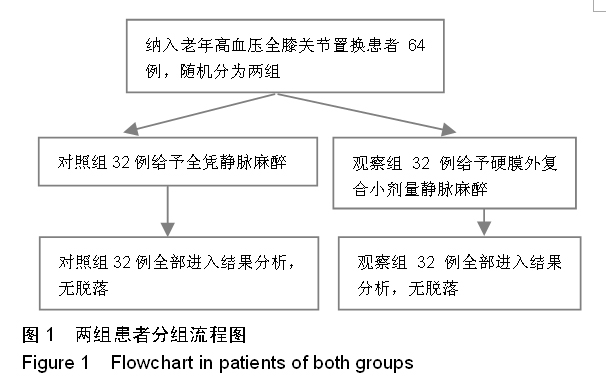
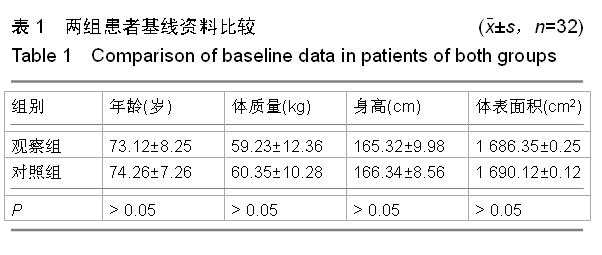
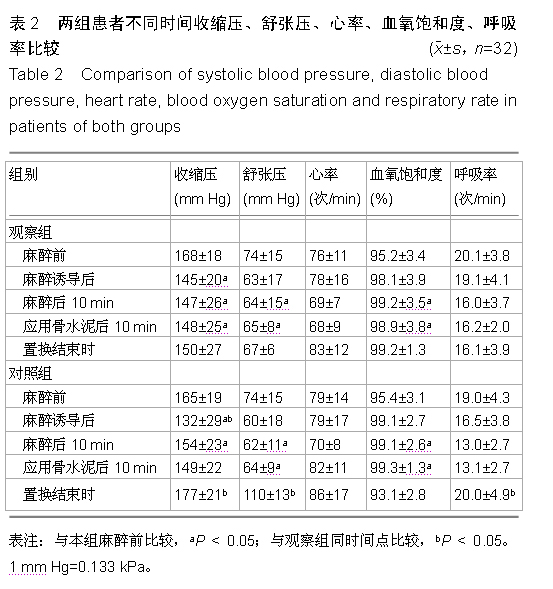
| [1] 董补怀,张彦声,代畔,等.腰-硬联合麻醉用于老年人髋关节置换术100例[J].陕西医学杂志,2006,35(2):217-220.
[2] 田春芳,宋玉芳,曹芳,等.两种麻醉方法在老年高血压患者关节置换术中的应用观察[J].山东医药,2009,49(23):84-85.
[3] 任良,王伟东,王雪梅,等.人工全髋关节置换术中应用银杏达莫针对高血压老年患者的保护作用[J].中国生化药物杂志,2014, 39(3): 81-83.
[4] 宛春甫,赵东,朱鹤,等.硬膜外阻滞复合全麻用于老年患者膝关节置换手术的可行性[J].河北医药,2008,30(8):1171-1172.
[5] 金陵,马正良,陶佳,等.不同麻醉方法对老年高血压下肢手术患者血流动力学的影响[J].江苏医药,2009,35(9):1011-1013.
[6] 罗建军,孟根其其格,张毅,等.脉压对老年高血压患者全身麻醉后术中血液动力学不稳定影响的研究[J].中国老年学杂志,2013, 33(14):3340-3342.
[7] Paxton EW, Inacio MC, Khatod M, et al. Kaiser Permanente National Total Joint Replacement Registry: Aligning Operations With Information Technology. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468 (10):2646-2663.
[8] 徐怡琼,罗艳,于布为,等.骨科手术患者全身麻醉苏醒期高血压的发生情况[J].上海医学,2013,36(2):102-105.
[9] 罗建军,张毅.术中应用参附注射液对老年高血压患者全髋关节置换术的麻醉效果影响[J].时珍国医国药,2013,24(10): 2457-2458.
[10] 张海山,王大龙,左振芳,等.Supreme 喉罩与气管插管对老年高血压患者人工膝关节置换术应激反应的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2014,30(6):577-580.
[11] 王玉群,张彤艳,陈淑梅,等.腰-硬联合麻醉在老年全髋关节置换术中的应用[J].吉林医学,2006,27(11):1412-1412.
