中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (19): 2959-2964.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.19.002
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员对心肌梗死后心电图和血流动力学指标的影响
吕志伟
- 伊犁师范学院,新疆维吾尔自治区伊宁市 835000
-
出版日期:2015-05-06发布日期:2015-05-06 -
作者简介:吕志伟,男,1982年生,新疆维吾尔自治区昌吉市人,汉族,2009年陕西师范大学毕业,硕士,讲师,主要从事运动心血管生物方面的研究。 -
基金资助:|新疆伊犁师范学院2013年度一般科研项目(2013YSYB38):新疆伊犁州2013-2015年教育规划课题(课题编号:TY165,课题批准号:TLJ13291)
Effects of aerobic exercise and bone marrow stem cells mobilization on hemodynamics and electrocardiogram of myocardial infarction rats
Lv Zhi-wei
- Yili Normal University, Yining 835000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2015-05-06Published:2015-05-06 -
About author:Lv Zhi-wei, Master, Lecturer, Yili Normal University, Yining 835000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the General Scientific Research Project of Yili Normal University in 2013, No. 2013YSYB38; the Educational Program of Yili Prefecture in 2013-2015, No. TY165-TLJ13291
摘要:
背景:心电图和血流动力学是评价心功能康复的有效指标,目前已经证实有氧运动或骨髓干细胞动员单一因素干预均可对心肌梗死动物心电图和血流动力学产生良好影响,而二者联合干预对心电图和血流动力学指标的影响尚未见文献报道。 目的:探讨有氧运动联合骨髓干细胞动员对缺血心脏心电图和血流动力学部分指标的影响。 方法:结扎大鼠左冠状动脉前降支制作急性心肌梗死模型,心肌梗死运动组和心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠于造模后1周在电动跑台进行有氧运动训练,每周训练5 d,持续8周。心肌梗死动员剂组和心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠在造模后3 h皮下注射生理盐水稀释的重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子10 μg/(kg•d),连续使用5 d。8周后检测心电图和血流动力学部分指标评价心功能。 结果与结论:心肌梗死大鼠左心室收缩压、左室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率值均明显降低,左室舒张末压升高,提示心梗后心脏已发生心功能不全;心肌梗死运动组和心肌梗死动员剂组大鼠左心室收缩压、左室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率值均有一定程度的升高,左室舒张末压有所下降,提示有氧运动和骨髓干细胞动员均能改善心梗大鼠心肌收缩和舒张功能;心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠心功能的各项评价指标更接近于正常对照组大鼠,说明有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员显著增强了大鼠心肌收缩性能,使心肌收缩/舒张功能都得到显著改善。
中图分类号:
引用本文
吕志伟. 有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员对心肌梗死后心电图和血流动力学指标的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(19): 2959-2964.
Lv Zhi-wei. Effects of aerobic exercise and bone marrow stem cells mobilization on hemodynamics and electrocardiogram of myocardial infarction rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(19): 2959-2964.
