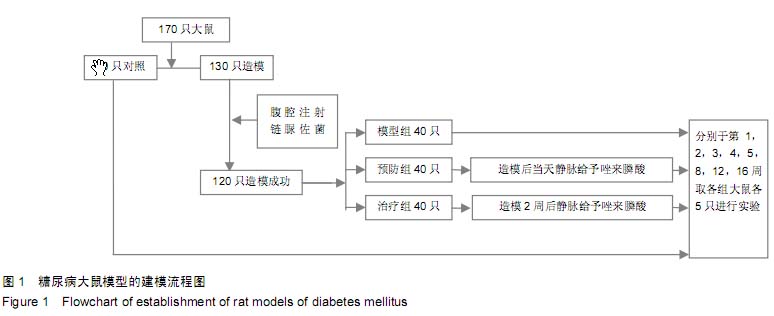
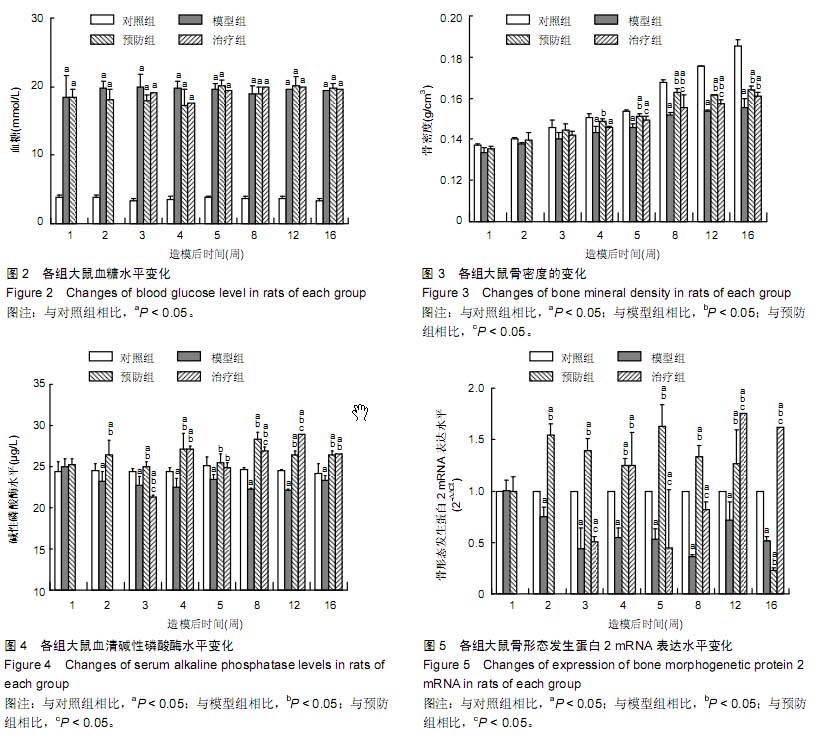
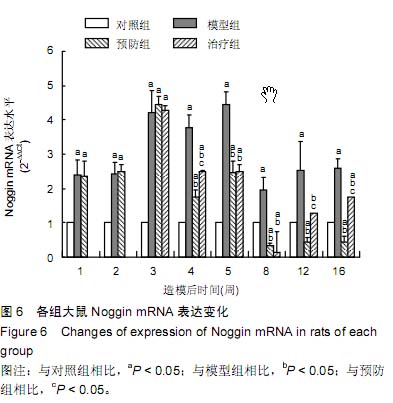
| [1] Janghorbani M, Hu FB, Willett WC, et al. Prospective study of type 1 and type 2 diabetes and risk of stroke subtypes: the Nurses' Health Study. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(7):1730-1735.
[2] Neumann T, Sämann A, Lodes S, et al. Glycaemic control is positively associated with prevalent fractures but not with bone mineral density in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2011;28(7):872-875.
[3] Cosman F. Treatment of osteoporosis and prevention of new fractures: role of intravenously administered bisphosphonates. Endocr Pract. 2009;15(5):483-493.
[4] Diab DL, Watts NB. Bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012;41(3): 487-506.
[5] Huang S, Lin H, Zhu X, et al. Zoledronic acid increases bone mineral density and improves health-related quality of life over two years of treatment in Chinese women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endokrynol Pol. 2014;65(2): 96-104.
