| [1] Herkowitz HN. Spine update: Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine.1995;20: 1084-1090.
[2] Figueiredo N, Martins JW, Arruda AA, et al. Tlif: Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2004;62(3B):815-820.
[3] 汤志兵,杨惠林,陈康武.轻度峡部裂性滑脱症的治疗进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012, 22(10): 951-954.
[4] Kuang L, Xu D, Li G, et al. Surgical treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis by transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94(29): 2293-2296.
[5] 黄剑峰,宁锦龙,岑定善,等.两种椎间融合方式在治疗腰椎滑脱症中的应用研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(10): 2819-2822.
[6] Lee CK, Vessa P, Lee JK. Chronic disabling low back pain syndrome caused by internal disc derangements.The results of disc excision and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 1995;20: 356-361.
[7] Santos ER, Goss DG, Morcom RK, et al. Radiologic assessment of interbody fusion using carbon fiber cages. Spine. 2003;28: 997-1001.
[8] Satomi K, Hirabayashi K, Toyama Y, et al. A clinical study of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Radiographic analysis and choice of treatment]. Spine. 1992;17(11): 1329-1336.
[9] 王展,王文己.后外侧植骨融合与360°环周融合修复腰椎滑脱症的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(53): 8685-8692.
[10] Zhou ZJ, Zhao FD, Fang XQ, et al. Meta-analysis of instrumented posterior interbody fusion versus instrumented posterolateral fusion in the lumbar spine. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;15(3): 395-310.
[11] Park Y, Ha JW, Lee YT, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis and degenerative spondylosis: 5-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(6):1813-1823.
[12] Liu XY, Wang YP, Qiu GX, et al. A systematic review with meta-analysis of posterior interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion in lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J.2014;23(1):43-56.
[13] Zhao J, Zhang F, Chen X, et al. Posterior interbody fusion using adiagonai cage with unilateral transpedicular screw fixation for lumbar stenosis. Clin Neurosci. 2011;18: 324-328.
[14] 张庆明,沈惠良,曹立,等.颗粒骨打压植骨在腰椎后路融合手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(11):801-806.
[15] Wang JC, Mummaneni PV, Haid RW. Current treatment strategies for the painful lumbar motion segment: Posterolateral fusion versus interbody fusion. Spine. 2005; 30(16):S33-43.
[16] 秦彦超,马迅.两种椎间融合方法治疗腰椎滑脱症的疗效比较[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2010,41(5):458-461.
[17] 王晖,吴小涛,熊传芝,等.后路椎弓根内固定椎体间融合术治疗腰椎滑脱症[J].解剖与临床,2007,12(1):35-39.
[18] 海涌,陈晓明,陈志明,等.后路椎间融合术治疗成人腰椎滑脱的前瞻性研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2004, 24(10):586-589.
[19] 周焕河,贺斌,吴春富,等.经前路椎间植骨融合治疗腰椎滑脱疗效分析[J].吉林医学,2013,33(8):1634-1635.
[20] 杨大鹏.经前路椎间植骨融合治疗腰椎滑脱的手术方法及效果观察[J].中国医药指南, 2013,11(13):570-571.
[21] Lin TY, Liao JC, Tsai TT, et al. The effects of anterior vacuum disc on surgical outcomes of degenerative versus spondylolytic spondylolisthesis: At a minimum two-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15: 329.
[22] 夏志宏,管国义,项征.后路钉棒系统内固定加椎间植骨融腰椎滑脱症临床分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2015, 24(6): 661-662.
[23] 朱国军. Cage植骨融合治疗退行性腰椎滑脱症疗效观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2015, 24(4):404-406.
[24] Nam WD, Cho JH. The importance of proximal fusion level selection for outcomes of multi-level lumbar posterolateral fusion. Clin Orthop Surg.2015;7(1):77-84.
[25] Sato J, Ohtori S, Orita S, et al. Radiographic evaluation of indirect decompression of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbarinterbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2015. [Epub ahead of print]
[26] Hao Y, Yu L, Zhang Y, et al. [Effectiveness of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion via Luxor retractor associated with Mantis pedicle screw in treatment of moderate and severe lumbar spondylolisthesis]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(12):1509-1513.
[27] Feng Y, Chen L, Gu Y, et al. Restoration of the spinopelvic sagittal balance in isthmic spondylolisthesis: posterior lumbarinterbody fusion may be better than posterolateral fusion. Spine J. 2015;15(7):1527-1535.
