|
[1] 首家保,陈彬,芦慎,等.不同敷料修复创面的实验研究及临床应用评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(8):1479-1482.
[2] 陈胜杰.壳聚糖-细菌纤维素的制备及体外生物相容性评价[D].海南大学,2012.
[3] Pivec T,Persin Z,Kolar M,et al.Modification of cellulose non-woven substrates for preparation of modern wound dressings.Text Res J.2014;84(1):96.
[4] 林晓华,黎志超,俞金龙,等.新型复合生物抗菌敷料的抗菌强度、吸湿能力及细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16): 2901-2912.
[5] 李晶,薛斌.新型医用敷料的分类及特点[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(12):2225-2232.
[6] Gouda M.Nano-zirconium oxide and nano-silver oxide/ cotton gauze fabrics for antimicrobial and wound healing acceleration. J Ind Text.2012;41(3):222.
[7] Li X,Robinson SM,Gupta A,et al.Functional gold nanoparticles as potent antimicrobial agents against multi-drug-resistant bacteria.ACS Nano.2014;8(10):10682-10686.
[8] Gupta N,Khurana N,Adviarekar R.Synthesis and application of nano copper oxide for antimicrobial property.Int J Chem Rea Eng.2013;2:2583-2595.
[9] 王昱征,薛向欣,杨合.硼掺杂二氧化钛纳米材料的合成及其抗菌活性的研究[J].中国化学工程学报,2014,22(4):474-479.
[10] Rigo C,Ferroni L,Tocco I, et al. Active silver nanoparticles for wound healing.Int J Mol Sci.2013;14(3):4817-4840.
[11] Nesamony J,Singh PR,Nada SE,et al.Calcium alginate nanoparticles synthesized through a novel interfacial cross-linking method as a potential protein drug delivery system.J Pharm Sci.2012;101(6):2177-2184.
[12] 钟浩权,叶伟杰,王小英,等.纳米银的研究进展[J].纳米技术,2012, 2(3):50-57.
[13] Percival SL,Thomas J,Linton S,et al.The antimicrobial efficacy of silver on antibiotic-resitant bacteria isolated from burn wound.Int Wound J. 2012;9(5):488-493.
[14] 刘继松,章祥洲,徐东卫,等.纳米银无菌敷料在小儿深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的临床应用[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2013,38(10):1270-1271.
[15] 刘韬,徐海栋.银离子敷料促慢性创面愈合效应[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,42(17):7494-7500.
[16] 荣卫军,王丽,李洁,等.纳米银敷料在皮肤撕脱伤术后感染伴坏死创面中的应用[J].西南国防医药,2013,23(11):1203-1204.
[17] 黄建文,徐月敏.细菌纤维素在组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3):420-425.
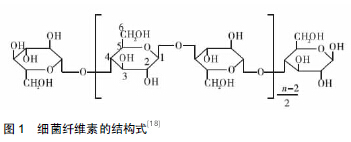
[18] 曾威,蔡志星,梁安生,等.细菌纤维素中羟基在仿生矿化中的作用[J].天津科技大学学报,2015,30(2):38-42.
[19] Fu L,Zhang J,Yang G.Present status and applications of bacterial cellulose-based materialsfor skin tissue repair. Carbohydr Polym.2013;92(2):1432-1442.
[20] Lin WC,Lien CC,Yeh HJ,et al.Bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose-chitosan membranes for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr Polym.2013;94(1):603-611.
[21] 张秀菊,林志丹,陈文彬,等.细菌纤维素纳米复合材料的研究进展[J].合成纤维, 2010,39(1):1-6.
[22] 蔡志江.细菌纤维素纳米复合物的研究进展[J].材料导报,2010, 24(2):77-92.
[23] Kim J,Kwon S,Ostler E.Antimicrobial effect of silver-impregnated cellulose:potenital for antimicrobial therapy. J Biol Eng.2009;3:20.
[24] Sureshkumar M,Siswanto DY,Lee CK.Magnetic antimicrobial nanocomposite based on bacterial cellulose and silver nanoparticles.J Mater Chem.2010;20:6948-6955.
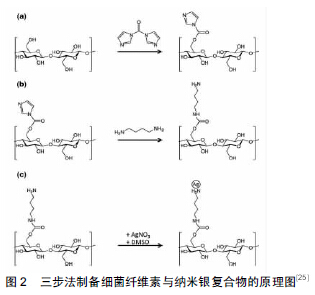
[25] Berndt S,Falko Wesarg F,Wiegand C,et al.Antimicrobial porous hybrids consisting of bacterial nanocellulose and silver nanoparticles.Cellulose.2013;20:771-783.
[26] Lina F,Yue Z,Jin Z,et al.Bacterial Cellulose for Skin Repair Materials.Biomed Eng.2012:250-274.
[27] Wu J,Zheng Y,Song W,et al.In situ synthesis of silver-nanoparticles/bacterial cellulose compositesfor slow-released antimicrobial wound dressing.Carbohydr Polym. 2014;102:762-771.
[28] 吴健,郑裕东,高爽,等.纳米银在细菌纤维素凝胶膜中的原位合成及性能表征[J].高等学校化学学报,2013,34(1):210-217.
[29] 温晓晓,郑裕东,吴健,等.纳米银/氧化细菌纤维素复合抑菌材料的制备和表征[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2014,43(S1):220-224.
[30] 杨加志,刘晓丽,黄立勇,等.具有抗菌性能的新型载银细菌纤维素纳米纤维[J].中国化学工程学报,2013,21(12):1419-1424.
[31] Zhuang X,Fang Y,Chen W. Preparation of Silver/Bacterial Cellulose Composite Membrane and Study on its Antimicrobial Activity. Synth React Inorg M.2013;43:907-913.
[32] de Santa Maria LC,Santos AL,Oliveira PC,et al. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles impregnated into bacterial cellulose.2009;63(s 9-10):797-799.
[33] Maria LC,Santos AL,Oliveira PC,et al.Preparation and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Impregnated in Bacterial Cellulose.Polimeros.2010;20(1):72-77.
[34] Yang G,Xie J,Hong H,et al.Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticle impregnated bacterial cellulose membrane: Effect of fermentation carbon sources of bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym.2012;87:839-845.
[35] Liu C,Dong Yang D,Wang Y,et al.Fabrication of antimicrobial bacterial cellulose-Ag/AgCl nanocomposite using bacterial as versatile biofactory.J Nanopart Res.2012;14:1084-1096.
[36] Fontana JD,de Souza AM,Fontana CK,et al.Acetobacter cellulose pellicle as a temporary skin substitute.Appl Biochem Biotechnol.1990;24-25:253-264..
[37] 刘继松,章祥洲,徐东卫,等.纳米银无菌敷料在小深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的临床应用[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2013,38(10):1270-1271.
[38] 陈萍,兰大华,张庆.纳米银创伤治疗肿瘤化疗中心静脉置管患者导管相关性感染63例[J].临床医药,2009,18(17):68-69.
[39] 邱吉苗,谢翠华,李春荣.含银离子敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡50例[J].广东医学,2007,28(3):472.
[40] 张放,贲道锋,吕开阳,等.银离子生物敷料封闭网状植皮创面临床观察:前瞻性病例对照研究[J].第二军医大学学报,2012,33(8): 864-867.
[41] 刘韬,徐海栋.银离子敷料促慢性创面愈合效应[J].中国组织工程研究.2013,17(42):7494-7500. |