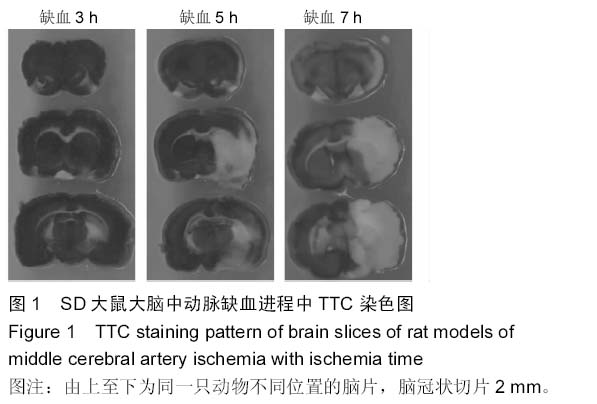
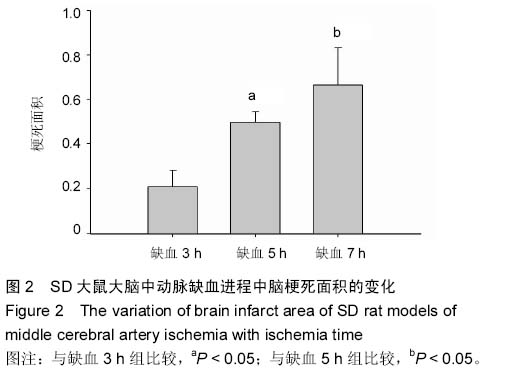
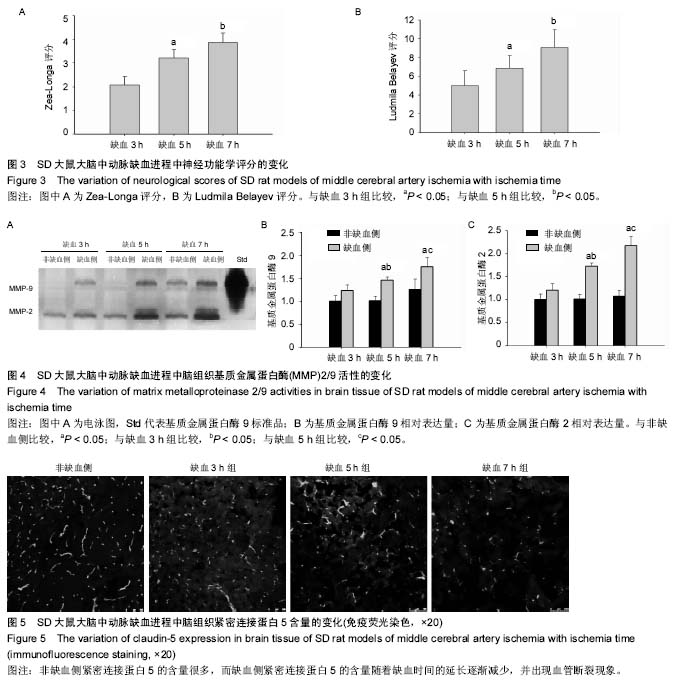
| [1] Banerjee P,Jana S,Chakraborty S,et al.Inflammation and MMPs in alcohol-induced liver diseases and protective action of antioxidants.Indian J Biochem Biophys.2013; 50(5): 377-386.
[2] Cavdar Z,Ozbal S,Celik A,et al.The effects of alpha-lipoic acid on MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities in a rat renal ischemia and re-perfusion model. Biotech Histochem.2014; 89(4):304-314.
[3] Tang X,Zhong W,Tu Q,et al.NADPH oxidase mediates the expression of MMP-9 in cerebral tissue after ischemia- reperfusion damage.Neurol Res.2014;36(2):118-125.
[4] Li M,Ma RN,Li LH,et al.Astragaloside IV reduces cerebral edemapost-ischemia/reperfusion correlating the suppression of MMP-9 and AQP4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;715(1-3): 189-195.
[5] Cao J,Geng L,Wu Q,et al. Spatiotemporal expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) is regulated by the Ca2+-signal transducer S100A4 in the pathogenesis of thoracic aortic aneurysm.PLoS One.2013;8(7):e70057.
[6] Moniche F,Montaner J,Gonzalez-Marcos JR,et al.Intra-arterial bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation correlates with GM-CSF, PDGF-BB, and MMP-2 serum levels in stroke patients: results from a clinical trial. Cell Transplant.2014;23 Suppl 1:S57-S64.
[7] Bai X,Zhang X,Chen L,et al. Protective effect of naringenin in experimental ischemic stroke: down-regulated NOD2, RIP2, NF-kappaB, MMP-9 and up-regulated claudin-5 expression. Neurochem Res.2014;39(8):1405-1415.
[8] Sapojnikova N,Kartvelishvili T,Asatiani N,et al.Correlation between MMP-9 and extracellular cytokine HMGB1 in prediction of human ischemic stroke outcome. Biochim Biophys Acta.2014;1842(9):1379-1384.
