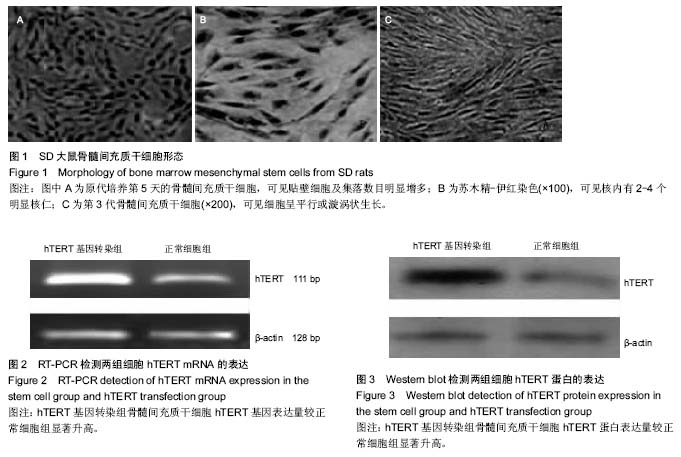
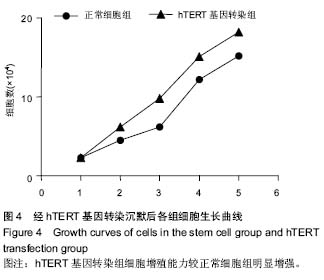
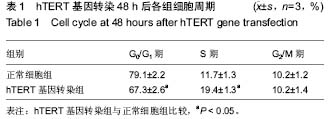
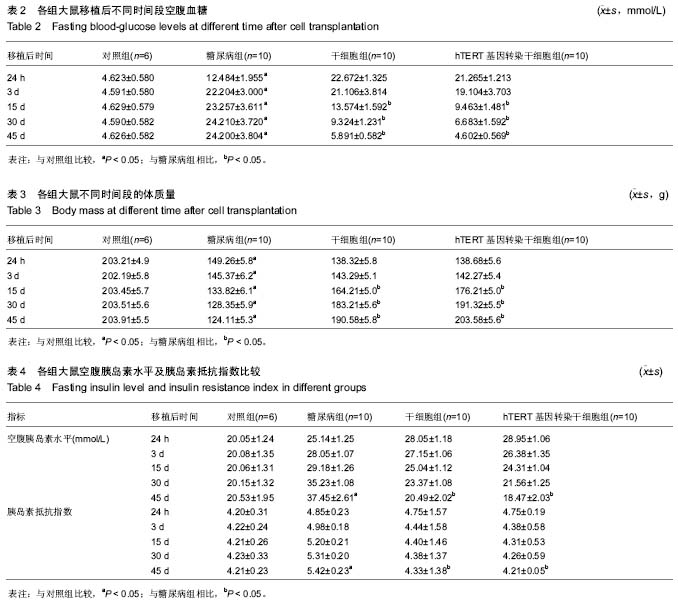
| [1] Dong W, Qian Y, Yang L. Telomerase, hTERT and splice variants in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 2014;38(7):830-835.
[2] Noureini SK, Wink M. Antiproliferative effects of crocin in HepG2 cells by telomerase inhibition and hTERT down-regulation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(5): 2305-2309.
[3] Avci CB, Yilmaz S, Dogan ZO, et al. Quercetin-induced apoptosis involves increased hTERT enzyme activity of leukemic cells. Hematology. 2011;16(5):303-307.
[4] Biron-Shental T, Amiel A, Anchidin R, et al. Telomere length and telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression in patients with hepatitis C. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013; 60(127):1713-1716.
[5] 杨柏梁,郭丽,任淑萍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对糖尿病大鼠疗效观察[J].中国公共卫生,2009,25(8):973-974.
[6] 王燕,赵霞,范斌,等.2型糖尿病血压控制与未来出现肾病终点的观察性研究[J].首都医科大学报,2012,33(4):472-476.
[7] 雷川云,柯亭羽,徐勉.干细胞移植治疗2型糖尿病急性心肌梗死的研究进展[J].中国医药科学,2013,3(19):36-38.
[8] 单莎瑞,黄国志.干细胞抗衰老的理论研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4347-4354.
[9] 郑培,安沂华,王晓东,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效观察[J].武警医学,2013,24(5):398-401.
[10] 陈崇岩,吴德全.干细胞分化为胰岛素分泌细胞研究进展[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2013,25(4):347-349.
[11] 谭笑,汪年松.干细胞治疗糖尿病肾病的研究进展[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2013,14(8):738-740.
[12] 刘小银,莫朝晖.干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变的研究进展[J].医学综述,2013,19(17):3175-3179.
[13] 谢婷,欧阳建,陈军浩,等.犬骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为胰岛样细胞的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2010,18(4):298-302.
[14] Pievani A, Borleri G, Pende D, et al. Dual-functional capability of CD3+CD56+ CIK cells, a T-cell subset that acquires NK function and retains TCR-mediated specific cytotoxicity. Blood. 2011;118(12):3301-3310.
[15] 葛亮,赵建勇,孙诚谊,等.大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞体外转染为胰岛素分泌细胞的实验研究[J].中华消化外科杂志,2013,12(8): 592-596.
[16] Zhao D, Wu H, Li F, et al. Electromagnetic field change the expression of osteogenesis genes in murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2008;28(2):152-155.
[17] Choi KS, Shin JS, Lee JJ, et al. In vitro trans-differentiation of rat mesenchymal cells into insulin-producing cells by rat pancreatic extract. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 330(4):1299-1305.
[18] 贾延劫,周燕,杨于嘉,等.干细胞诱导分化为胰岛的研究进展[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2004,20(1):87-89.
[19] Alexanian AR, Maiman DJ, Kurpad SN, et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of neurally modified mesenchymal stem cells induced by epigenetic modifiers and neural stem cell environment. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(6):1123-1130.
[20] 张金池,欧阳亮远,吴佳文,等. 体外诱导糖尿病鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向血管内皮样细胞分化的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012, 29(1):55-57.
[21] 朱沙俊,陆玉华,朱建伟,等.骨髓间充质干细胞自体介入移植治疗糖尿病Beagle犬[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(10): 1498- 1500.
[22] 李煜环,宋振顺,范子扬,等.骨髓间充质干细胞体外对1型糖尿病大鼠淋巴细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011, 28(2): 209-211.
[23] 林雨佳,高峰,吴德全,等.大鼠胰岛细胞联合移植骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(3):172-176.
[24] 庞荣清,张成,项鹏,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导为胰岛样细胞后自体移植治疗糖尿病猕猴[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2008,24(1): 70-73.
[25] Hess D, Li L, Martin M, et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells initiate pancreatic regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(7): 763-770.
[26] 邵珠林,徐向进,陈频,等.利拉鲁肽诱导骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化及移植治疗1型糖尿病大鼠的研究[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2014, 6(3):172-177. |