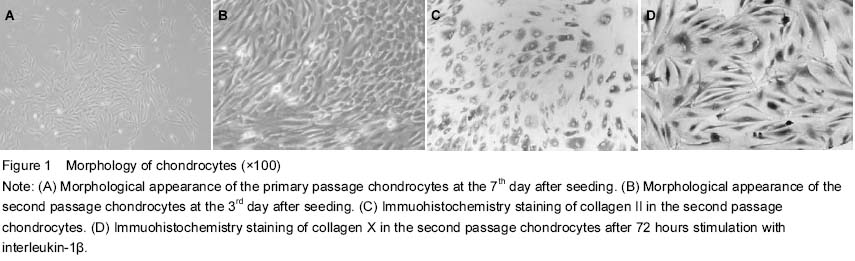
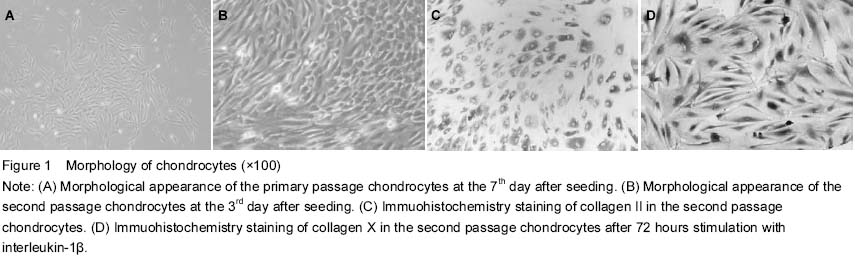
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Design
Cell biology in vitro.
Time and setting
The experiment was completed at the Central Laboratory of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital during July 2013 to April 2014.
Materials
For use of animal subjects, this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital (China). All the tissues were obtained from 10 C57BL/6J mice (each 5 in male and female, 3 days old, specific pathogen free level, temperature of 20-26 ℃, relative humidity of 40%-70%) provided by the Animal Centre of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital (license No. SYXK(Yue)2010-0106).
Methods
Isolation and culture of chondrocytes
C57BL/6J mice, 3 days old, were selected, killed and sterilized with 75% ethyl alcohol for 3 minutes. After removing the fat, blood, fibrous connective tissues and cartilage tissues in which metaphyseal ossification did not occur were washed with cold PBS (Gibco, USA) three times in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, then cut into 1 mm3 small pieces in 60-mm culture dishes, and treated with trypsinized for 30 minutes at 37 ℃ in 5% CO2 and 1 mg/mL type II collagenase (Sigma, USA) for 4 hours. After removing tissue debris through a cell strainer, isolated cells were re-suspended in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Gibco) and supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL streptomycin. Cell viability was assessed by trypan blue staining (Beyotime, China) and cytometry. Cells were seeded at a density of 1×106/mL in two 25-cm2 culture bottles at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Half of the culture medium was replaced after 24 hours, and then the medium was changed at a 3-day interval until 85% confluence was reached. The cells were digested regularly with 0.25% trypsin (Gibco) and sub-cultured at 1:3 splits. The cells were separated and purified depending on differential adherent time. Inverted microscope (Olympus, Japan) was employed to observe the synovial cells.
Identification of chondrocytes
Chondrocytes were seeded at a density of 1×105 cells per well in 6-well plates (treated with polylysine) and cultured at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 48 hours. Then the cells were washed with PBS, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde buffer (pH 7.4) for 30 minutes at room temperature. The sections were incubated with 0.01% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes and sealed with 5% bovine serum albumin for 30 minutes, respectively, before being incubated with monoclonal antibodies of collagen II and collagen X (Abcam, England) at 4 ℃ overnight. Afterwards, the cells were washed with PBS three times, fixed in EnVisionTM antibody working solution for 40 minutes at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere. 3,3'-diaminobenzidine was used as a chromogenic agent after the cells were washed with PBS. The slides were covered and examined with microscopes (DM6000M, Leica). ddH2O and nonspecific antibody in mice were used in negative control instead of collagen II or X antibodies respectively.
Grouping
The second passage chondrocytes were seeded at a density of 1×105 cells per well in 6-well plates. Experimental cells were divided into four groups according to different situation: control group was not treated with interleukin-1β, and remaining three groups were treated with 10 μg/L interleukin-1β (Cell Signaling, USA) for 24, 48 and 72 hours, respectively. Each group had three wells.
