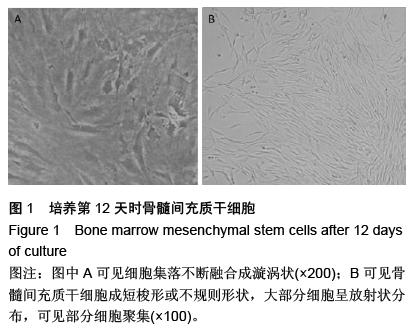
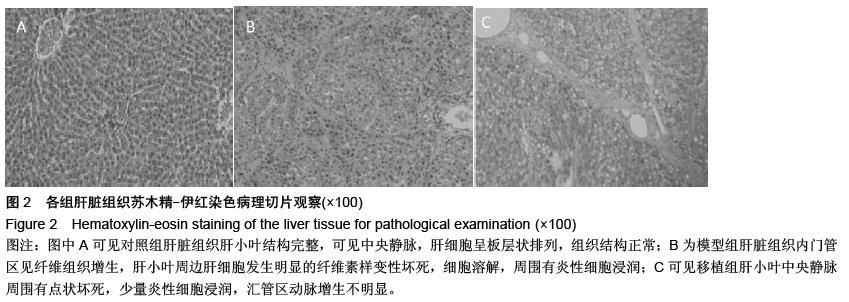
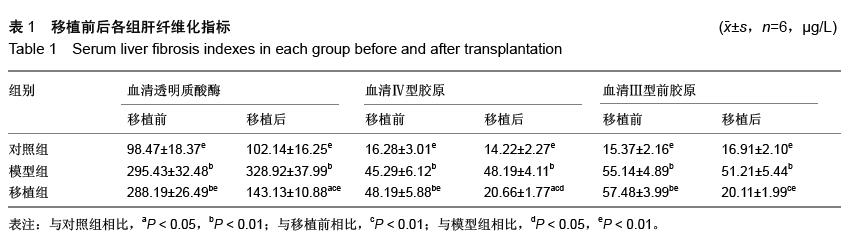
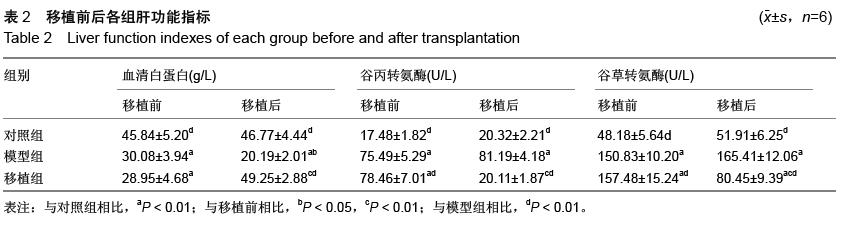
| [1] Truong NH, Nguyen NH, Le TV, et al. Comparison of the Treatment Efficiency of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation via Tail and Portal Veins in CCl4-Induced Mouse Liver Fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:5720413.
[2] Liu Y, Yang X, Jing Y, et al. Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2015;5:17762.
[3] Wang J, Xu L, Chen Q, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing FGF4 contribute to liver regeneration in an animal model of liver cirrhosis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):12774-12782.
[4] Zhu Y, Miao Z, Gong L, et al.Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells expressing TIMP-1-shRNA improves hepatic fibrosis in CCl?-treated rats.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(8):8912-8920.
[5] Baligar P, Mukherjee S, Kochat V, et al. Molecular and Cellular Functions Distinguish Superior Therapeutic Efficiency of Bone Marrow CD45 Cells Over Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Liver Cirrhosis.Stem Cells. 2016;34(1):135-147.
[6] Jang YO, Jun BG, Baik SK,et al. Inhibition of hepatic stellate cells by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in hepatic fibrosis.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015; 21(2):141-149.
[7] Song YM, Lian CH, Wu CS, et al. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplanted via the portal vein or tail vein on liver injury in rats with liver cirrhosis.Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(4):1292-1298.
[8] Ahmed SK, Mohammed SA, Khalaf G, et al. Role of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of CCL4 Induced Liver Fibrosis in Albino Rats: A Histological and Immunohistochemical Study. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7(2):87-97.
[9] Meier RP, Mahou R, Morel P,et al.Microencapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells decrease liver fibrosis in mice.J Hepatol. 2015;62(3):634-641.
[10] Ayatollahi M, Hesami Z, Jamshidzadeh A, et al. Antioxidant Effects of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Oxidative Damage in Rat Livers. Int J Organ Transplant Med. 2014;5(4):166-173.
[11] 张孝良,商中华,王满仓,等.不同时期骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肝纤维化的作用[J].中国现代医生,2010, 48(5): 11-12.
[12] Tsai PC, Fu TW, Chen YM, et al. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly in the treatment of rat liver fibrosis. Liver Transpl. 2009;15(5):484-495.
[13] Novo E, Busletta C, Bonzo LV, et al. Intracellular reactive oxygen species are required for directional migration of resident and bone marrow-derived hepatic pro-fibrogenic cells.J Hepatol. 2011;54(5):964-974.
[14] Chu AS, Diaz R, Hui JJ, et al. Lineage tracing demonstrates no evidence of cholangiocyte epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in murine models of hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 2011;53(5):1685-1695.
