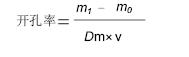| [1] 程琳,李玉宝,左奕,等.纳米轻基磷灰石/聚酞胺多孔支架材料的制备及其结晶行为研究[J].功能材料,2007,38(1):47-52.
[2] 蒋电明,权正学,欧云生.n-HA/PA66复合生物活性支撑材料在重建椎体结构中的初步临床应用[J].重庆医学, 2007, 36(11): 1010-1012.
[3] 蒋电明,权正学,黄伟.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性人工椎板的初步临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2007,21(5): 441-444.
[4] 蒋电明,权正学,欧云生.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性人工椎体在胸腰椎爆裂骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤杂志, 2006, 22(12):884-887.
[5] 王群波,蒋电明,李智.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合人工椎体治疗胸腰椎椎体肿瘤的效果[J].第三军医大学学报, 2006, 28(3): 263-265.
[6] Ito Z,Matsuyama Y,Sakai Y,et al. Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(21): E1101-1105.
[7] Watanabe K,Yamazaki A,Morita O,et al.Clinical outcomes of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar foraminal stenosis: preoperative diagnosis and surgical strategy. J Spinal Disord Tech.2011;24(3):137-141.
[8] Thian ES,Huang J,Ahmad Z,et al.Influence of nanohydroxyapatite patterns deposited by electrohydrodynamic spraying on osteoblast response.J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;85(1): 188-194.
[9] Abd El-Fattah H,Helmy Y,El-Kholy B,et al.In vivo animal histomorphometric study for evaluating biocompatibility and osteointegration of nano-hydroxyapatite as biomaterials in tissue engineering.J Egypat Natl Canclust.2010;22(4): 241-250.
[10] 梁熙,蒋电明,倪卫东.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合骨填充材料修复良性骨肿瘤骨缺损临床疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2007,21(8):785-788.
[11] 吴佳奇,杨天府,刘洋,等.多孔PA66 /n-HA复合MSCs修复兔膝关节骨软骨缺损的初步研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2008,25(6): 1349-1353.
[12] 郭涛,杨天府,肖杰,等.新型生物复合材料聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石+聚酰胺66修复关节软骨及软骨下骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(14):2623-2627.
[13] 张健,安洪,周爱国.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺复合材料人工肱骨头柄界面成骨的实验研究[J].激光杂志,2008,29(2):94-95.
[14] 梁勇,蒋电明.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66椎间融合器对山羊颈椎的融合效果研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2007, 29(24): 2333- 2335.
[15] 肖智博,吕富荣,吕发金,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺复合材料预防椎板切除后椎管狭窄、粘连的初步影像研究[J].重庆医科大学学报,2006,31(4):489-493.
[16] Wemer J,Lirmcr-Krcmar B,Friess W,et al.Mechanical properties and in vitro cell compatibility of hydroxyapatite ceramicswith graded pore structure.Biomaterials.2002; 23(21): 4285-4294.
[17] Ioletti DP,Takei H,Lin T,et al.The effects of calcium phosphate cementparticles on osteoblast function. Biomaterials. 2000; 21(10):1103-1114.
[18] 张凯,王大平,朱伟民,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与纳米羟基磷灰石支架材料题外相容性研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2011, 29(2): 213-217.
[19] Phipps MC,Clem WC,Catledge SA,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell responses to bone-mimetic electrospun matrices composed of poly caprolactone,collagen I and nanoparticulate hydroxyapatite.PLoS One.2011;6(2):e16813.
[20] 李鸿,李玉宝.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺 66 多孔材料制备和生物安全性初步评价[J].生物医学工程杂志,2008,25(5):1126-1129.
[21] 王明波,李玉宝,牟元华,等.纳米轻基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇/明胶复合水凝胶的结构与性能研究[J].功能材料,2006,37(9):1477-1480.
[22] 王迎军,杜昶,赵娜如,等.仿生人工骨修复材料研究[J].华南理工大学学报:自然科学版,2012,40(10):51-58.
[23] 廖世波,赖琛,张志雄,等.骨修复复合材料及其相关问题的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2012,31(5):755-761.
[24] Kolk A,Handschel J,Drescher W,et al.Current trends and future perspectives of bone substitute materials: from space holders to innovative biomaterials.J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg. 2012;40(8):706-718.
[25] Heo SJ,Kim SE,Wei J,et al.Fabrication and characterization of novel nano-and micro-HA/PCL composite scaffolds using a modified rapid prototyping process. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;89(1):108-116.
[26] Tsai SW,Hsu FY,Chen PL.Beads of collagen- nanohydroxyapatite composites prepared by a biomimetic process and the effects of their surface texture on cellular behavior in MG63 osteoblast-like cells.Acta Biomater. 2008; 4(5):1332-1341.