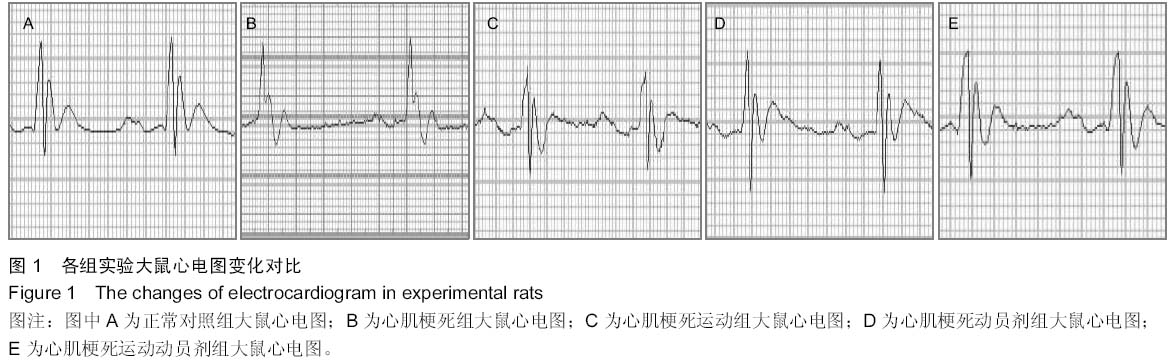
2.1 实验动物数量分析 共有49只SD大鼠参加实验,其中4只大鼠在心肌梗死手术中死亡,属于动物模型制备过程中的正常死亡现象,其余45只大鼠至8周实验结束后无死亡。另外大鼠在心肌梗死手术后共有2组18只进行了有氧运动训练计划,在实验过程中由于天气炎热,大鼠出现轻微疲劳现象,因此将运动时间由原来的上午11点调整为上午8点,调整后轻微运动疲劳现象消失。在实验过程中还发现,心肌梗死运动组和心肌梗死运动动员组大鼠在饮食、反应、毛发、睡觉等行为学方面,表现明显优于心肌梗死组,说明有氧运动和骨髓干细胞动员干预方法是正确和可靠的。
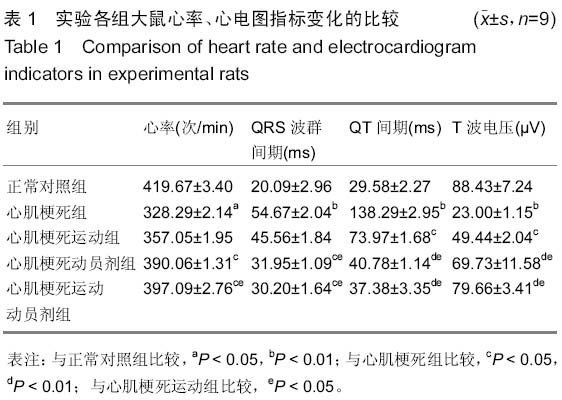
2.2 实验大鼠心电图指标变化 实验结果显示,与正常对照组相比,心肌梗死组大鼠心率和T波电压显著降低,QRS波群间期和QT间期显著性延长;与心肌梗死组大鼠相比,心肌梗死运动组大鼠心率回升,但差异无显著性意义,QT间期降低,T波电压显著提高,而QRS波群间期无显著变化,心肌梗死动员剂组大鼠各项指标均有显著变化,心率和T波电压显著升高,QRS波群间期和QT间期显著降低;心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠各项指标均有显著变化,心率和T波电压显著升高,QRS波群间期和QT间期显著降低(图1,表1)。
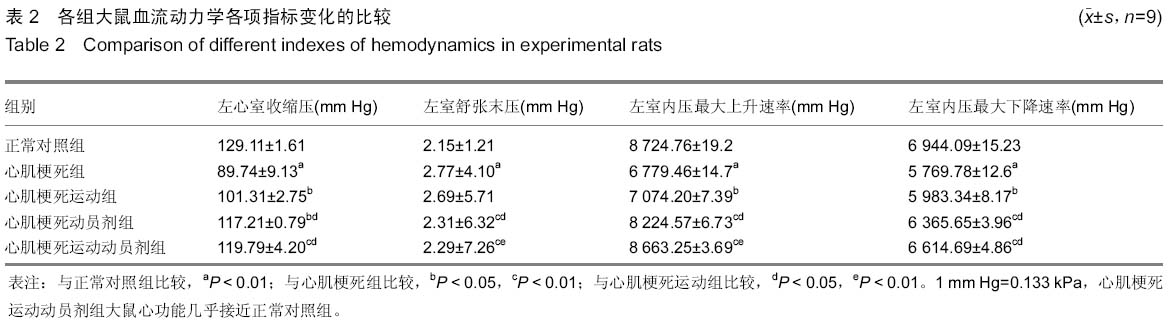
2.3 实验各组大鼠血流动力学指标变化 实验各组大鼠血流动力学监测结果显示,心肌梗死组大鼠与正常对照组比较,左心室收缩压、左室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率值明显降低,左室舒张末压升高;与心肌梗死组相比,心肌梗死运动组大鼠左心室收缩压、左室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率值均有一定增高,左室舒张末压有所下降,但差异无显著性意义;心肌梗死动员剂组左心室收缩压、左室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率均显著高于心肌梗死组,而左室舒张末压显著降低;心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠心功能各项指标几乎接近于正常对照组大鼠,表明有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员后,显著降低了心肌梗死大鼠左室舒张末压,明显升高了左心室收缩压,增强了心肌收缩性能,使心肌收缩/舒张功能都得到显著改善(表2)。
|
[1] Rüder C, Haase T, Krost A, et al. Combinatorial G-CSF/AMD3100 treatment in cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104644.