[9] Tsuji K,Aoki T,Tejima E,et al.Tissue plasminogen activator promotes matrix metalloproteinase-9 upregulation after focal cerebral ischemia.Stroke.2005; 36(9):1954-1959.
[10] Zhao H,Wang R,Wu X,et al.Erythropoietin delivered via intra-arterial infusion reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress in brain microvessels of rats following cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015;10(1): 153-161.
[11] Wang R, Wu X, Liang J et al.Intra-artery infusion of recombinant human erythropoietin reduces blood-brain barrier disruption in rats following cerebral ischemia and reperfusion.Int J Neurosci.2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[12] Won S,Lee JH,Wali B,et al.Progesterone attenuates hemorrhagic transformation after delayed tPA treatment in an experimental model of stroke in rats: involvement of the VEGF-MMP pathway.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2014;34(1): 72-80.
[13] Wang L,Li Z,Zhang X,et al.Protective effect of shikonin in experimental ischemic stroke: attenuated TLR4, p-p38MAPK, NF-kappaB, TNF-alpha and MMP-9 expression, up-regulated claudin-5 expression, ameliorated BBB permeability. Neurochem Res.2014; 39(1):97-106.
[14] Dong W, Qi Z, Liang J,et al.Reduction of zinc accumulation in mitochondria contributes to decreased cerebral ischemic injury by normobaric hyperoxia treatment in an experimental stroke model.Exp Neurol.2015.[Epub ahead of print]
[15] Marinescu M,Bouley J,Chueh J,et al.Clot injection technique affects thrombolytic efficacy in a rat embolic stroke model: implications for translaboratory collaborations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2014;34(4):677-682.
[16] Bai X,Zhang X,Chen L,et al.Protective effect of naringenin in experimental ischemic stroke: down-regulated NOD2, RIP2, NF-kappaB, MMP-9 and up-regulated claudin-5 expression. Neurochem Res.2014;39(8):1405-1415.
[17] Golab P,Boguszewska-Czubara A,Kielbus M,et al.The rtPA increases MMP-9 activity in serum during ischaemic stroke. Neurol Neurochir Pol.2014;48(5):309-314.
[18] Maradni A,Khoshnevisan A,Mousavi SH,et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and MMP inhibitors on intracranial aneurysms: a review article. Med J Islam Repub Iran.2013;27(4):249-254.
[19] Lukaszewicz-Zajac M, Mroczko B, Slowik A. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J Neural Transm. 2014; 121(11):1387-1397.
[20] Chao HM,Chuang MJ,Liu JH,et al.Baicalein protects against retinal ischemia by antioxidation, antiapoptosis, downregulation of HIF-1alpha, VEGF, and MMP-9 and upregulation of HO-1.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2013;29(6): 539-549.
[21] Lukaszewicz-Zajac M,Mroczko B,Kornhuber J,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in the tumors of central nervous system (CNS). J Neural Transm.2014;121(5):469-477.
[22] Rosell A,Ortega-Aznar A,varez-Sabin J,et al.Increased brain expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 after ischemic and hemorrhagic human stroke.Stroke.2006; 37(6):1399-1406.
[23] Liang J,Qi Z,Liu W,et al.Normobaric hyperoxia slows blood-brain barrier damage and expands the therapeutic time window for tissue-type plasminogen activator treatment in cerebral ischemia. Stroke.2015;46(5):1344-1351.
[24] Zhao H,Wang R,Wu X,et al.Erythropoietin delivered via intra-arterial infusion reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress in brain microvessels of rats following cerebral ischemia and reperfusion.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.2015;10(1):153-161.
[25] Inzitari D, Giusti B, Nencini P,et al. MMP9 variation after thrombolysis is associated with hemorrhagic transformation of lesion and death.Stroke.2013;44(10):2901-2903.
[26] Jin X,Liu J,Yang Y,et al.Spatiotemporal evolution of blood brain barrier damage and tissue infarction within the first 3h after ischemia onset.Neurobiol Dis.2012; 48(3):309-316.
[27] Liu J,Jin X,Liu KJ,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to blood-brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage.J Neurosci.2012;32(9):3044-3057.
[28] Yang Y,Estrada EY,Thompson JF,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2007; 27(4):697-709.
[29] Latour LL,Kang DW,Ezzeddine MA,et al. Early blood-brain barrier disruption in human focal brain ischemia Ann Neurol. 2004;56(4):468-477.
[30] Yang Y, Thompson JF, Taheri S,et al.Early inhibition of MMP activity in ischemic rat brain promotes expression of tight junction proteins and angiogenesis during recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013;33(7):1104-1114.
[31] Asahi M,Asahi K,Jung JC,et al. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2000;20(12):1681-1689.
[32] Wang X,Tsuji K, Lee SR,et al. Mechanisms of hemorrhagic transformation after tissue plasminogen activator reperfusion therapy for ischemic stroke. Stroke.2004; 35(11 Suppl 1): 2726-2730. |