[27] Fukui N,Sato T,Kuboki Y,et al.Bone tissue reaction of nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen composite at the early stage of implantation.Biomed Mater Eng.2008;18(1):25-33.
[28] Cunniffe GM,Dickson GR,Partap S,et alDevelopment and characterization of a collagen nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(8):2293-2298.
[29] Zhou J,Xu C,Wu G,et al.In vitro generation of osteochondral differentiation of human marrow mesenchymal stem cells in novel collagen hydroxyapatite layered scaffolds.Acta Biomater. 2011;7(11):3999-4006.
[30] 任天斌,宋莹,冯明,等.热压-盐析法制备骨组织工程的工艺及性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13 (42): 8281-8285.
[31] Gupta A,Tripathi G,Lahiri D,et al.Compression molded ultra high molecular weight polyethylene-hydroxyapatite-aluminum oxide-carbon nanotube hybrid composites for hard tissue replacement.J Mater Sci Technol.2013;29(6):514-522.
[32] Fouad H,Elleithy R,Alothman OY.Thermo-mechanical,wear and fracture behavior of high-density polyethylene/ hydroxyapatite nano composite for biomedical applications: effect of accelerated ageing.J Mater Sci Technol. 2013;29(6): 573-581.
[33] 王珍萍,黄苏萍,周科朝.原位矿化法制备羟基磷灰石/高密度聚乙烯复合材料[J].粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2006,11(6):363-366.
[34] 李东梅,张盛忠,陈涛,等.羟基磷灰石/超高分子量聚乙烯复合材料的组织相容性及骨传导性试验研究[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2004,20(5):180-183.
[35] 周聪颖,李启期,魏杰,等.纳米氟磷灰石-聚醚醚酮种植体骨整合效能研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2013,29(1):20-24.
[36] 蒋电明,权正学,黄伟,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性人工椎板的初步临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2007, 21(5):441-444.
[37] 代震宇,李军,蒋电明,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸复合材料生物安全性评价[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,32(21):2294-2299.
[38] 许勇,朱立新,田京.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料与兔骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(8):1423-1426.
[39] 黄谦,吴涛,梁杰.全骨髓培养法和密度梯度离心法分离hBMSCs 的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009, 23 (11): 1360-1364.
[40] Xiao Y,Gong T,Zhou S.The functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by in situ deposition of hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials.2010;31(19):5182-5190. |
.jpg)
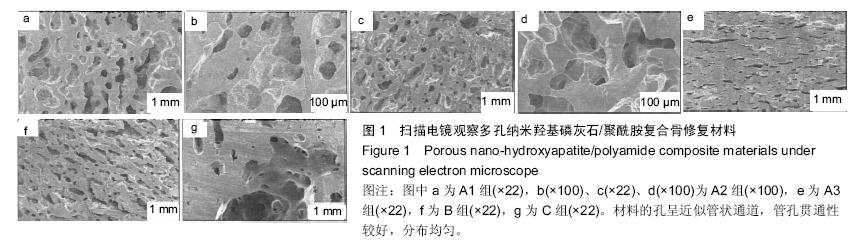
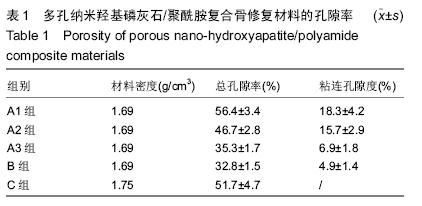
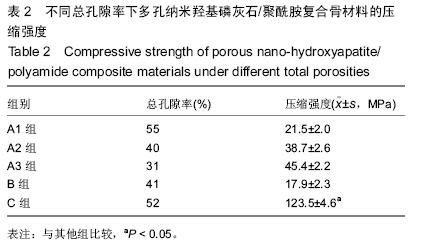
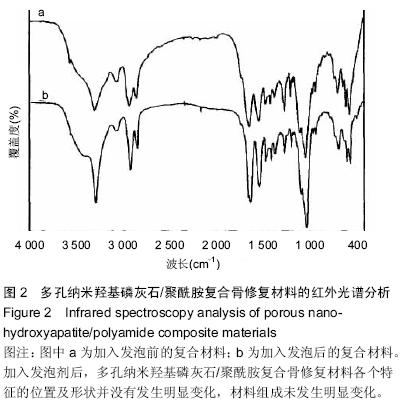
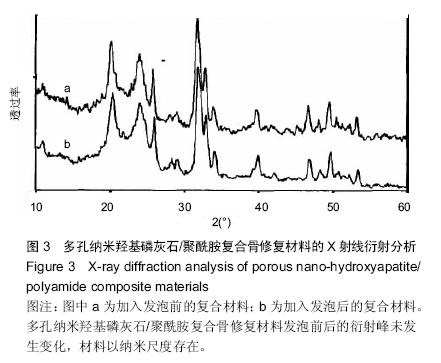
.jpg)
.jpg)