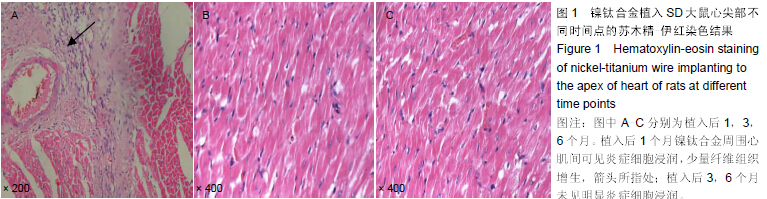
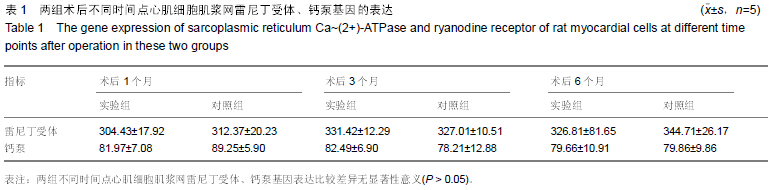
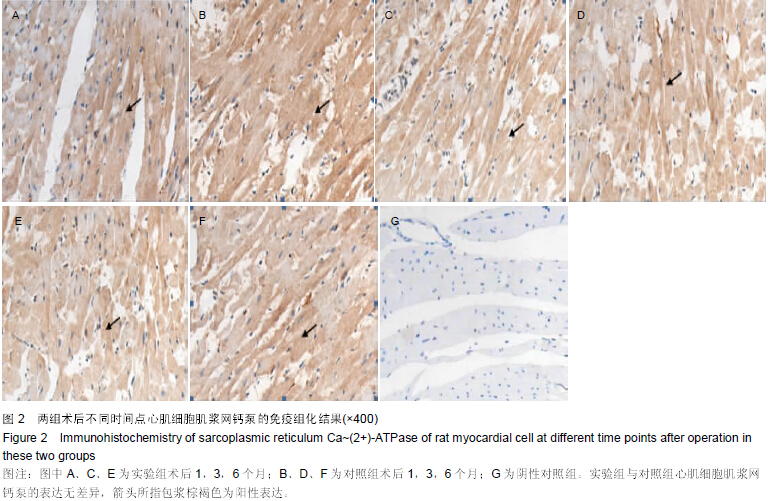
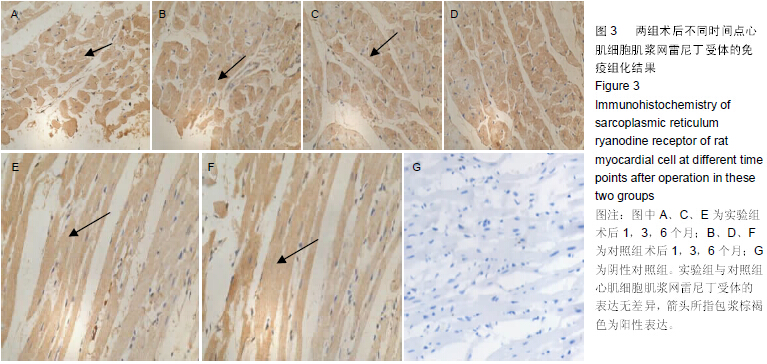
|
[1] 肖燕燕.小儿先天性心脏病诊治的展[J].中国临床医生,2013, 41(5):13-14.
[2] Bhole V,Miiler P,Mehta C,et al.Clinical evaluation of the new Amplatzer duct occlude II for patent arterial duct occlusion.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv,2009;74(5):762-769.
[3] 赵鹏军,余志庆,高伟,等.第二代动脉导管未闭封堵器封堵动脉导管的临床研究[J].临床儿科杂志,2011,29(12):1174-1177.
[4] Halabi A,Hijazi ZM.A new device to close secundum atrial septal defects: first clinical use to close multiple defects in a child.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2008;71(6): 853- 856.
[5] Bia kowski J,Szkutnik M,Fiszer R,et al.Application of Cardio- O- Fix occluders for transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus and interatrial communications: Preliminary experience. Cardiol J.2010;17(6):607- 611.
[6] Saritas T,Kaya MG,Lam YY,et al.A comparative study of Cardi- O- Fix septal occluder versus Amplatzer septal occluder in percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defects.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2013;82(1):116-121.
[7] Silvestry FE,Naseer N,Wiegers SE,et al. Percutaneoustranscatheter closure of patent foramen ovale with the Amplatzer Cribriform septal occluder.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2008;71(3):383-387.