[2] Hibbert B, Hayley B, Beanlands RS, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor therapy for stem cell mobilization following anterior wall myocardial infarction: the CAPITAL STEM MI randomized trial. CMAJ. 2014;186(11):E427-434.
[3] Cheng Z, Liu X, Ou L, et al. Mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008; 22(5):363-371.
[4] Soncin R, Pennone J, Guimarães TM, et al. Influence of exercise order on electromyographic activity during upper body resistance training. J Hum Kinet. 2014;44:203-210.
[5] Korzeniowska-Kubacka I, Bilińska M, Michalak E, et al. Influence of exercise training on left ventricular diastolic function and its relationship to exercise capacity in patients after myocardial infarction. Cardiol J. 2010;17(2):136-142.
[6] Turan RG, Brehm M, Köstering M, et al. Effects of exercise training on mobilization of BM-CPCs and migratory capacity as well as LVEF after AMI. Med Klin (Munich). 2006;101 Suppl 1:198-201.
[7] Garza MA, Wason EA, Zhang JQ. Cardiac remodeling and physical training post myocardial infarction. World J Cardiol. 2015;7(2):52-64.
[8] Wojakowski W, Landmesser U, Bachowski R, et al. Mobilization of stem and progenitor cells in cardiovascular diseases. Leukemia. 2012;26(1):23-33.
[9] Shi XC, Cai MX, Tian ZJ. Research advance on cardiomyocyte proliferation induced by aerobic exercise and stem cell mobilization. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2014;45(4): 276-281.
[10] 蔡梦昕,张娟娟,史秀超,等.有氧运动和G-CSF干预对心梗大鼠心肌细胞再生的影响及其机制探讨[J].体育科学, 2013,33(5): 50-58
[11] Xu X, Wan W, Powers AS, et al. Effects of exercise training on cardiac function and myocardial remodeling in post myocardial infarction rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44(1):114-122.
[12] Batista ML Jr, Santos RV, Oliveira EM, et al. Endurance training restores peritoneal macrophage function in post-MI congestive heart failure rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007; 102(5): 2033-2039.
[13] Ripa RS. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor therapy to induce neovascularization in ischemic heart disease. Dan Med J. 2012;59(3):B4411.
[14] Ishida N, Iwata H, Shimabukuro K, et al. Effects of omentopexy combined with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in a rabbit heart model. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011; 39(3):375-380.
[15] 晏凯利,曾秋棠,李宾公.自体骨髓干细胞动员治疗大鼠实验性心肌梗死[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2005,13(5):322-324.
[16] Bekler A, Gazi E, Erba? G, et al. Relationship between presence of fragmented QRS on 12-lead electrocardiogram on admission and long-term mortality in patients with non-ST elevated myocardial infarction. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2014; 42(8):726-732.
[17] Mathieu E, Lamirault G, Toquet C, et al. Intramyocardial delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-seeded hydrogel preserves cardiac function and attenuates ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2012; 7(12):e51991.
[18] Duran JM, Makarewich CA, Sharp TE, et al. Bone-derived stem cells repair the heart after myocardial infarction through transdifferentiation and paracrine signaling mechanisms. Circ Res. 2013;113(5):539-552.
[19] Henning RJ. Stem cells in cardiac repair. Future Cardiol. 2011; 7(1):99-117.
