1.1 设计 材料学实验。
1.2 时间及地点 于2007年11月至2009年6月在中国医科大学实验技术中心完成。
1.3 材料
试件:溶胶-共沉淀法制备的ZrO2/Al2O3复合粉体(ZrO2/Al2O3比例分别为1∶1、4∶1),经模压成型,1 450 ℃烧结成型,试样尺寸为3 mm×2 mm×30 mm,于2006年5月至2008年9月在沈阳理工大学表面技术中心制作完成[16]。
细胞株:选用对数生长期的L- 929细胞(小鼠成纤维细胞株),由中国医科大学实验技术中心提供。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 体外细胞毒性实验
材料浸提液的制备:试样(ZrO2/Al2O3比例分别为1∶1,4∶1)以无水乙醇超声清洗20 min,再用蒸馏水冲洗,常规消毒、干燥。置DMEM培养基中,37 ℃,静置24 h,即得到材料浸提液。试件表面积与浸提液量之比0.5 cm2/mL,符合关于浸提液每毫升材料表面积大于0.5 cm2,小于6 cm2的规定。
细胞的传代培养与细胞悬液的制备:取复苏后的L-929细胞,放入37 ℃、95%相对湿度、体积分数5%CO2培养箱中静置培养,选取快速生长期的细胞,用体积分数0.25%胰蛋白酶消化后,制备成细胞浓度约为1.0×108 L-1的细胞悬液,备用。
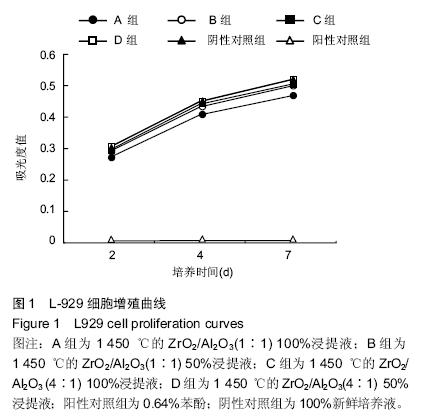
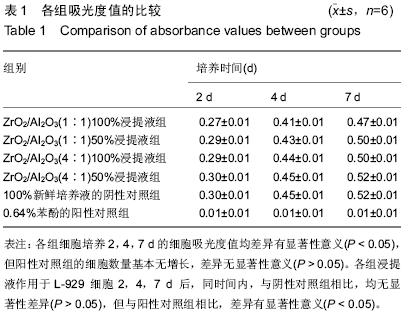
材料浸提液与细胞接种培养及分组:取96孔培养板,以200 μL/孔接种细胞悬液于96孔板,置37 ℃、体积分数5% CO2保温培养箱培养24 h,弃去原培养液进行浸提液200 μL交换,实验分6组:ZrO2/Al2O3(1∶1)100%浸提液组、ZrO2/Al2O3(1∶1)50%浸提液组、ZrO2/Al2O3(4∶1) 100%浸提液组、ZrO2/Al2O3(4∶1) 50%浸提液组,以及体积分数0.64%苯酚的阳性对照组和100%新鲜培养液的阴性对照组,n=6。以同样顺序接种96孔板,置于37 ℃、5%CO2保温培养箱培养,分别于培养2,4,7 d后观察结果。细胞计数,每次结果取均值,并绘制生长曲线。
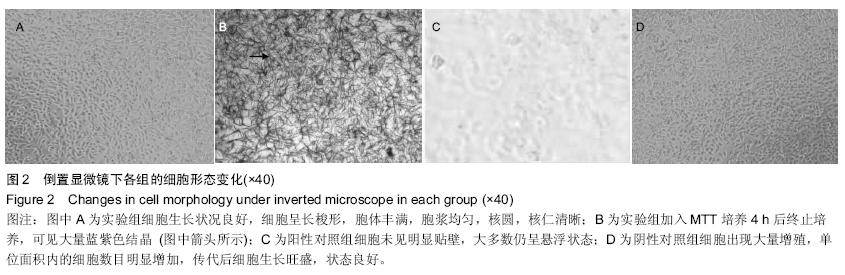