[8] Musto C,Cifarelli A,Fiorilli R,et al.Comparison between the new Gore septal and Amplatzer devices for transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale. Short- and mid- term clinical and echocardiographic outcomes.Circ J.2013;77(12): 2922-2927.
[9] Nyboe C,Hjortdal VE,Nielsen- Kudsk JE.First experiences with the GORE Septal Occluder in children and adults with atrial septal defects.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2013; 82(6): 929-934.
[10] Freixa X,Garceau P,Asgar AW.First experience with the new GORE Septal Occluder for the closure of multiple atrial septal defects. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2013;81(7):1238-1242.
[11] 马依彤,杨毅宁,汤宝鹏,等.应用Amplatzer偏心性封堵器介入治疗膜部室间隔缺损[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2003,11(2): 60-62.
[12] 宋治远,何国祥,舒茂琴,等.应用 Amplatzer 偏心性封堵器治疗膜周部室间隔缺损的体会[J].中华儿科杂志,2004,42(11): 862-863.
[13] 王震,周谨,张密林,等.应用小腰大边封堵器封堵多出口膜部瘤型室间隔缺损[J].临床心血管病杂志,2007,23(8):624-625.
[14] Lertsapcharoen P,Khongphatthanayothin A,La- orkhun V,et al.Transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus with a selfexpanding platinum- coated nitinol device.J Invasive Cardiol.2009;21(6):286-289.
[15] Lairakdomrong K,Srimahachota S,Lertsapcharoen P,et al.Clinical results of large secundum atrial septal defect closure in adult using percutaneous transcatheter Cocoon atrial septal occluder.J Med Assoc Thai.2013;96(9): 1127-1134.
[16] Zhou Y,Chen F,Huang X,et al. A new coated nitinol occluder for transcatheter closure of ventricular septal defects in a canine model.Biomed Res Int.2013;2013:507919.
[17] Morgan G,Lee KJ,Chaturvedi R,et al.A biodegradable device (BioSTAR) for atrial septal defect closure in children. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2010;76(2):241-245.
[18] Zhu YF,Huang XM,Cao J,et al.Animal experimental study of the fully biodegradable atrial septal defect (ASD) occluder.J Biomed Biotechnol.2012;2012:735989.
[19] Tiso N,Stephan D,Nava A,et al.Identification of mutation in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene in families affected with arrhythmogenic right cardiomyopathy type2( ARVD2). Hum Mol Genet.2001;10(3):189-194.
[20] Chelu MG,Sama S,Sood S,et al.Calmodul in kinase mediated sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak promotes atrial fibrillation in mice.J Clin Invest.2009;119(7):1940-1951.
[21] Qi M,Xia HJ,Dai DZ,et al.A novel endothelin receptor antagonist CPU0213 improves diabetic cardiac insufficiency attributed to up-regulation of the expression of FKBPl2.6, SERCA2,and PLB in rats.Cardiovasc Pharmacol.2006;47(6): 729-735.
[22] Betzenhauser MJ,Marks AR.Ryanodine receptor channel path.Pflugers Arch.2010;460(2):467-480.
[23] King JH,Zhang Y,Lei M,et al.Atrial arrhythmia, triggering events and conduction abnormalities in isolated murine RyR2-P2328S hearts.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013;207(2): 308-323.
[24] Nomikos M,Thanassoulas A.Altered RyR2 regulation by the calmodulin F90L mutation associated with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and early sudden cardiac death. FEBS Lett.2014;588(17):2898-2902.
[25] Gonano LA,Petroff MV.Subcellular mechanisms underlying digitalis-induced arrhythmias: role of calcium/ calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) in the transition from an inotropic to an arrhythmogenic effect.Heart Lung Circ.2014;23(12):1118-1124.
[26] Zaza A,Rocchetti M.Calcium store stability as an antiarrhythmic endpoint.Curr Pharm Des.2015;21(8): 1053-1061.
[27] Roux-Buisson N,Gandjbakhch E,Donal E,et al.Prevalence and significance of rare RYR2 variants in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: results of a systematic screening.Heart Rhythm.2014;11(11):1999-2009.
[28] 李政宁,伍伟锋.先天性心脏病经导管封堵术后人体血清镍浓度的变化及其与IL-6、IL-10的关系[J].临床心血管病杂志, 2014, 30(6):489-491.
[29] 丁仲如,秦永文.国产镍钦合金材料热氧化表面改性后组织相容性评价[J].第二军医大学学报,2007,28(4):495-499.
[30] 杨云龙国产新型钛镍合金室间隔缺损封堵器的组织相容性研究[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2009,24(1):842-843. |