[15] Kato J, Koda M, Kishina M, et al. Therapeutic effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, irbesartan, on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis using FLS-ob/ob male mice.Int J Mol Med. 2012;30(1):107-113.
[16] Buechler C, Wanninger J, Neumeier M.Adiponectin, a key adipokine in obesity related liver diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(23):2801-2811.
[17] Henderson NC, Iredale JP. Standing down the guard: stellate cells leave quietly. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143(4):890-892.
[18] 中华医学会肝病学分会和感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2006,9(1):8-18.
[19] Brown A, Goodman Z. Hepatitis B-associated fibrosis and fibrosis/cirrhosis regression with nucleoside and nucleotide analogs. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;6(2):187-198.
[20] Jun DW, Tak WY, Bae SH, et al. Recent trends in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2012;18(1):22-28.
[21] Poynard T, McHutchison J, Manns M, et al. Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(5):1303-1313.
[22] Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA. Progressive fibrosis during corticosteroid therapy of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2004;39(6):1631-1638.
[23] Mathurin P, O'Grady J, Carithers RL, et al. Corticosteroids improve short-term survival in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis: meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gut. 2011;60(2):255-260.
[24] Violi F, Cangemi R. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363(12):1185-1186.
[25] 何潇,徐海帆.肝纤维化治疗进展[J].医学综述, 2009, 15(23):3639-3642.
[26] 崔东来,姚希贤,姚金锋,等. 丹参抗大鼠肝纤维化作用与机制研究[J].中华临床医药杂志,2002,3(13):5-7.
[27] 李校天,杨书良,王军民,等. 丹参对肝星状细胞丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路的抑制作用[J].解放军医学杂志, 2006, 31(1):22-24.
[28] 余小虎,朱金水,朱祖明,等. 氧化苦参碱对肝纤维化大鼠肝组织细胞因子表达水平的影响[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2006,9(5):257-259.
[29] 王清兰,陶艳艳,沈丽,等.扶正化瘀方影响转化生长因子β1/Smad 信号通路的抗肝纤维化作用机制[J].中西医结合学报,2012,10(5):561-568.
[30] 都金星,刘平,孙明瑜,等. 下瘀血汤对四氯化碳诱导的肝硬化大鼠肝脏血管新生的抑制作用[J].中西医结合学报, 2011,9(8):878-886.
[31] Cheng K, Yang N, Mahato RI. TGF-beta1 gene silencing for treating liver fibrosis. Mol Pharm. 2009; 6(3):772-779.
[32] Takami T, Terai S, Sakaida I. Novel findings for the development of drug therapy for various liver diseases: Current state and future prospects for our liver regeneration therapy using autologous bone marrow cells for decompensated liver cirrhosis patients. J Pharmacol Sci. 2011;115(3):274-278.
[33] Chen YX, Weng ZH, Zhang SL. Notch3 regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(12):1397-1403.
[34] Seki N, Toh U, Kawaguchi K, et al. Tricin inhibits proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells in vitro by blocking tyrosine phosphorylation of PDGF receptor and its signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2012; 113(7):2346-2355.
[35] 杨文,覃山羽,姜海行,等.骨髓间充质干细胞体外调控肝星状细胞死亡受体5的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(27):4947-4952.
[36] Wang PP, Xie DY, Liang XJ, et al. HGF and direct mesenchymal stem cells contact synergize to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation through TLR4/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43408.
[37] 欧阳石,刘树人,程涛,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞肝动脉移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(36):6455-6461.
[38] 陈双庆,王培军,李铭华,等.磁标记骨髓间充质干细胞对肝细胞癌的抑制作用[J].临床放射学杂志,2009,28(10): 1454-1458.
[39] Xie C, Xie DY, Lin BL, et al. Interferon-β gene-modified human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibiting AKT/FOXO3a pathway. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(5): 1198-1205.
[40] 李兰娟.肝衰竭诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志,2006,45(12): 1053.
[41] Hang HL, Xia Q. Role of BMSCs in liver regeneration and metastasis after hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(1):126-132.
[42] Milwid JM, Ichimura T, Li M, et al. Secreted factors from bone marrow stromal cells upregulate IL-10 and reverse acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012: 392050.
[43] 刘婷,贺永文.高迁移率族蛋白B1在急性肝功能衰竭小鼠中的表达变化[J].中华传染病杂志,2010,28(4):209-213.
[44] 易珍,孙水林,刘翠云,等.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞对急性肝衰竭HMGB1的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2012, 20(16):1396-1401.
[45] 顾劲扬,施晓雷,袁献温,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞诱导肝细胞耐受肝功能衰竭血清细胞毒性的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(2):308-311.
[46] Schrepfer S, Deuse T, Reichenspurner H, et al. Stem cell transplantation: the lung barrier. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(2):573-576.
[47] 何秀华,李东良,江军,等.移植途径对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞归巢及肝功能恢复的影响[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2012,1(1):57-62.
[48] di Bonzo LV, Ferrero I, Cravanzola C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword in hepatic regenerative medicine: engraftment and hepatocyte differentiation versus profibrogenic potential. Gut. 2008;57(2):223-231. |
.jpg)