[12] 张明德,王敏.静吸复合全麻与靶控输注对老年高血压患者麻醉深度的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(20):5748-5749.
[13] Tay Swee Cheng R, Klainin-Yobas P, Hegney D, et al. Factors relating to perioperative experience of older persons undergoing joint replacement surgery: an integrative literature review.Disabil Rehabil. 2014;37(1):9-24.
[14] Cabrita HA, de Godoy Santos AL, Gomes Gobbi RG. Necrose avascular da cabeça femoral em pacientes HIV positivos: resultados iniciais do tratamento cirúrgico por substituição articular cerâmica-cerâmica/ Avascular necrosis of the femoral head in HIV-infected patients: preliminary results from surgical treatment for ceramic-ceramic joint replacement. Rev Bras Ortop. 2012;47(5):626-630.
[15] 王锐,王玉英.15例老年髋关节置换术麻醉体会[J].山东医药, 2004,44(35):61-62.
[16] 张承哲.静吸复合全麻与靶控输注对老年高血压患者麻醉深度的影响对照研究[J].医学信息,2013,26(30):204-205.
[17] 郭小文,黄蓉蓉,金海燕,等.腰-硬联合麻醉与全麻在老年高血压患者髋关节置换术的应用比较[J].浙江医学,2010,32(3): 393-395.
[18] 刘佩蓉,刁枢,孙海峰,等.硝普钠控制性降压对老年高血压患者髋关节置换术后认知功能和脑氧代谢的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志, 2009,25(6):500-501.
[19] Hills AJ, Ahmed N, Matthews NS. Concurrent Bilateral Total Temporomandibular Joint Replacement Surgery and Conventional Maxillary Osteotomy Utilizing Virtual Surgical Planning Web-Based Technology. J Craniofac Surg. 2014; 25(3):954-956.
[20] 成毅.老年全髋关节置换术患者的麻醉分析[J].中国基层医药, 2008,15(z1):52.
[21] 冯兆明,朱俊峰,顾国华,等.地尔硫(卓)对老年高血压病患者全髋关节置换术围术期心肌的保护作用[J].中国医药,2012,7(1): 21-22.
[22] 杨芳,蔺改雯.老年高血压患者行人工髋关节置换术围术期护理体会[J].山西医药杂志(下半月版),2011,40(8):401-402.
[23] 黄文,余一兰,林永宝,等.静吸复合全身麻醉与靶控输注对老年高血压患者麻醉深度的影响对比研究[J].吉林医学,2014,35(29): 6564-6564.
[24] 杨玲,冯春存.腰硬联合麻醉与气管插管全麻应用于人工全膝关节置换术的临床观察[J].昆明医科大学学报,2014,35(8): 140-141, 143.
[25] Emin A, Andreas B, Lukas S. Simultaneous bilateral hip replacement reveals superior outcome and fewer complications than two-stage procedures: a prospective study including 1819 patients and 5801 follow-ups from a total joint replacement registry. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11(1): 245.
[26] 宋莉,吴秋萍,李萍,等.循证护理预防老年高血压病患者行人工髋关节置换术后并发深静脉血栓[J].检验医学与临床,2013,10(18): 2484-2484,2499.
[27] 檀文好,庞晓军,黎必万,等.右美托咪定复合硝酸甘油控制性降血压用于老年患者髋关节置换术30例[J].医药导报,2014,33(9): 1175-1178.
[28] 段慧.两种麻醉方式用于高龄患者全髋关节置换术的效果比较[J].医学临床研究,2010,27(11):2150-2151.
[29] Wylde V, Gooberman-Hill R, Horwood J, et al. The effect of local anaesthetic wound infiltration on chronic pain after lower limb joint replacement: A protocol for a double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011; 12(1):53.
[30] 吴礼平,程文高,曹启旺,等.腰硬联合麻醉复合全身麻醉在老年患者髋关节置换术中的麻醉效果[J].湖北民族学院学报(医学版), 2012,29(4):46-47.
[31] 汤国亮.0.5%布比卡因腰麻联合硬膜外麻醉用于ASAⅡ-Ⅲ级老年患者脐平面以下手术120例效果观察[J].中国药物经济学, 2013, 8(5):244.
[32] 臧学慧,查振刚,冯永洪,等.全髋关节置换后早期并发深静脉血栓的多因素Logistic回归分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(17):3054-3057.
[33] Lester LE, Bevins JW, Hughes C. Range of motion of the metacarpophalangeal joint in rheumatoid patients, with and without a flexible joint replacement prosthesis, compared with normal subjects. Clin Biomech. 2012;27(5):449-452. |