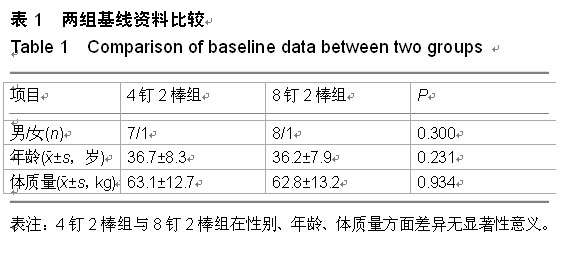
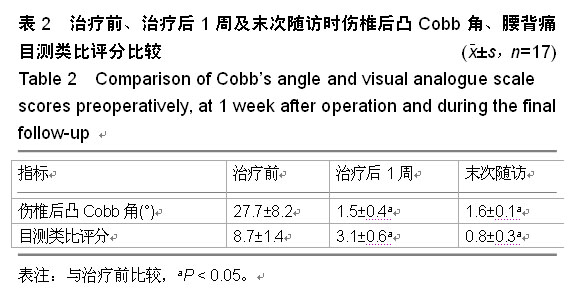
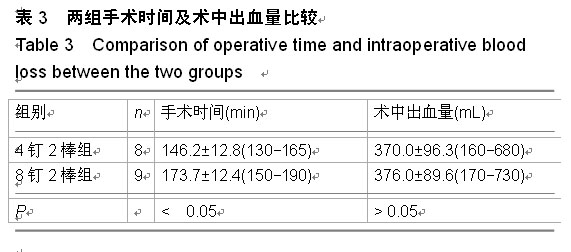
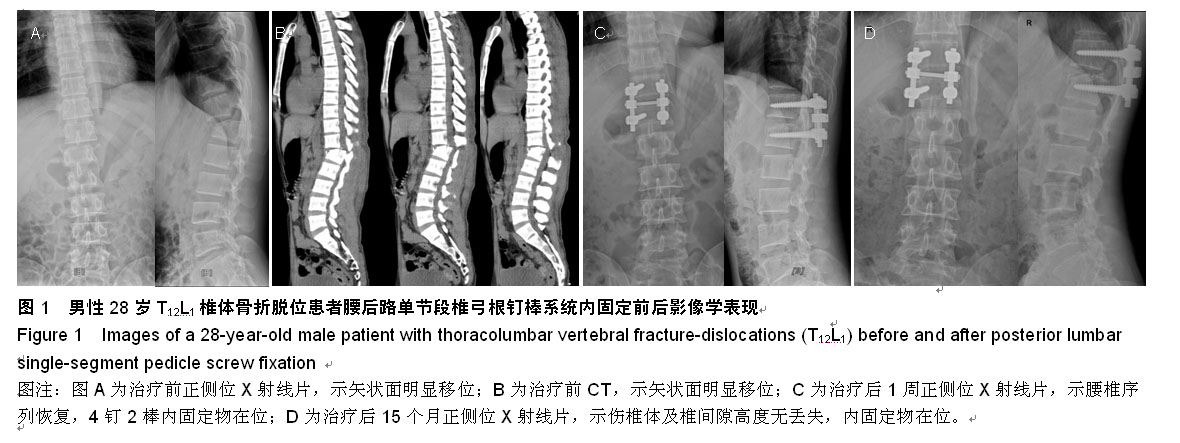
| [1] Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, et al. A comprehensi classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J. 1994;3(4):184-201.
[2] 郝定均.胸腰椎骨折分型研究进展及临床意义[J].美中国际创伤杂志,2012,11(1):9-12.
[3] 夏小鹏,成红兵,刘鹏,等.胸腰椎损伤分型及评分系统的临床应用价值[J].吉林医学,2012,33(7):1430-1431.
[4] 梁伟之,张海波,贾俊峰,等.椎弓根钉置入治疗胸腰段骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,44(16):8308-8315.
[5] 宋升,孙振中,芮永军,等.椎弓根钉棒系统置入复位内固定胸腰段椎体爆裂骨折的椎管形态变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22): 4047-4054.
[6] 印飞,张绍东.单节段椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(4):377-379.
[7] Moelmer M, Gehrchen M, Dahl B. Long-term functional results after short-segment Long-term functional results after short-segment pedicle fixation of thoracolumbar fractures. Injury. 2013;44(12):1843-1846.
[8] 王宇,孔超,鲁世保,等.经伤椎单节段与跨伤椎短节段固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效对比[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(3): 141-145.
