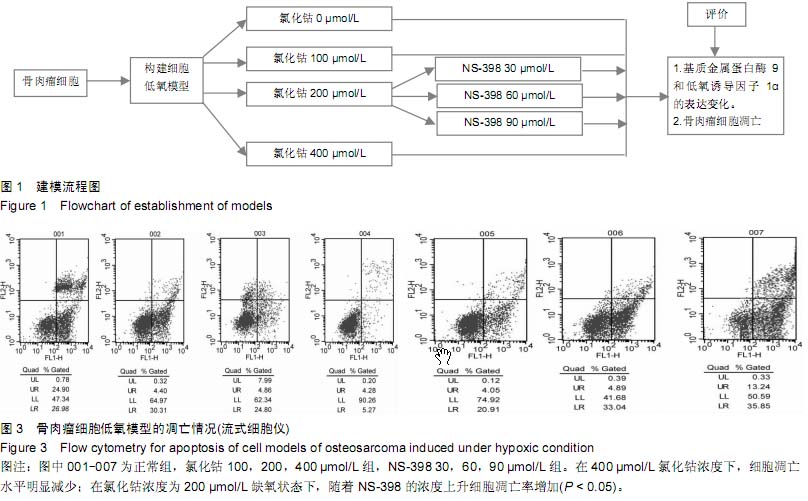
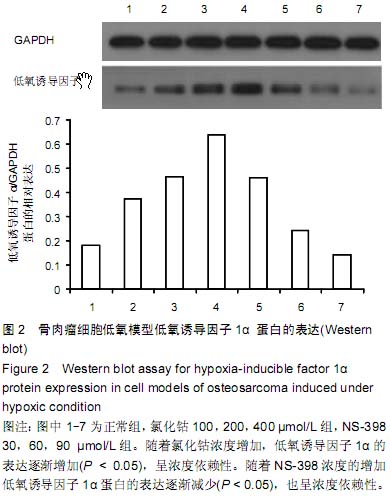
| [1] Greenwald JA, Mehrara BJ, Specter JA, et al. Biomolecular mechanisms of calvarial bone induction: immature versus mater. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;105(4):1382-1392.
[2] Fukada K, Takahashi-Yanaga F, Sakoguchi-Okada N, et al. Celecoxib induces apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of survivin in HeLa cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 357:1166-1171.
[3] 3Ranasinghe WK, Baldwin GS, Bolton D, et al. HIF1α expression under normoxia in prostate cancer- which pathways to target? J Urol. 2014.
[4] Fujikuni N, Yamamoto H, Tanabe K, et al. Hypoxia-mediated CD24 expression is correlated with gastric cancer aggressiveness by promoting cell migration and invasion. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(11):1411-1420.
[5] Wong CC, Tse AP, Huang YP, et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 is critical to tumor microenvironment and metastatic niche formation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2014; 60(5): 1645-1658.
[6] Chai L, Ying HF, Wu TT, et al. Clinical features and hypoxic marker expression of primary sinonasal and laryngeal small-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a small case series. World J Surg Oncol. 2014;12:199.
[7] Sasahira T, Kirita T, Yamamoto K, et al. Transport and Golgi organisation protein 1 is a novel tumour progressive factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(12): 2142-2151.
[8] Jin Y, Wang H, Liang X, et al. Pathological and prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression in epithelial ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35(8):8149-8159.
[9] Zhong Q, Wang S, Li C, et al. Expressions and correlation of HPA, CK2beta and HIF-1alpha in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(3): 157-161.
[10] Zhou Z, Liu F, Zhang ZS, et al. Human rhomboid family-1 suppresses oxygen-independent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74(10):2719-2730.
[11] Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res. 2014;74(9):2455-2464.
[12] Lin S, Ma R, Zheng XY, et al. Meta-analysis of immunohistochemical expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α as a prognostic role in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(4):1107-1113.
[13] Snell CE, Turley H, McIntyre A, et al. Proline-hydroxylated hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) upregulation in human tumours. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88955.
