| [1] Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, Numerical investigations on the osseointegration of uncemented endoprostheses based on bio-active interface theory, Comput Mech. 2012;50: 367-381.
[2] Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, Lewinski G, et al, Numerical studies on alternative therapies for femoral head necrosis, Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10:627-640.
[3] Zhao DW, Cui DP, Tian FD, et al. Treatment of early stage osteoneccosis of the femoral head with autilogous implantation of bone marrow-derived and cultured mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 2012;50:325-330.
[4] Schileo E, Taddei F, Cristofolini L, et al. Subject-specific finite element models implementing a maximum principal strain criterion are able to estimate failure risk and fracture location on human femurs tested in vitro. J Biomech. 2008;41:356-367.
[5] Schileo E, Cristofolini L, Grassi L, et al. To what extent can linear finite element models of human femora predict failure under stance and fall loading configurations. J Biomech. 2014; 47:3531-3538.
[6] Schileo E, Dall’Ara E, Taddei F, et al, An accurate estimation of bone density improves the accuracy of subject-specific finite element models. J Biomech. 2008; 41:2483-2491.
[7] Floerkemeier T, Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, et al. Core decompression and osteonecrosis intervention rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: clinical outcome and ?nite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2011;35:1461-1466.
[8] Taddei F, Cristofolini L, Martelli S. Subject-specific finite element models of long bones: an in vitro evaluation of the overall accuracy. J Biomech. 2006;39:2457-2467.
[9] Taddei F, Pani M, Zovatto L, et al. A new meshless approach for subject-specific strain predictionin long bones: evaluation of accuracy. Clin Biomech. 2008;23:1192-1199.
[10] Calori GM, Mazza E, Colombo M, et al. Treatment of AVN using the induction chamber technique and a biological-based approach: indications and clinical results. Injury. 2014;45:369-373.
[11] Cheng HY, Chu KT, Shen FC, et al. Stress effect on bone remodeling and osseointegration on denta implant with novel nano/microporous surface functionalization. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2013;101A:1158-1164.
[12] Huang HL, Hsu JT, Fuh LJ, et al. Bone stress and interfacial sliding analysis of implant designs on an immediately loaded maxillary implant: a non-linear finite element study. J Dent. 2008;36:409-417.
[13] Yang J, Xiang HJ. A three-dimensional finite element study on the biomechanical behavior of an FGBM dental implant in surrounding bone. J Biomech. 2007;40:2377-2385.
[14] Joshua A, Neil M, Boyd SK. Bone strength at the distal radius can be estimated from high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography and the finite element method. Bone. 2008;42:1203-1213.
[15] Cristofolini L, Juszczyk M, Martelli S, et al. In vitro replication of spontaneous fractures of the proximal human femur. J Biomech. 2007;40:2837-2845.
[16] Juszczyk MM, Cristofolini L, Salv M. Accurate in vitro identification of fracture onset in bones: Failure mechanism of the proximal human femur. J Biomech. 2013;46:158-164.
[17] Fanuscu M, Hung V, Poncelet VB. Implant biomechanics in grafted sinus: a finite element analysis. J Oral Implantol. 2004;30:59-68.
[18] Michael J, Jack G, Kelly S, et al. Approach to the patient evaluation using static and dynamic hip pathomechanics. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2012;20:260-272.
[19] Mont MA, Ragland PS, Etienne G. Core decompression of the femoral head forosteonecrosis using percutaneous multiple small-diameter drilling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;429:131-138.
[20] Nguyen H, Dieter H, Gross T, et al. Micro-finite element (μFE) modeling of the siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) third proximal phalanx: the functional role of curvature and the flexor sheath ridge. J Hum Evol.2014;67:60-75.
[21] Wazen RM, Currey JA, Guo HQ. Micromotion-induced strain fields influence early stages of repair at bone-implant interfaces. Acta Biomaterialia. 2013;9:6663-6674.
[22] Shuler MS, Rooks MD, Roberson JR. Porous tantalum implant in early osteonecrosis of the hip: preliminary report on operative, survival, and outcomes results. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:26-31.
[23] Shah SH, Kapoor CS, Jhaveri MR, et al. Analysis of outcome of avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by core decompression and bone grafting. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6:160-166.
[24] Steinberg M. The advantages of core decompression for treating avascular necrosis. UPOJ. 2000;13:84-88.
[25] Stronach BM, Duke JN, Rozensweig SD, et al. Subtrochanteric fracture after core decompression and placement of a tantalum strut for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplast. 2010;25(7):1168.e5-e7.
[26] Sumner DR, Turner TM, Igloria R, et al. Functional adaptation and ingrowth of bone vary as a function of hip implant stiffness. J Biomech. 1998;31:909-917.
[27] Floerkemeier T, Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, et al. Core decompression and osteonecrosis intervention rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: clinical outcome and finite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2011;35:1461-1466.
[28] Veillette CJ, Mehdian H, Schemitsch EH, et al. Survivorship analysis and radiographic outcome following tantalum rod insertion for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:48-55.
[29] Shim VB, Fernandez JW, Gamage PB, et al. Subject-specific finite element analysis to characterize the influence of geometry and material properties in achilles tendon rupture. J Biomech. 2014;47:3598-3604.
[30] Simon U, Augat P, Ignatius A, et al. Influence of the stiffness of bone defect implants on the mechanical conditions at the interface-a finite element analysis with contact. J Biomech. 2003;36:1079-1086. |

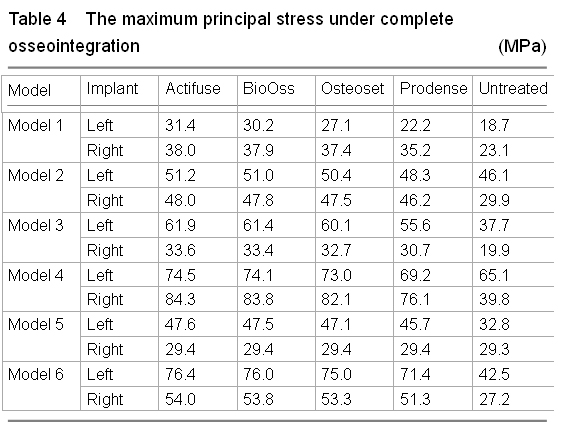
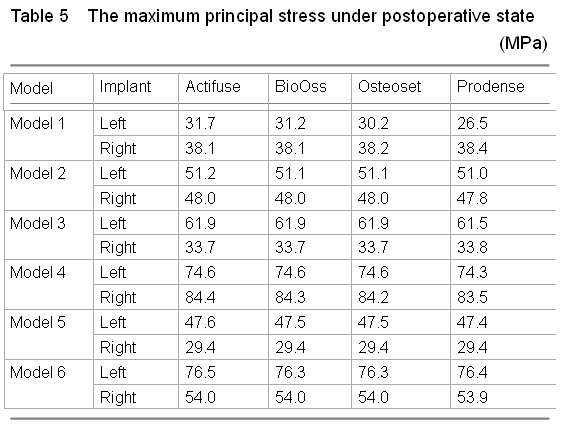
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)