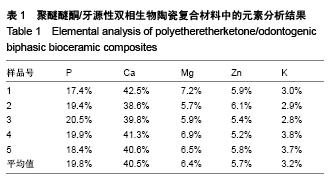
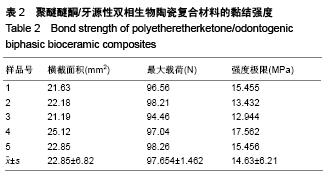
| [1] Dennes JT,Schwartz J.A nanoscale adhesion layer to promote cell attachment on PEEK.J Am Chem Soc,2009; 131:3456-3457.
[2] 蔡卫全,马睿,翁履谦,等.原位聚合羟基磷灰石/聚醚醚酮复合材料[J].化工新型材料,2010,38(6):55-63.
[3] Kyomoto M,Ishihara K.Self-initiated surface graft polymerization of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine on poly(ether ether ketone)by photoirradiation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2009;1(3):537-542.
[4] Briem D,Strametz S,Schroder K,et al.Response of primary fibroblasts and osteoblasts to plasma treated polyetheretherketone(PEEK)surfaces.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;16(7):671-677.
[5] Dorozhkin SV.Calcium orthophosphates in nature,biology and medicine.Materials. 2009;2:399-498.
[6] Katzer A,Marquardt H,Westendorf J,et al. Polyetheretherketone cytotoxicity and mutagenicity in vitro.Biomaterials.2012;23(8):1749-1759.
[7] Gonverse GL,Conrad TL,Merrill CH,et al.Hydroxxyapatite whisker reinforced polyetherketoneketone.Acta Boimaterials. 2010;6:856-863.
[8] Converse GL,Conrad TL,Roeder RK.Hydroxyapatite whisker reinforced polyetherketoneketone bone ingrowth scaffolds.Acta Boimaterials.2010;32:856-863.
[9] Masayuki K,Toru M.Self-initiated surface grafting with poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine)on poly(ether-ether-ketone).Biomaterials.2010;31:1017-1024.
[10] Cheol MH,Lee EJ.The electron beam deposition of titanium on polyetheretherketone (PEEK)and the resulting enhanced biological properties. Biomaterials. 2010;31: 3465-3470.
[11] Lim JY,Shaughnessy MC,Zhou ZY,et al.Surface energy effects on osteoblast spatial growtfi and mineralization. Biomaterials.2008;29:1776-1784.
[12] Kay S,Thapa A,Haberstroh KM,et al.Nanostructured polymer/nanophase ceramic composites enhance osteoblast and chondrocyte adhesion.Tissue Eng. 2012;8:753-761.
[13] Lee JH,Jang HL,Lee KM,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the bioactivity of hydroxyapatite-coated polyetheretherketone biocomposites created by cold spray technology.Acta Biomaterials.2013;9:6177-6187.
[14] Simona S,Antonella P,Stefania L,et al.Improved functions of human hepatocytes on NH3 plasma-grafted PEEK-WC-PU membranes.Biomaterials.2009;30:4348-4356.
[15] Dennes TJ,Jeffrey S.A Nanoscale Adhesion Layer to Promote Cell Attachment on PEEK.J Am Chem Soc.2009; 131(10):3456-3457.
[16] Wang M,Bonfield W.Chemically coupled hydroxyapatite- polyethylene composites:structure and properties. Biomaterials.2011;22:1311-1320.
[17] Hooshmand T,van Noort R,Keshwad A.Storage effect of a pre-activated silane on the resin to ceramic bond.Dental Material.2014;20:635-642.
[18] Dorozhkin sv.Biphasic,triphasic and multiphasic calcium orthophosphates.Acta Biomaterialia.2012;8:963-977.
[19] Levengood SK,Poellmann MJ,Clark SG,et al.Human endothelial colony forming cells undergo vasculogenesis within biphasic calcium phosphate bone tissue engineering constructs.Acta Biomaterialia.2011;7(12):4222-4228.
[20] Prabhakaran MP,Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L,Ramakrishna S.Eleetrospun composite nanofibers for tissue regeneration. J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2011;11:3039-3057.
[21] Zhang H.Eleetrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite scaffolds for guided bone tissue regeneration.J Bioact Compat Polym.2011;26:16-23.
[22] Zou D,Zhang Z,He J,et al.Repairing critical-sized calvarial defects with BMSCs modified by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and a phosphate cement scaffold.Biomaterials.2011;32:9707-9718.
[23] Sturgeon JL,Brown PW.Effects of carbonate on hydroxyapatite formed from CaHP04 and Ca4(P04)20.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20:1787-1794.
[24] Chen G,Li W,Yu X,et al.Study of the cohesion of TTCP/DCPA phosphate cement through evolution of cohesion time and remaining percentage.J Mater Sci. 2009;44:828-834.
[25] Sayer M,Stratilatov AD,Reid JW,et al.Structure and composition of siliconstabilized tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials.2013;24:369-382.
[26] Reid JW,Pietak AM,Sayer M,et al.Phase formation and evolution in the silicon substituted tricalcium phosphate/ apatite system. Biomaterials. 2015;26:2887-2897.
[27] Jang JH,Castano O,Kim HW.Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2009;61:1065-1083.
[28] Arcangeli E,Kon E,Delcogliano M,et al.Nanocomposite biomimetic scaffold in knee osteochondral defect regeneration:An animal study.J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2009;7:52-62.
[29] Khadka A,Li JH,Li YB,et al.Evaluation of hybrid porous biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 6 and bone marrow-derived stem cell construct in repair of calvarial critical size defect.J Craniofac Surg.2011;22:1852-1858.
[30] Schneider OD,Weber F,Bninner TJ,et al.In vivo and in vitro evaluation of flexible,cottonwool-like nanocomposites as bone substitute material for complex defects.Acta Biomater. 2009;5:1775-1784.
[31] Gupta V,Aseh A,Rios CN,et al.Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin-derived curcumin nanoparticles for cancer therapy.Int J Nanomed.2009;4:115-122.
[32] Chow LC.Next generation calcium phosphate-based biomaterials.Dent Mater J.2009;28:1-10.
[33] Ishikawa K.Bone substitute fabrication based on dissolution-precipitation reactions. Materials. 2010;3: 1138-1155.
[34] Becker A,Epple M,Mttller KM,et al.A comparative study of clinically well-characterized human atherosclerotic plaques with histological,chemical and ultrastructural methods.J Inorg Biochem.2014;98(12):2032-2038.
[35] Dorozhkin SV.Amorphous calcium(ortho)phosphates.Acta Biomater.2010;6:4457-4475.
[36] Sinyaev VA,Shustikova ES,Levchenko LV,et al.Synthesis and dehydration of amorphous calcium phosphate.Inorg Mater.2011;37:619-622.
[37] Kumar R,Cheang P,Khor KA.Phase composition and heat of crystallization of amorphous calcium phosphate in ultra-fine radio frequency suspension plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite powders.Acta Mater.2014;52:1171-1181.
[38] Wu YJ,Tseng YH,Chan JCC.Morphology control of fluorapatite crystallites by citrate ions.Cryst Growth Des. 2010;10:4240-4242.
[39] Choi WY,Kim HE,Kim MJ,et al.Production and characterization of calcium phosphate(CaP) whisker-reinforced poly(e-caprolactone)composites as bone regenerative.Mater Sci Eng C.2010;30:1280-1284. |