结果观察:分别于浸提液交换后的2,4,7 d取出一块96孔板,先置倒置相差显微镜下观察细胞形态,然后向各孔中加入20 μL MTT液(质量浓度5 g/L),继续培养4 h后终止培养,小心吸去上清,并以PBS缓冲液清洗2遍。每孔加入150 μL DMSO,新鲜DMEM培养液,置摇床上低速振荡10 min,使结晶物充分溶解,在酶标仪490 nm处测各孔的吸光度值。
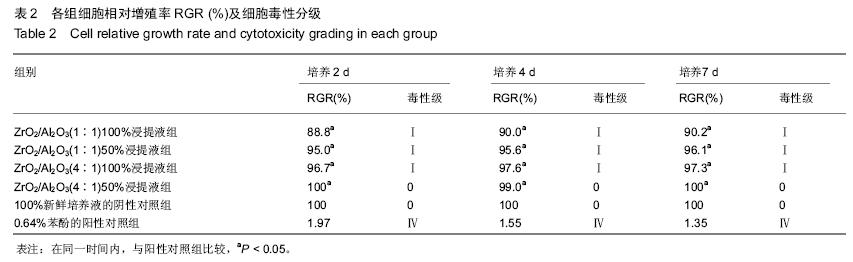
各实验组的细胞相对增殖率(RGR):
.jpg)
按0-5级方式将各组的RGR值转换为细胞毒性。
1.4.2 急性溶血实验
浸提液的制备:试样(ZrO2/Al2O3比例分别为1∶1、 4∶1)以无水乙醇超声清洗20 min,再用蒸馏水冲洗,在 121 ℃、33 MPa下灭菌处理,置于烘箱内烘干。然后置于玻璃瓶中,加入生理盐水使其达到表面积1.5 cm2/mL,然后在37℃水浴条件下浸泡72 h,即得到材料浸提液。
新鲜稀释兔血制备:抽取新西兰兔血10 mL,立即注入有质量浓度20 g/L草酸钾抗凝剂的试管中,从中取4 mL,加入含5 mL生理盐水的试管中,制成新鲜抗凝稀释兔血。
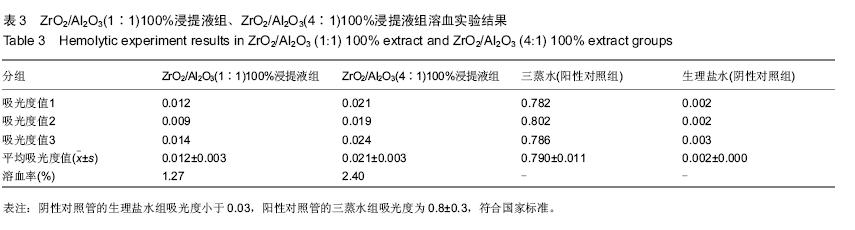
实验分组:ZrO2/Al2O3(1∶1)100%浸提液组、ZrO2/Al2O3(4∶1) 100%浸提液组、以及三蒸水的阳性对照组和生理盐水的阴性对照组。
每组取3个试管置于37 ℃恒温水浴中保持30 min后,各试管中加入稀释兔血0.2 mL,轻轻混匀,再置于37 ℃恒温水浴中保持60 min。
离心所有试管(2 500 r/min,5 min),分别吸取各试管中上清液,上清置于比色皿内,用MPS22000型岛津紫外分光光度仪在紫外线波长为545 nm波长下测吸光度值, 并计算溶血程度。
结果评价:溶血率按下列公式计算:溶血率(HR) =(样品吸光度-阴性对照吸光度)/(阳性对照吸光度-阴性对照吸光度)×100%
评判标准:溶血率大于5%时,可判断该材料具有溶血作用。阳性吸光度值应为0.8±0.3,阴性对照管吸光度应不大于0.03。若材料的溶血率< 5%则说明材料符合医用材料的溶血实验要求。
1.5 主要观察指标 对各组细胞浸提液进行细胞毒性评价并绘制生长曲线;计算各组细胞相对增殖率RGR(%)及细胞毒性分级;细胞相容性评价及进行溶血实验,计算溶血率(HR)。
1.6 统计学分析 计量资料采用
x±s表示,应用Excel及SPSS 19.0软件进行数据分析,组间均数差异的比较采用单因素方差分析和SNK-q 检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。
.jpg)
.jpg)