中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (38): 6133-6139.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.38.012
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
富血小板血浆与透明质酸钠修复兔膝骨关节炎
吉恒东1,霍小燕2,张厚庆3,王余山3,石 瑄3,霍 雷3
- 1泰州市人民医院风湿科,江苏省泰州市 225300; 2江苏大学社区卫生服务站,江苏省镇江市 212000;南京医科大学附属苏州明基医院骨科,江苏省苏州市 215000
-
通讯作者:霍雷,主治医师,南京医科大学附属苏州明基医院骨科,江苏省苏州市 215000 -
作者简介:吉恒东,男,1968年生,江苏省泰州市人,汉族,主任医师,主要从事骨关节炎研究。
Platelet-rich plasma with sodium hyaluronate in repair of rabbit knee osteoarthritis
Ji Heng-dong1, Huo Xiao-yan2, Zhang Hou-qing3, Wang Yu-shan3, Shi Xuan3, Huo Lei3
- 1 Department of Rheumatism, Taizhou People’s Hospital, Taizhou 225300, Jiangsu Province, China
2 Community Healthy Service of Jiangsu Province, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China3 Department of Orthopedics, BenQ Medical Centre Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Contact:Huo Lei, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, BenQ Medical Centre Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Ji Heng-dong, Chief physician, Department of Rheumatism, Taizhou People’s Hospital, Taizhou 225300, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
背景:研究表明,透明质酸钠可抑制膝骨关节炎对软骨的破坏,加速软骨细胞的再生,达到稳定和修复关节软骨的目的。
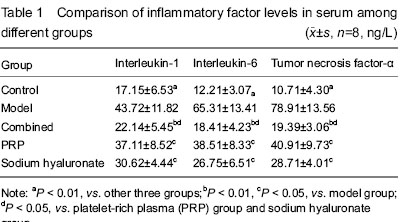
结果与结论:与对照组比较,其余4组白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平均升高(P < 0.01);联合组、透明质酸钠组、富血小板血浆组白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平均低于模型组(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),且以联合组下降最显著。模型组关节软骨破坏明显,联合组、透明质酸钠组、富血小板血浆组关节软骨破坏程度轻于模型组,且以联合组破坏程度最轻。表明透明质酸钠配合自体富血小板血浆关节内注射可降低膝骨关节炎的炎症反应,保护关节软骨,效果优于单一药物注射。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
吉恒东,霍小燕,张厚庆,王余山,石 瑄,霍 雷. 富血小板血浆与透明质酸钠修复兔膝骨关节炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(38): 6133-6139.
Ji Heng-dong, Huo Xiao-yan, Zhang Hou-qing, Wang Yu-shan, Shi Xuan, Huo Lei. Platelet-rich plasma with sodium hyaluronate in repair of rabbit knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(38): 6133-6139.
Forty rabbits were all included in result analysis.
ELISA detection of inflammatory factor levels in serum
Compared with the control group, the levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α were all increased in the other four groups (P < 0.01). Compared with the model group, the levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α were lowered significantly in the combined, sodium hyaluronate and PRP groups (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05), and the most significant decline was in the combined group (Table 1).
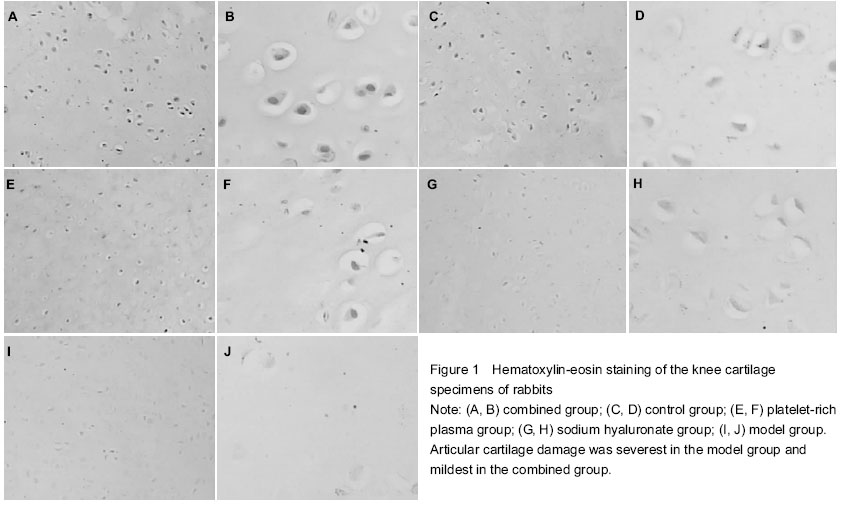
Light microscope observation of the articular cartilage
In the combined group, the cartilage tissues were stained uniformly, chondrocytes were full and arranged in neat that gathered together, some cells appeared to have karyopyknosis (Figures 1A, B). In the control group, the cartilage matrix was pink and stained uniformly, and cells were full and arranged in neat (Figures 1C, D). In the PRP group, the cartilage matrix was evenly colored, sparse cell arrangement was found, cell clusters were visible and some cells were concentrated (Figures 1E, F). In the sodium hyaluronate group, the cartilage tissues became thinning, some chondrocytes exhibited hypertrophy, cell arrangement was more disordered, there were cell clusters, even damaged cells, and some cells were concentrated (Figures 1G, H). In the model group, the cartilage tissues became significantly thinner, presenting with extensive surface fragmentation and exfoliation, fissures reached deep into the subchondral bone, the matrix was colored slightly, there were cell clusters and local cell damage, cell arrangement was the most disordered and sparse, a plurality of chondrocytes gathered together, and karyopyknosis was found (Figures 1I, J).