[9] 鲍宏玮,严力生,钱海平,等.胸腰椎骨折后路长节段固定与短节段固定的疗效分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(1):76-78.
[10] 邢飞,樊道斌,陈宏赋,等.单节段椎弓根固定椎体内打压植骨治疗胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(2):134-136.
[11] 蒋荣辉,程黎明.胸腰椎骨折分类的研究进展[J].医学综述,2013,19(8):1432-1435.
[12] McCormack T, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (phila pa 1976).1994; 19(15):1741-1744.
[13] Gelb D, Luding S, Karp JE, et al. Successful treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with short-segment pedicle instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010; 23(5):293-301.
[14] 郝刚,孙天胜,李绍光,等.短节段椎弓根螺钉置入内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(39):7237-7241.
[15] Vaccaro AR, Zeiller SC, Hulbert RJ, et al. The thoracolumbar injury severity score: a proposed treatment algorithm. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(3):209-215.
[16] Vaccaro AR, Lehman RA Jr, Hurlbert RJ, et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(20):2325-2333.
[17] 张志成,孙天胜,李放,等.胸腰椎损伤分类及损伤程度评分系统的初步评估[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(1):18.
[18] 吕游,张大明,李瑞,等.三种胸腰段骨折分类法的可信度和可重复性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2001,21(7):566.
[19] Vaccaro AR, Oner C, Kepler CK, et al. AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system: fracture description, neurological status, and key modifiers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(23):2028-2037.
[20] 崔尚斌,魏富鑫,刘少喻,等.单节段与跨伤椎短节段固定的对比研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17):2710-2716.
[21] 苏明海,张勇,徐院生,等.后路复位长节段固定植骨融合治疗胸腰椎骨折脱位[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(4):376-378.
[22] Defino HL, Scarparo P. Fractures of thoracolumbar spine: monosegmental fixation. Injury. 2005;36suppl 2: B90-97.
[23] Defino HL, Herrero CF, Romeiro CF. Monosegmental fixation for the treatment of fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Indian J Orthop. 2007;41(4):337-345.
[24] Liu S, Li H, Liang C, et al. Monosegmental transpedicular fixation for selected patients with thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(1):38-44.
[25] Finkelstein JA, Wai EK, Jackson SS, et al. Single-level fixation of flexion distraction injuries. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16(3):236-242.
[26] Denis F. Spinal instability as defined by the three-column spine concept in acute spinal trauma. Clin Othop Relat Res. 1984;(189): 65-76.
[27] 魏思奇,孙永建,王建民,等.伤椎置钉单节段内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(7):695-696.
[28] 唐焕章,徐皓,林松庆,等.一期后路手术矫治胸椎及胸腰段脊椎骨折脱位[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(6):609-611.
[29] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2012:798-799.
[30] Beringer W, Potts E, Khairi S, et al. Percutaneous pedicle screw instrumentation for temporary internal bracing of nondisplaced bony Chance fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(3):242-247.
[31] 许效坤,左炳光.后路短节段固定治疗胸腰椎骨折是否需要融合[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(9):820-821.
[32] 孙军战,赵克义.非植骨融合在经椎弓根后路短节段固定治疗胸腰椎骨折中的可行性[J].颈腰痛杂志,2011,32(3):192-194.
[33] 孙天全,厉运收.经椎弓根后路短节段非融合固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(18):1670-1672.
[34] Kim YM, Kim DS, Choi ES, et al. Nonfusion method in thoracolumbar and lumbar spinal fractures. Spine. 2011;36(2): 170-176.
[35] 刘仲凯,郝定均,吴起宁,等.非融合手术方式治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(19):778-780.
[36] 杨子明,郭昭庆,党耕町,等.胸腰椎骨折诊断与治疗热点问题高峰论坛纪要[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(8):505-508.
[37] 林子丰,王万明,魏梅洋.后路非融合研究进展[J].临床外科杂志,2014,22(5):372-373.
[38] Kim HY, Kim HS, Kim SW, et al. Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Unstable Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Burst Fracture: A Prospective Study on Selective Consecutive Patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012;51(4): 203-207.
[39] Jindal N, Sankhala SS, Bachhal V. The role of fusion in the management of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine treated by short segment pedicle screw fixation: a prospective randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(8):1101-1106.
[40] Toyone T, Ozawa T, Inada K, et al. Short-segment fixation without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fractures with neurological deficit can preserve thoracolumbar motion without resulting in post-traumatic disc degeneration: a 10-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(17): 1482-1490. |