Measurement of cell activity by MTT assay
Adherent cells were digested and re-suspended by 0.25% trypsin. Then the cells at a density of 1×105/mL were seeded (1×104/well, 100 μL) in sextuplicate on a 96-well plate. After being cultured for 24 hours with PBS substrate, the cells were cultured with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco) for 24 hours. After the fetal bovine serum was abandoned, the first column of 96-well plates were set to zero set wells (only medium), the second column were blank wells (only cells), the third column were experimental wells (the cells were treated with interleukin-1β for 24, 48 and 72 hours respectively) , and then cultured at 37 ℃ in 5% CO2. After the medium was removed, 10 μL MTT (5 mg/mL) was added into each well 4 hours before the indicated time point. After the culture liquid in wells was abandoned, 150 μL dimethyl sulphoxide was added per well and shaken at a low speed for 10 minutes. The absorbance value (A value) was measured by scanning the plates at 490 nm wavelength with a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, USA). Cell activity was calculated based on the mean of results from sextuple wells. Experimental wells A value=absorbance value of experimental wells-absorbance value of zero set wells. Blank wells A value=absorbance value of blank wells-absorbance value of zero set wells. Cells activity=experimental wells A value/blank wells A value×100%.
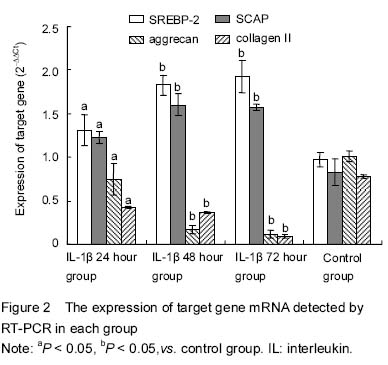
Detection of mRNA expression of SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP), SREBP-2, aggrecan and collagen II by real-time PCR
cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription kit (Invitrogen, USA). The reaction was based on a 20 μL volume containing 1 μL extracted RNA as template, 1 μL OligodT (50 μmol/L) and 1 μL dNTP (10 mmol/L), and RNase free dH2O was added to 14 μL and then incubated for 5 minutes at 65 ℃. After being refrigerated on ice and briefly centrifuged, the following components were added: 4 μL 5×first strand synthesis buffer, 1 μL M-MuL reverse transcriptase and 1 μL RNase inhibitor. The PCR was performed at 30 ℃ for 10 minutes, 42 ℃ for 45 minutes and 95 ℃ for 5 minutes, respectively, and then the PCR products were stored at -20 ℃ before use. FQ-PCR was carried out with the Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Invitrogen) on an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystem, USA) at 95 ℃ for 15 minutes, 40 cycles of denaturation at 94 ℃ for 15 seconds, followed by annealing for 30 seconds at 55 ℃, and elongation for 30 seconds at 72 ℃. The RT-PCR reaction was based on a 20 μL volume containing 1 μL of above cDNA as template, 10 μL of SYBR Premix Ex Taq, 0.5 μL of each of primers and 0.4 μL of correction dye solution, and sterile water were added to 20 μL. The amplification of gene was repeated for 40 cycles based on three major steps according to annealing temperature. The specificity of RT-PCR amplification products was estimated by the melting curve, with GADPH as internal reference. Primers were synthesized by Primer Premier 5.0 software, and the sequences were shown as follows: GADPH, 5’-AAC GAC CCC TTC ATT GAC CT-3’ (forward), 5’-TGG AAG ATG GTG ATG GGC TT-3’ (reverse); SREBP-2, 5’-CCC TGG AAG TGA CCG AGA GT-3’ (forward), 5’-GAC AGT AGC AGG TCA CAG GT-3’ (reverse); SCAP, 5’- AGT TTC TGA GCA GCC TAC GT -3’ (forward), 5’-CGA TCT TGC GTG TGG AGA AG-3’ (reverse); aggrecan, 5’-GTC ACA GAG CTT GGA GGA CT-3’ (forward), 5’-TGA CCC AGA TGA AAG GTC CC-3’ (reverse); collagen Ⅱ, 5’-AGG TGT TCG AGG AGA CAG TG-3’ (forward), 5’-CAA CAA TGC CCC TTT GAC CA-3’ (reverse). The result was calculated by 2-ΔΔCt method.
Main outcome measures
The effects of interleukin-1β to the expression of SCAP, SREBP-2, aggrecan and collagen II in articular chondrocytes.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed with SPSS 17.0 (SPSS, USA). Categorical data were presented as mean±SD. Data comparison between two groups was analyzed by t test. A P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.