| [1] Huang ZF, Zhao B, Liu ZR, et al. Clinical research for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with the method combined with oral and external use which under the guidance of The Juanbizhuanggu theory. Zhongguo Xiandai Yisheng. 2013; 51(33):86-87. [2] Liu MH, Dong JW. Voltaren emulgel treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a clinical observation. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2011;9 (32):88-89.
[3] Neogi T. Clinical significance of bone changes in osteoarthritis. Ther Adv MusculoskeletDis. 2012;4(4):259-567.
[4] Kapidzi?-Basi? N, Kikanovi? S, Hoti Hadziefendi? A, et al. Changes in social relations as a consequence of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Reumatizam. 2013;60(1):42-46.
[5] Wang SD, Wang YZ, Zeng LY, et al. Research progress of the induction and detection methods of chondrocyte sapoptosis in vitro. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2014;(1):100-104.
[6] Ou Y, Tan C, An H, et al. Selective COX-2 inhibitor ameliorates osteoarthritis by repressing apoptosis of chondrocyte. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18(6):BR247-252.
[7] Zamli Z, Adams MA, Tarlton JF, et al. Increased chondrocyte apoptosis is associated with progression of osteoarthritis in spontaneous Guinea pig models of the disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17729-17743.
[8] Intekhab-Alam NY, White OB, Getting SJ, et al. Urocortin protects chondrocytes from NO-induced apoptosis: a future therapy for osteoarthritis? Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e717.
[9] Zhao Z, Ji H, Jing R, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy reduces progression of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits by reducing nitric oxide level and chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(11):1547-1553.
[10] Turajane T, Tanavaree A, Labpiboonpong V, et al. Outcomes of intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(9):1845-1852.
[11] Kato Y, Mukudai Y, Okimura A, et al. Effects of hyaluronic acid on the release of cartilage matrix proteoglycan and fibronectin from the cell matrix layer of chondrocyte cultures: interactions between hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995;43:158-159.
[12] Homandberg GA, Hui F, Wen C, et al. Hyaluronic acid suppresses fibronectin fragment mediated cartilage chondrolysis: I. In vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997;5(5):309-319.
[13] Conaghan PG. A turbulent decade for NSAIDs: update on current concepts of classification, epidemiology, comparative efficacy, and toxicity. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(6):1491-1502.
[14] Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(4):465-474.
[15] Ragle RL, Sawitzke AD. Nutraceuticals in the management of osteoarthritis : a critical review. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(9):717-731.
[16] Kahan A, Uebelhart D, De Vathaire F, et al. Long-term effects of chondroitins 4 and 6 sulfate on knee osteoarthritis: the study on osteoarthritis progression prevention, a two-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(2):524-533.
[17] Lee KS, Wilson JJ, Rabago DP, et al. Musculoskeletal applications of platelet-rich plasma: fad or future? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(3):628-636.
[18] Su JM, Jin Y, Qu Q, et al. The expression of microRNA130a during chondrogenic differentiation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2010;30(5):520-523.
[19] Moser C. Response to: cytokine profile of autologous conditioned serum for treatment of osteoarthritis, in vitro effects on cartilage metabolism and intra-articular levels after injection. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):410.
[20] Pan HL, Yao Y, Wang GW, et al. Variety and significance of IL-1 levels in blood and syn ovial fluid of osteoarthritis model animals. Haerbin Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2001;35(3):192-194.
