β1的影响[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2009,31(10):935-937.[15] 白洁,赵红斌,王朝旭,等.脉冲电磁场对去势大鼠腰椎细胞因子IL-6、TNF-α和骨密度的影响[J].西北国防医学杂志,2011,32(2):115-117.[16] He J, Zhang Y, Chen J,et al.Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on the expression of NFATc1 and CAII in mouse osteoclast-like cells.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015;27(1):13-19.[17] Barnaba SA, Ruzzini L, Di Martino A,et alClinical significance of different effects of static and pulsed electromagnetic fields on human osteoclast cultures.Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(4):1025-1031. [18] Li K, Ma S, Li Y,et al.Effects of PEMF exposure at different pulses on osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 cells.Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(9):921-927. [19] Brighton CT, Wang W, Seldes R,et al.Signal transduction in electrically stimulated bone cells.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(10):1514-1523.[20] Petecchia L, Sbrana F, Utzeri R,et al.Electro-magnetic field promotes osteogenic differentiation of BM-hMSCs through a selective action on Ca(2+)-related mechanisms. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13856.[21] 秦茵.低频脉冲电磁场治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床观察[J].福州总医院学报,2009,16(3):256-257.[22] 尹晶,王俊华,王刚,等.低强度脉冲电磁场对绝经后骨质疏松症患者U-DPD与BMD的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2011,17(9):773-775.[23] 谢小波,崔红岩,庞丽云,等.脉冲电磁场用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛的疗效评估及分析[J].国际生物医学工程杂志, 2011,34(2):107-110.[24] 杨闯,周贤刚,何成奇.低频脉冲电磁场为主治疗骨质疏松症疼痛的影响因素分析[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2008,30(10):706-708.[25] [25] Giusti A, Giovale M, Ponte M,et al.Short-term effect of low-intensity, pulsed, electromagnetic fields on gait characteristics in older adults with low bone mineral density: a pilot randomized-controlled trial.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13(2):393-397.[26] 覃裕,邱冰,朱思刚,等.唑来膦酸盐联合脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(8):945-948.[27] 黄小娟.降钙素配合低频脉冲电磁场治疗骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].中国医学装备,2014,(5):66-67,68.[28] 孙锦波,吴军,包远祥,等.脉冲电磁场联合阿仑膦酸钠和注射用骨肽治疗骨质疏松症的临床观察[J].大家健康(下旬版),2014,(5): 155.[29] 黄明炜,廖勇敢,李艳丽,等.补肾益骨膏联合低频脉冲电磁场治疗老年原发性骨质疏松症临床观察[J].中国老年保健医学,2013,11(4):43-45. |
.jpg)