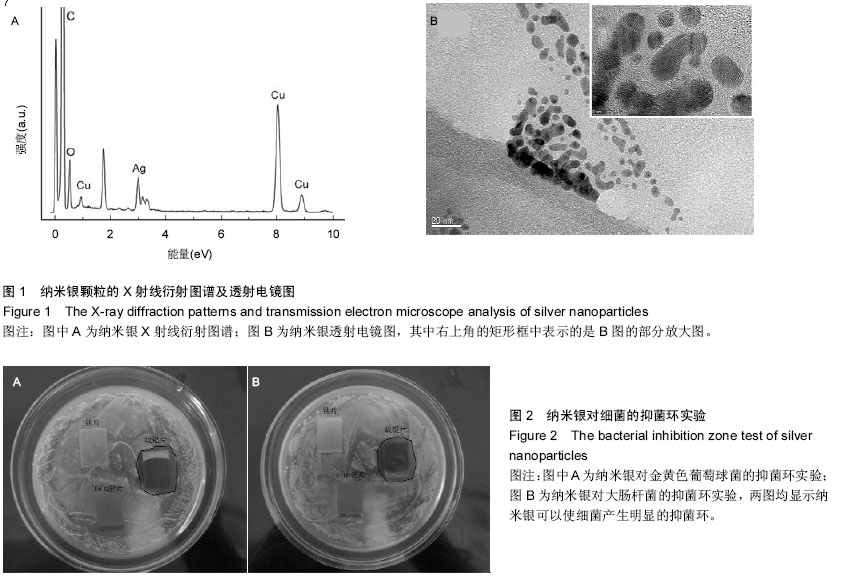
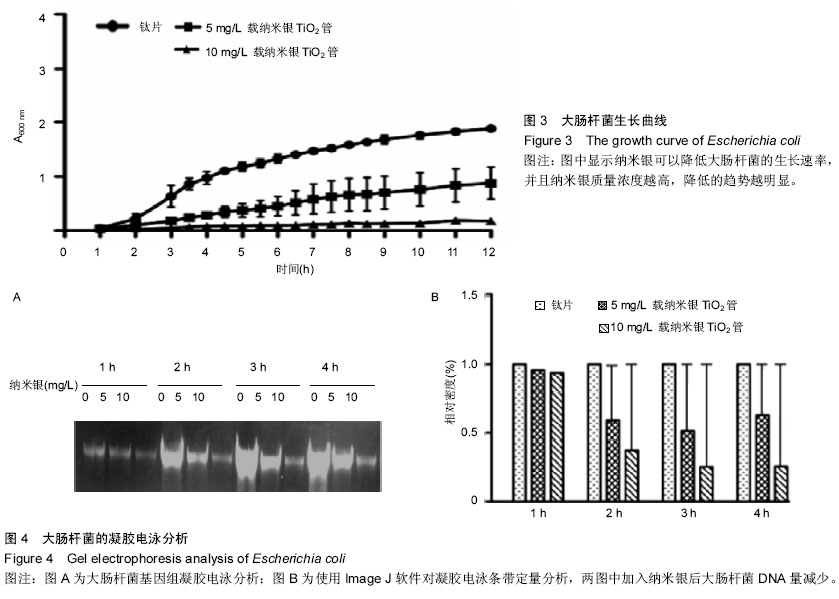
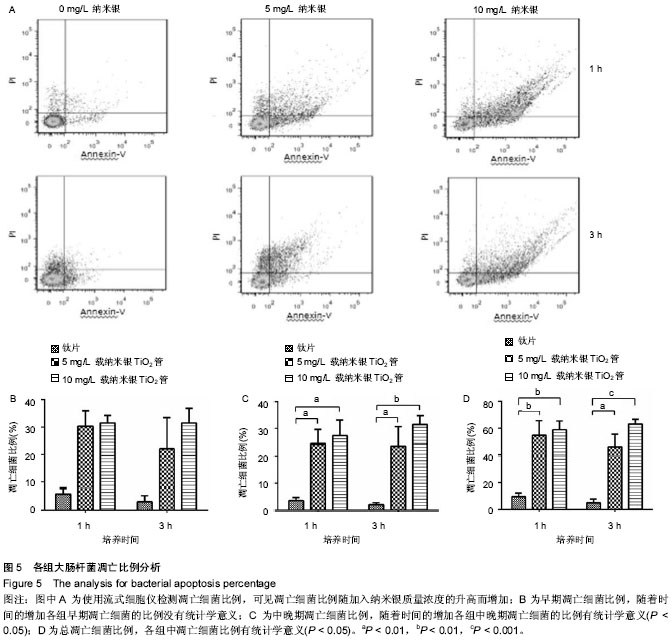
| [1] Siddhartha S,Roy A,Singh G,et al.Characterization of enhanced antibacterial effects of novel silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology.2007;18:1-9.
[2] Faedmaleki F,H Shirazi F,Salarian AA,et al.Toxicity Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Mice Liver Primary Cell Culture and HepG2 Cell Line.Iran J Pharm Res.2014;13(1):235-242.
[3] Sondi I,Salopek-Sondi B.Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study of E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria.J Colloid Interface Sci.2004;275(1):177-182.