[21] Jiao YT, Wang DZ, Hu J. Effect of IL-1 and dexamethasone on proliferation, metabolization and precollagen gene expression of human condylar cartilage cells.Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2000;16(2):94-95.
[22] Westacott CI, Sharif M. Cytokines in osteoarthritis: mediators or markers of joint destruction? Semin Arthritis Rheum.1996;25(4):254-272.
[23] Pelletier JP, DiBattista JA, Roughley P, et al. Cytokines and inflammation in cartilage degradation. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993;19(3):545-568.
[24] Kotake S, Sato K, Kim KJ, et al. Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(1):88-95.
[25] Reboul P, Pelletier JP, Tardif G, et al. The new collagenase, collagenase-3, is expressed and synthesized by human chondrocytes but not by synoviocytes. A role in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(9):2011-2019.
[26] Zheng SM, Dong TH, Liu JE. Determination of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in kneen osteoarthritis patients. Zhonghua Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 1998;5(6):544.
[27] Neidal J, Sihulze M, Sova L, et al. Practical significance of cytokine determination in joint fluid in patients with arthroses or rheumatoid arthritis. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1996;134(4):381-385.
[28] Turajane T, Tanavaree A, Labpiboonpong V, et al. Outcomes of intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(9):1845-1852. |
| [1] | 蒋红英, 朱 亮, 余 曦, 黄 靖, 向小娜, 兰正燕, 何红晨. 富血小板血浆干预脊髓损伤患者压力性损伤的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | 何祥忠, 陈海云, 刘 军, 吕 阳, 潘建科, 杨文斌, 何静雯, 黄俊翰. 富血小板血浆联合微骨折对比微骨折治疗膝关节软骨病变的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [3] | 黎永华, 冯 强, 谭仁霆, 黄世福, 邱金龙, 尹 恒. 杜仲活性成分抗膝骨关节炎滑膜炎病变分子机制的网络药理学阐述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [4] | 邓桢翰, 黄 勇, 肖璐璐, 陈昱霖, 朱伟民, 陆 伟, 王大平. 骨形态发生蛋白在关节软骨再生过程中的作用与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [5] | 李 黎, 马 力. 磁性壳聚糖微球固定化乳糖酶及其酶学性质[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [6] | 杨 威, 陈泽华, 易志勇, 黄旭东, 韩清民, 张荣华. 关节腔内注射透明质酸与安慰剂治疗早中期膝骨关节炎的疗效差异:基于随机、双盲、对照、临床试验的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(23): 3760-3766. |
| [7] | 周安琪, 唐渝菲, 吴秉峰, 向 琳. 骨膜组织工程设计:共性与个性的结合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [8] | 郎丽敏, 何 生, 姜增誉, 胡奕奕, 张智星, 梁敏茜. 导电复合材料在心肌梗死组织工程治疗领域的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [9] | 刘 鋆, 杨 龙, 王伟宇, 周玉虎, 吴 颖, 卢 涛, 舒莉萍, 马敏先, 叶 川. 聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [10] | 任文博, 廖远朋. 基于CiteSpace对创伤性骨关节炎研究热点与内容的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [11] | 蒋昇源, 李 丹, 姜建浩, 杨上游, 杨淑野. 假体无菌性松动过程中Co2+对成骨前体细胞的生物学反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [12] | 左秀芹, 尹飒飒, 谢惠敏, 贾子善, 张立宁. 富血小板血浆在肌骨修复领域应用的适用性与相关规范[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(20): 3239-3245. |
| [13] | 卢明峰, 赵立连, 邢基斯, 何利雷, 许 挺, 王昌兵. 前交叉韧带重建后二次关节镜探查关节软骨的转归分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(2): 222-227. |
| [14] | 韩 磊, 刘海英, 张 浩. 步态周期下各级骨关节炎软骨力学行为的数值分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(18): 2810-2815. |
| [15] | 解 健, 苏俭生. 静电纺丝取向纳米纤维作为组织工程生物支架的优势与特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
Design
Data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 3.0, and a value of P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Currently, the first-line drugs for osteoarthritis also include acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, but these drugs often brings a series of adverse reactions to
Findings from this experiment show that intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate with autologous PRP can reduce the levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in rabbit knee osteoarthritis, reduce inflammation, protect the articular cartilage, which has better effects than single drug injection. 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
实验观察透明质酸钠配合自体富血小板血浆关节内注射修复膝骨关节炎的效果,发现透明质酸钠配合自体富血小板血浆关节内注射可降低兔膝骨关节炎白细胞介素、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α的水平,减轻炎症反应,保护关节软骨,疗效优于单一药物注射。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||