Design
A randomized controlled animal experiment.
Time and setting
This study was performed at the Experimental Center, Wuhan University Renmin Hospital, China between June 2013 and December 2014.
Materials
Twenty-four mature New Zealand white rabbits about 2.2-2.8 kg were bought from the Animal Center of Medical College of Wuhan University (license No. SYXK (E) 2010-0057) and randomly divided into normal control, model, and sodium hyaluronate groups.
|
Reagents and instruments:
|
|
Reagents and instruments
|
Source
|
|
Sodium hyaluronate
|
Bausch & Lomb FREDA
|
|
ABI 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System
|
ABI Company, USA
|
|
Trizol
|
Invitrogen Technologies, USA
|
|
RT-PCR kit
|
TaKaRa, China
|
Methods
Grouping
Animals in the model and sodium hyaluronate groups were anesthetized intravenously with ketamine hydrochloride (1.0 mg/kg), and received unilateral anterior cruciate ligament transection. A medial parapatellar incision was made on the skin and a medial arthrotomy was performed. The patella was dislocated and the knee placed in full flexion. The anterior cruciate ligament was visualized and transected without destroying the articular cartilage. The knee was irrigated with physiological saline. Then the capsule and skin were closed respectively. Postoperatively the animals were caged (60 cm×
60 cm×40 cm) without any immobilization and maintained under the same environmental condition. During the first 5 days after the operation, each rabbit received an intramuscular injection of 200 000 units of penicillin every day to prevent infection. At 4 weeks after surgery, rabbits in the model group were not injected after unilateral anterior cruciate ligament transection, and rabbits in the sodium hyaluronate group received 0.3 mL of 1% sodium hyaluronate via intra-articular injection, once a week for 5 weeks.
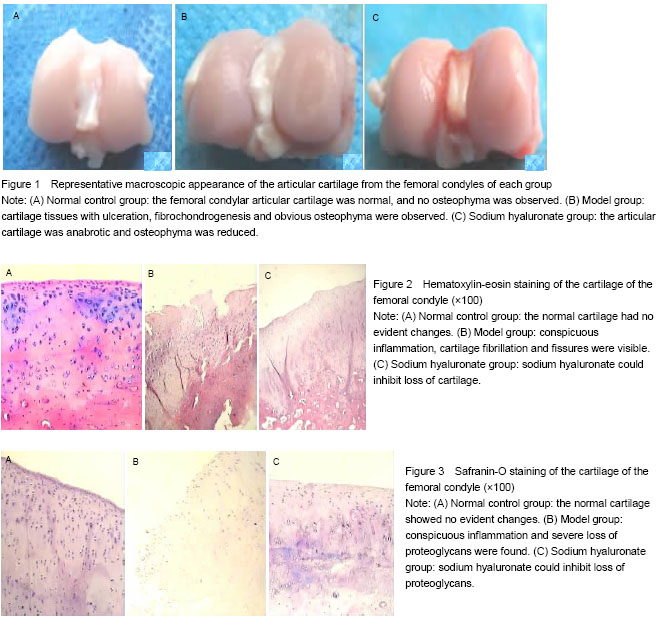
Macroscopic observation
All animals were killed and knees were harvested at 11 weeks after modeling. Degenerative changes of femoral condyles in the cartilage were observed under dissecting microscope and the osteoarthritis severity was graded on a scale of 0-4[7], as follows: 0=surface smooth with normal color; 1=surface rough with minimal fibrillation or a slight yellowish discoloration; 2=cartilage erosion extending into the superficial or middle layers; 3=cartilage ulceration extending into the deep layers; 4=cartilage depletion with subchondral bone exposed.
Microscopic observation
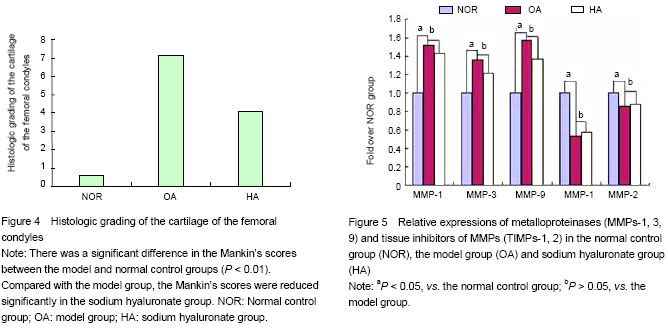
At 11 weeks post-operation, tissues from eight rabbits of each group were dissected, fixed in neutral buffered 4% formaldehyde in 0.1 mol/L PBS (pH 7.4) for 48 hours, decalcified in 10% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid for 3-4 weeks, dehydrated in graded alcohols, and embedded in paraffin. Sections, 5 µm thick, were stained with both hematoxylin and eosin for general morphology, or with 0.1% safranin-O and fast green to demonstrate sulfated proteoglycans (PGs). The area of positively stained safranin-O metachromasia, indicative of PGs, and the total area of the joint cartilage in frontal sections were measured. Each data point represented results obtained from measurements of two sections from each of three individual animals belonging to the same group. Regenerative cartilage was histologically scored using Mankin’s histopathology grading system[8]. The grading system used a 14-point score. Higher points indicate severer cartilage degeneration.
Real-time quantitative PCR
At 11 weeks post-operation, the total RNA extracted were used the Trizol reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The RNA samples were quantified by A260 nm. Then RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA using RT-PCR kit according to protocol. The cDNA was analyzed immediately or stored at -20 ℃. Quantitative PCR amplification was performed by ABI 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System and the SYBR Green I fluorescent dye method was used to quantify cDNA. The sequences are shown as Table 1.
.jpg)
The final volume of the real-time PCR reaction was 10 μL and included SYBR Premix Ex Taq 5 μL, primer
(10 μmol/L) 0.2 μL each, 50×ROX Reference Dye 0.2 μL, template 1 μL, adjusted to 10 μL with distilled water. PCR cycling conditions consisted of an initial denaturing step for 10 seconds at 95 ℃, and then 40 cycles of 5 seconds at 95 ℃, 30 seconds at 60 ℃. A stable and reliable standard curve was established using synthesized oligonucleotides resembling cDNA fragments in 5-fold decrements as template. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from the same sample was used as internal control and the relative contents of the copy numbers of the target gene’s mRNA were calculated, through which we could determine the gene expression level and its trend of change. Specificity of each reaction was controlled by melting curve analysis. A negative PCR control containing water instead of cDNA was performed. Real-time PCR was conducted in triplicate in three independent experiments.
Gross morphology of articular cartilage under the anatomical microscope; morphology of articular cartilage under the optical microscope; mRNA expression of MMPs-1, 3, 9 and TIMPs-1, 2.
.jpg)