[14] White NM, Masui O, Newsted D, et al. Galectin-1 has potential prognostic significance and is implicated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression through the HIF/mTOR signaling axis. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(5):1250-1259.
[15] Wang W, He YF, Sun QK, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in breast cancer prognosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;428:32-37.
[16] Mouriaux F, Sanschagrin F, Diorio C, et al. Increased HIF-1α expression correlates with cell proliferation and vascular markers CD31 and VEGF-A in uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(3):1277-1283.
[17] Ranasinghe WK, Sengupta S, Williams S, et al. The effects of nonspecific HIF1α inhibitors on development of castrate resistance and metastases in prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 2014;3(2):245-251.
[18] Wang N, Dong CR, Jiang R, et al. Overexpression of HIF-1α, metallothionein and SLUG is associated with high TNM stage and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;7(1):322-330.
[19] Ping W, Sun W, Zu Y, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(5):4401-4409.
[20] Xu Y, Yao HB, Jin Y, et al. Expressions of Jumonji domain containing protein 2C and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in gastric carcinoma and their clinical significance. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;93(42):3375-3378.
[21] Yang SL, Liu LP, Jiang JX, et al. The correlation of expression levels of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in hepatocellular carcinoma with capsular invasion, portal vein tumor thrombi and patients' clinical outcome. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014;44(2):159-167.
[22] Feng L, Tao L, Dawei H, et al. HIF-1α expression correlates with cellular apoptosis, angiogenesis and clinical prognosis in rectal carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 2014;20(3):603-610.
[23] Jeon HM, Kim do H, Jung WH, et al. Expression of cell metabolism-related genes in different molecular subtypes of triple-negative breast cancer. Tumori. 2013;99(4):555-564.
[24] Chen Z, He X, Xia W, et al. Prognostic value and clinicopathological differences of HIFs in colorectal cancer: evidence from meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e80337.
[25] Schweiger T, Kollmann D, Nikolowsky C, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is associated with early pulmonary spreading of primary colorectal carcinoma and tobacco smoking. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;46(1):92-99.
[26] Bhalla S, Evens AM, Prachand S, et al. Paradoxical regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) by histone deacetylase inhibitor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e81333.
[27] Chang J, Erler J. Hypoxia-mediated metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;772:55-81.
[28] Cho?nzonov EL, Spirina LV, Kondrakova IV, et al. Expression of the transcription factors NF-kappaB and HIF-1 in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck: association with disease prognosis. Vopr Onkol. 2013;59(5):575-579.
[29] Wang KR, Jiang T, Wu TT, et al. Expression of hypoxia-related markers in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the head and neck. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11: 294.
[30] Tafreshi NK, Lloyd MC, Bui MM, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX as an imaging and therapeutic target for tumors and metastases. Subcell Biochem. 2014;75:221-254.
[31] Lee SH, Jaganath IB, Manikam R, et al. Inhibition of Raf-MEK-ERK and hypoxia pathways by Phyllanthus prevents metastasis in human lung (A549) cancer cell line. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013;13:271.
[32] Fraga A, Ribeiro R, Príncipe P, et al. The HIF1A functional genetic polymorphism at locus +1772 associates with progression to metastatic prostate cancer and refractoriness to hormonal castration. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(2):359-365.
[33] Masaaki T, Sugiyama M, Matsuoka H, et al. Matrixmetalloprotei-vases may contrabute compensationally to tumer invasion in T1colorectalcarcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(5b):4169-4173.
[34] Kim YY, Lee EJ, Kim YK, et al. Anti-cancer effects of celecoxib in head and neck carcinoma. Mol Cell. 2010;29(2): 185-194.
[35] Ramos-Desimone N, Hahn-Dantona E, Siplcy J, et al. Activation of matrix metalloproteinasc-9(mmp-9) via a converging plasmin/stromelysin-1 cascade enhances tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13066-13076.
[36] 强延会,王栓科.塞来昔布抑制骨肉瘤细胞黏附侵袭及其机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,11:1648-1650. |