| [1] 李能莲,李光明,骆亚莉,等.HIF-1α和HIF-2α在胃癌中的表达及意义[J].基础医学与临床,2010,30(6):619-622.
[2] 王瑞权,黄志芳,陈志梅,等.HIF-1α及IMP3 在胃癌中的表达及意义[J].现代实用医学,2011,23(10):1183-1185.
[3] 王红磊,王洪涛,赵鹏,等.IGF-II、HIF-1α和CD105在胃癌中的表达及其意义[J].临床医学工程,2011,18(5):668-670.
[4] 曹桂侠,程朝辉,周冬梅.替吉奥联合奥沙利铂治疗晚期胃癌的临床观察[J].肿瘤基础与临床,2011,24(1):27-29.
[5] 王月,蔡哲,成建,等.替吉奥联合奥沙利铂治疗老年进展期胃癌的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(9):1504-1505.
[6] Prince SN, Foulstone EJ, Zaccheo OJ, et al. Functional evaluation of novel soluble insulin-like growth factor(IGF)-11-specific ligand traps based on modified domain II of the human IGF2 receptor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6(2): 607-617.
[7] 石岩岩.幽门螺杆菌毒力因子致胃癌机制的研究现状[J].中国微创外科杂志,2011,11(7):649-651.
[8] 王守练,陆瑞琪,姜波健.干细胞表面标志物CD133在胃癌中的研究进展[J].国际外科学杂志,2012,39(1):78.
[9] 崔明,李子禹,邢加迪,等.腹腔镜与开腹胃癌根治术D2淋巴结清扫的比较研究[J].中国微创外科杂志,2010,10(5):395-398.
[10] 叶民峰,陶锋,徐关根,等.腹腔镜辅助与开腹胃癌根治术治疗进展期胃癌的临床疗效分析[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(5):396-399.
[11] 杨娜,黄昌明,林涛,等.胃癌腹腔镜手术与开腹手术安全性及远期疗效比较的Meta分析[J].消化肿瘤杂志:电子版,2011,3(3): 144-150.
[12] 赵永亮,余佩武,钱锋,等.远端进展期胃癌腹腔镜辅助与开腹根治术的远期疗效比较[J].中华普通外科杂志,2011,26(9):713-716.
[13] 董峰,牛跃平,孙培春,等.腹腔镜辅助下与开腹胃癌根治术治疗进展期远端胃癌临床对照研究[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2013, 27(5):457-459.
[14] 滕方遒.腹腔镜手术治疗肝硬化合并胆囊结石的可行性及疗效分析[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(33):47-51.
[15] Zhao Y, Yu P, Hao Y, et al. Comparison of outcomes for laparoscopically assisted and open radical distal gastrectomy with lymphadenectomy for advanced gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(9):2960-2966.
[16] 李德福,徐国宏,朱静,等.腹腔镜与开腹手术治疗结直肠癌的临床疗效观察[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(15):71-73.
[17] 刘长兵,吴继锋.胃癌中TGF-β1、HIF-1α、VEGF 的表达及临床意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2013,29(7):733-736.
[18] 李明,李强.Neuropilin-1及VEGF在胃癌组织中的表达与微血管生成的关系[J].中国肿瘤临床,2014,41(5):332-336.
[19] 徐磊,孟刚.肿瘤干细胞相关标记物CD44及CD24在乳腺癌中的表达及其意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012,27(11): 1197-1201.
[20] 任秀红.饮食护理干预对全胃切除术后饮食相关并发症的影响[J].中国卫生标准管理,2013,24(z4):33-35.
[21] 范传玲,催梅,邢宝英.内镜直视下镍钛合金支架置入术治疗食管狭窄饮食护理干预[J].国际护理学杂志,2011,30(4):626-627.
[22] 李文琦,黄水平.生活方式对胃癌根治术患者预后的多因素研究[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(16):4076-4078.
[23] 张凯,孔令言.根治性次全胃切除术治疗进展期胃癌的评价[J].河北医学,2011,17(11):1488-1490.
[24] 李春兵,丁兆辉,许淼,等.C-反应蛋白与前白蛋白对急诊创伤性休克患者预后的评估[J].中国实验诊断,2010,14(11):1811-1813.
[25] 任明扬,张军,黄斌,等.三吻合器技术在腹腔镜下贲门癌切除22例分析[J].中华普外科手术学杂志(电子版),2010,4(2):30-32.
[26] Bornschein J, Rokkas T, Selgrad M, et al. Gastric cancer: clinical aspects, epidemiology and molecular background. Helicobacter. 2011;16(Supple 1):45-52.
[27] Fu X, Meng Z, Liang W, et al. miR-26a enhances miRNA biogenesis by targeting Lin28B and Zcchc11 to suppress tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene. 2014;33(34): 4296-4306.
[28] Wu Q, Yang Z, Wang F, et al. MiR-19b/20a/92a regulates the self-renewal and proliferation of gastric cancer stem cells. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(18):4220-5529.
[29] Hamerlik P,Lathia J D,Rasmussen R,et al. Autocrine VEGF-VEGFR-2-Neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell vi-ability and tumor growth. J Exp Med. 2012; 209(3):507-520.
[30] 张亚兰,朱静,田杰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与胶质瘤细胞非接触共培养后相关生物学特性分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,32(7): 630-633.
[31] 乔玲,叶丽红,张晓冬.人间充质干细胞抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖作用的实验研究[J].南开大学学报(自然科学版),2007,40:73-78.
[32] 邵志红,王培军,李铭华,等.大鼠骨髄间充质干细胞移植对Walker-256肝癌生长影响的实验研究[J].中国医学杂志,2009, 89:491-496. |
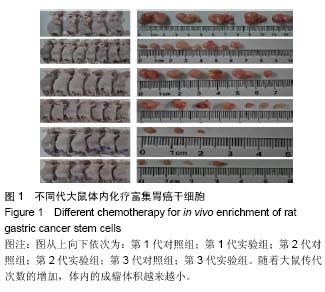
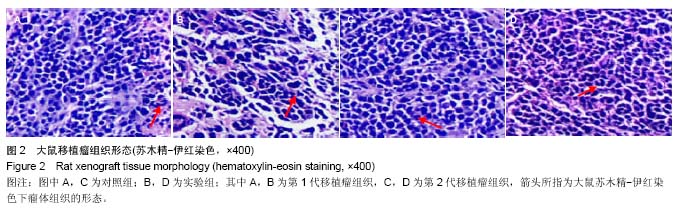
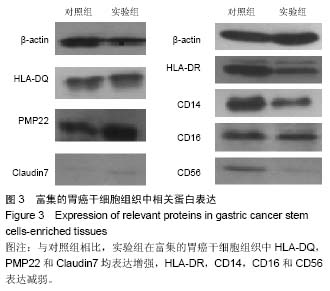
-lb.jpg)