[28] Jiang WY, Xu RM, Ma WH, et al. [Effect of reduction on spino-pelvic parameters in treating high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(9):726-729.
[29] Yamashita T, Sakaura H, Miwa T, et al. Modified posterior lumbar interbody fusion for radiculopathy following healed vertebral collapse of the middle-lower lumbar spine. Global Spine J. 2014;4(4):255-262.
[30] Gille O, Challier V, Parent H, et al. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: cohort of 670 patients, and proposal of a new classification. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6 Suppl):S311-315.
[31] Takahashi T, Hanakita J, Watanabe M, et al. Lumbar alignment and clinical outcome after single level asymmetrical transforaminal lumbarinterbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis with local coronal imbalance. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(9):691-697.
[32] Liao JC, Lu ML, Niu CC, et al. Surgical outcomes of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with anterior vacuum disc: can theintervertebral cage overcome intradiscal vacuum phenomenon and enhance posterolateralfusion? J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(6):851-859.
[33] Ding Y, Zhang W, Duan L, et al.[Effectiveness study on minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion assisted with microscope in treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(5):535-539.
[34] Morishita Y, Maeda T, Ueta T, et al. Pathophysiological effects of lumbar instrumentation surgery on lumbosacral nerve roots in the vertebral foramen: measurement of local pressure of intervertebral foramen. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(21): E1256-1260.
[35] 赵凤东,杨伟,刘军辉,等.经椎间孔腰椎椎体问融合术后融合器移位及其危险因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(10):922-927. |
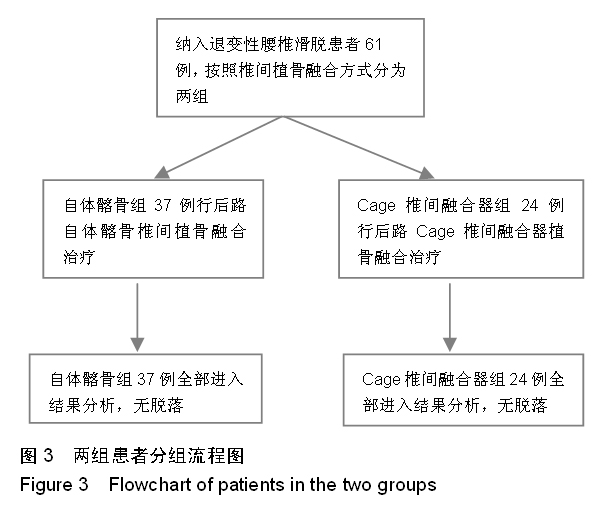
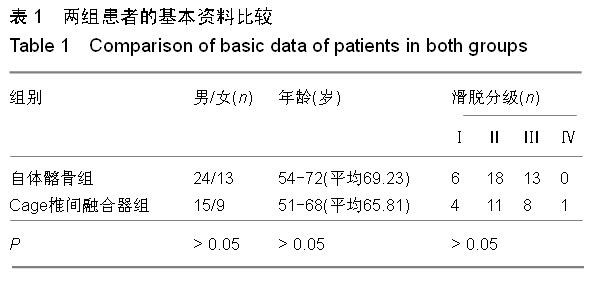
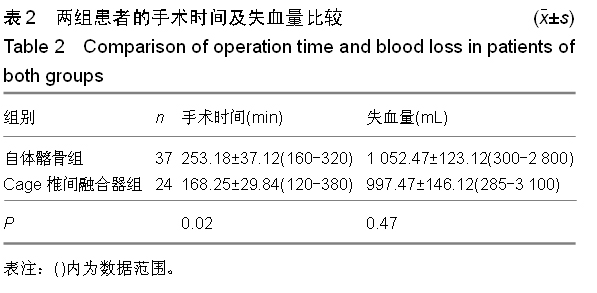
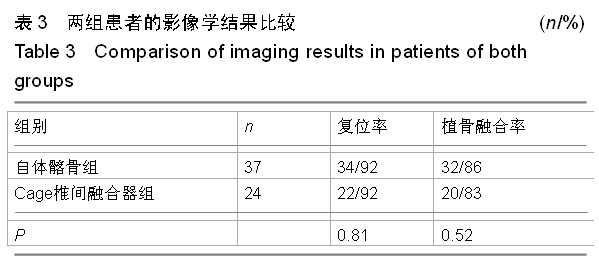

.jpg)
.jpg)