[6] Terpos E, Dimopoulos MA, Berenson J. Established role of bisphosphonate therapy for prevention of skeletal complications from myeloma bone disease. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011;77 Suppl 1:S13-23.
[7] Kamiya N. The role of BMPs in bone anabolism and their potential targets SOST and DKK1. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012; 5(2):153-163.
[8] Liu EY, Wactawski-Wende J, Donahue RP, et al. Does low bone mineral density start in post-teenage years in women with type 1 diabetes? Diabetes Care. 2003;26(8):2365-2369.
[9] Heap J, Murray MA, Miller SC, et al. Alterations in bone characteristics associated with glycemic control in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 2004; 144(1): 56-62.
[10] Ebeling PR, Burr DB. Positive effects of intravenous zoledronic acid on bone remodeling and structure: are different effects on osteoblast activity to other oral bisphosphonates responsible? J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(1):2-5.
[11] Debiais F. Biomarkers of bone remodelling. Bull Cancer. 2013;100(11):1093-1100.
[12] Bowe JE, Franklin ZJ, Hauge-Evans AC, et al. Metabolic phenotyping guidelines: assessing glucose homeostasis in rodent models. J Endocrinol. 2014;222(3):G13-25.
[13] Cui M, Yu L Z, Zhang N, et al. Zoledronic acid improves bone quality in the streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat through upregulating the expression of osteogenic genes. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:S635-S636.
[14] Yu LZ, Cui M, Sun J. Bone quality changes in the streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat and the effect of zolendronic acid through upregulating the expreesion of the osteogenetic genes. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(9):s405.
[15] Silva MJ, Touhey DC. Bone formation after damaging in vivo fatigue loading results in recovery of whole-bone monotonic strength and increased fatigue life. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(2): 252-261.
[16] 孙明霞,韩琳,王国明,等.1型糖尿病病人骨密度的变化及其影响因素[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2014,50(4):432-434.
[17] Massé PG, Pacifique MB, Tranchant CC, et al. Bone metabolic abnormalities associated with well-controlled type 1 diabetes (IDDM) in young adult women: a disease complication often ignored or neglected. J Am Coll Nutr. 2010;29(4):419-429.
[18] Mace PD, Cutfield JF, Cutfield SM. High resolution structures of the bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor in two crystal forms: implications for ligand binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(4):831-838.
[19] Cao X, Chen D. The BMP signaling and in vivo bone formation. Gene. 2005;357(1):1-8.
[20] Kanakaris NK, Petsatodis G, Tagil M, et al. Is there a role for bone morphogenetic proteins in osteoporotic fractures? Injury. 2009;40 Suppl 3:S21-26.
[21] Seeherman HJ, Li XJ, Smith E, et al. Intraosseous injection of rhBMP-2/calcium phosphate matrix improves bone structure and strength in the proximal aspect of the femur in chronic ovariectomized nonhuman primates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(1):36-47.
[22] Wang Y, Shan J, Yang W, et al. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) mediates high-glucose-induced calcification in vascular smooth muscle cells of saphenous veins. Inflammation. 2013;36(6):1592-1604.
[23] Zehentner BK, Haussmann A, Burtscher H. The bone morphogenetic protein antagonist Noggin is regulated by Sox9 during endochondral differentiation. Dev Growth Differ. 2002;44(1):1-9.
[24] Moffett SP, Dillon KA, Yerges LM, et al. Identification and association analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human noggin (NOG) gene and osteoporosis phenotypes. Bone. 2009;44(5):999-1002.
[25] Wu XB, Li Y, Schneider A, et al. Impaired osteoblastic differentiation, reduced bone formation, and severe osteoporosis in noggin-overexpressing mice. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(6):924-934.
[26] Baud'huin M, Solban N, Cornwall-Brady M, et al. A soluble bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor increases bone mass and bone strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109(30):12207-12212.
[27] Debeer P, Huysmans C, Van de Ven WJ, et al. Carpal and tarsal synostoses and transverse reduction defects of the toes in two brothers heterozygous for a double de novo NOGGIN mutation. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;134(3):318-320.
[28] Debeer P, Huysmans C, Van de Ven WJ, et al. Carpal and tarsal synostoses and transverse reduction defects of the toes in two brothers heterozygous for a double de novo NOGGIN mutation. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;134(3):318-320. |