[4] Panacek A,Kvítek L,Prucek R,et al.Silver colloid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity.J Phys Chem B.2006;110(33):16248-16253.
[5] Morones JR,Camacho A,Holt K,et al.The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology.2005;16:2346-2353.
[6] Baker C,Pakstis L,Pochan DJ,et al.Synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles.Nanosci Technol.2005;5:244-249.
[7] 袁鹏,何宏平.银系无机抗菌剂的研究进展[J].化工矿物与加工, 2002,31(10):5-9.
[8] 曲锋,许恒毅,熊勇华.纳米银杀菌机理的研究进展[J].食品科学, 2010,31(17): 420-424.
[9] Li WR,Xie XB,Shi QS,et al.Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.2010;85(4):1115-1122.
[10] Zhao LZ,Wang HR,Huo KF,et al.Antibacterial nano-structured titania coating incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials.2011;32:5706-5716.
[11] You C,Han C,Wang X,et al.The progress of silver nanoparticles in the antibacterial mechanism, clinical application and cytotoxicity. Mol Biol Rep.2012; 39(9): 9193-9201.
[12] Zhao L,Wang H,Huo K,et al.Antibacterial nano-structured titania coating incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials.2011;32(24):5706-5716.
[13] Liang HW,Zhang WJ,Ma YN,et al.Highly active carbonaceous nanofibers: a versatile scaffold for constructing multifunctional free-standing membranes. ACS Nano.2011; 5(10):8148-8161.
[14] Madhumathi K,Sudheesh Kumar PT,Abhilash S,et al. Development of novel chitin/nanosilver composite scaffolds for wound dressing applications.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(2):807-813.
[15] Jung WK,Koo HC,Kim KW,et al.Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol.2008; 74(7):2171-2178.
[16] Su HL,Chou CC,Hung DJ,et al.The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials.2009; 30(30): 5979-5987.
[17] Gordon O,Vig Slenters T,Brunetto PS,et al.Silver coordination polymers for prevention of implant infection: thiol interaction, impact on respiratory chain enzymes, and hydroxyl radical induction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2010;54(10): 4208-4218.
[18] Choi OK,Hu ZQ.Nitrification inhibition by silver nanoparticles.Water Sci Technol.2009;59(9):1699-1702.
[19] Yang W,Shen C,Ji Q,et al.Food storage material silver nanoparticles interfere with DNA replication fidelity and bind with DNA. Nanotechnology.2009;20(8):85-102.
[20] Lu L, Sun RW, Chen R, et al. Silver nanoparticles inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. Antivir Ther, 2008;13(2): 253-262.
[21] Chen M,Yang Z,Wu H,et al.Antimicrobial activity and the mechanism of silver nanoparticle thermosensitive gel.Int J Nanomedicine.2011;6:2873-2877.
[22] He T,Liu H,Zhou Y,et al.Antibacterial effect and proteomic analysis of graphene-based silver nanoparticles on a pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biometals. 2014;27(4):673-682.
[23] Erental A,Sharon I,Engelberg-Kulka H.Two programmed cell death systems in Escherichia coli: an apoptotic-like death is inhibited by the mazEF-mediated death pathway.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(3):e1001281.
[24] Dwyer DJ,Winkler JA.Identification and characterization of programmed cell death markers in bacterial models.Methods Mol Biol.2013;1004:145-159.
[25] Yarlagadda V,Akkapeddi P,Manjunath GB,et al.Membrane active vancomycin analogues: a strategy to combat bacterial resistance.J Med Chem.2014;57(11):4558-4568.
[26] Guilhelmelli F,Vilela N,Albuquerque P,et al.Antibiotic development challenges: the various mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and of bacterial resistance.Front Microbiol.2013;4:353.
[27] Cui L,Chen P,Chen S,et al.In situ study of the antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of silver nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem.2013; 85(11):5436-5443.
[28] Dwyer DJ,Camacho DM,Kohanski MA,et al.Antibiotic-induced bacterial cell death exhibits physiological and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Mol Cell.2012;46(5): 561-572.
[29] Hakansson AP,Roche-Hakansson H,Mossberg AK,et al.世纪Apoptosis-like death in bacteria induced by HAMLET, a human milk lipid-protein complex. PLoS ONE.2011;6(3): e17717.
[30] Dorsey-Oresto A,Lu T,Mosel M,et al.YihE kinase is a central regulator of programmed cell death in bacteria.Cell Rep. 2013;3(2):528-537.
[31] Morones-Ramirez JR,Winkler JA,Spina CS,et al.Silver enhances antibiotic activity against gram-negative bacteria. Sci Transl Med.2013;5(190):190ra181.
[32] Buttke TM,Sandstrom PA.Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis.Immunol Today. 1994;15:7-10.
[33] Xu H,Qu F,Lai W,et al.Role of reactive oxygen species in the antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biometals.2012;25(1): 45-53.
[34] Fadok VA,Voelker DR,Campbell PA,et al.Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages.J Immunol.1992;148(7):2207-2216.
[35] Tanouchi Y,Lee AJ,Meredith H,et al.Programmed cell death in bacteria and implications for antibiotic therapy.Trends Microbiol.2013;21(6):265-270.
[36] Fesik SW.Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer.2005;5(11):876-885. |