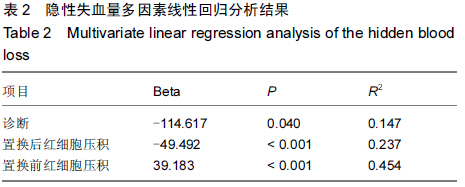
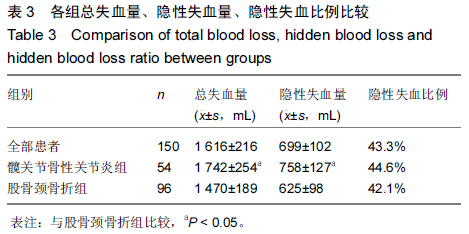
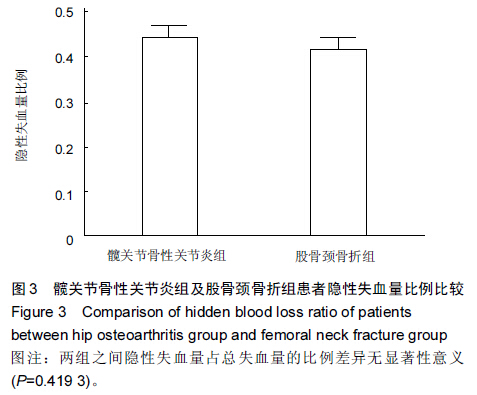
[2] 顾剑华,沈灏,陈云苏,等.人工髋关节置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2008,24(9):709-714.
[3] 覃健,余存泰,徐中和,等.全髋关节及全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的临床影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,6(5):323-326.
[4] Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Y, et al. Hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2011;26(7):1100-1105.
[5] Nadler SB, Flidlgo JU, Bloch T.Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;57(1):224-232.
[6] Gross JB.Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;580(3):277-280.
[7] 刘欣伟,苏佳灿,张春才,等.70岁以上高龄患者髋部骨折围手术期处理[J].创伤外科杂志.2009,11(5):457-461.
[8] Sehat KR, Evans R,Newman JH. How much blood;8 lost in total knee arthroplasty?Correct blood loss management should taken Ices into account. Knee. 2000;7(3)151-155.
[9] Faris PM, Ritter MA, Keating EM, et al. Unwashed filtered shed blood collected after knee and hip arthroplasties.A source of autologous red blood cells.J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1991;73(8):1169-1178.
[10] Erskinc JG, Fraser C, Simpson R, et al.Blood loss with knee joint replacement. J R Coil Surg Edinb.1981;26(5):295-297.
[11] McManus KT, Velchik MG, Alavi A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of postoperative bleeding in TKA patients with Tc-99m RNCs. J Nucl Med.1987;28 Suppl:565-567.
[12] Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B.Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. 2003;90(5): 596-599.
[13] Li J, Zhou Y, Jing J, et al. Comparison of effects of two anticoagulants on hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(4): 432-435.
[14] Foss NB, Kehlet H. Hidden blood loss after surgery for hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2006;88(8):1053-1059.
[15] Vaya A, Mira Y, Martinez M. Activation of Mood Coagulation in Pigs following lower limb gunshot trauma. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2001;12(6):477-485.
[16] Zhao J, Li J, Zheng W, et al. Low body mass index and blood loss in primary total hip arthroplasty: results from 236 consecutive ankylosing spondylitis patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:742393.
[17] Li J, Jing JH, Shi ZJ, et al. [Case-control study on effect of rivaroxaban on the risk of hidden bleeding after total hip arthroplasty]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(1):34-37.
[18] Cheng W, Xu H, Xiao Z, et al. Effect of autologous drained blood reinfusion on hidden blood loss and limb swelling following rivaroxaban anticoagulation for primary total hip arthroplasty. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014;34(3): 438-440.
[19] Bao N, Zhou L, Cong Y, et al. Free fatty acids are responsible for the hidden blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Med Hypotheses. 2013;81(1):104-107.
[20] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4):561-565.