[20] Cheng Z, Liu X, Ou L, et al. Mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008; 22(5): 363-371.
[21] Shintani S, Murohara T, Ikeda H, et al. Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001;103(23):2776-2779.
[22] 张勇,梁家立,王胜,等.联合应用粒细胞集落刺激因子和骨髓基质干细胞治疗急性心肌缺血的实验研究[J].南方医科大学学报, 2007, 27(1):43-45,48.
[23] Yan B, Wei JJ, Yuan Y, et al. IL-6 cooperates with G-CSF to induce protumor function of neutrophils in bone marrow by enhancing STAT3 activation. J Immunol. 2013;190(11): 5882-5893.
[24] Zhao JJ, Liu XC, Kong F, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve myocardial function in a swine model of acute myocardial infarction. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(3): 1448-1454.
[25] Leosco D, Rengo G, Iaccarino G, et al. Exercise promotes angiogenesis and improves beta-adrenergic receptor signalling in the post-ischaemic failing rat heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78(2):385-394.
[26] de Waard MC, van der Velden J, Bito V, et al. Early exercise training normalizes myofilament function and attenuates left ventricular pump dysfunction in mice with a large myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2007;100(7):1079-1088.
[27] Zheng H, Luo M, Shen Y, et al. Effects of 6 months exercise training on ventricular remodelling and autonomic tone in patients with acute myocardial infarction and percutaneous coronary intervention. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(9):776-779.
|
| [1] | 姜 涛, 马 磊, 李志强, 寿 玺, 段明军, 吴 硕, 马 创, 魏 琴. 血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向血管内皮细胞分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | 陈 扬, 黄邓高, 高元慧, 王顺兰, 曹 卉, 郑琳麟, 何浩伟, 罗思琴, 肖敬川, 张应爱, 张淑芳. 低强度脉冲场超声促进人脂肪间充质干细胞的增殖和黏附[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | 张立书, 刘安琪, 何小宁, 金 岩, 李 蓓, 金 钫. Alpl基因影响骨髓间充质干细胞治疗溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | 阮光萍, 姚 翔, 刘高米洋, 蔡学敏, 李自安, 庞荣清, 王金祥, 潘兴华. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗树鼩创伤性全身炎症反应综合征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | 莫剑玲, 何少茹, 冯博文, 简敏桥, 张晓晖, 刘财盛, 梁一晶, 刘玉梅, 陈 亮, 周海榆, 刘艳辉. 构建预血管化细胞膜片及血管形成相关因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | 陈 磊, 郑 蕊, 杰永生, 綦 惠, 孙 磊, 舒 雄. 脂肪血管基质成分复合骨软骨一体化支架的体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | 魏 琴, 张 雪, 马 磊, 李志强, 寿 玺, 段明军, 吴 硕, 贾麒钰, 马 创. 血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | 陈 晓, 郭 智, 陈丽娜, 刘玄勇, 张弋慧智, 李旭绵, 王月乔, 韦丽娅, 谢 晶, 蔺 莉. 自体外周血造血干细胞动员采集的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | 郭志斌, 吴春芳, 刘子洪, 张钰英, 迟博婧, 王 宝, 马 超, 张国彬, 田发明. 辛伐他汀可刺激骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | 李聪聪, 姚 楠, 黄丹娥, 宋 敏, 彭 莎, 李安安, 卢 超, 刘文刚. 人髌下脂肪垫干细胞的鉴定及成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | 高元慧, 向 杨, 曹 卉, 王顺兰, 郑琳麟, 何浩伟, 张应爱, 张淑芳, 黄邓高. 两种月龄近交系五指山小型猪脂肪间充质干细胞生物学特性的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | 曹 阳, 张军平, 彭 立, 丁 义, 李光辉. 兔主动脉内皮细胞的分离培养及生物学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | 代 敏, 王 帅, 张霓霓, 黄桂林, 余丽梅, 胡小华, 易 杰, 姚 礼, 张立刚. 低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞的生物学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | 覃艳春, 荣 震, 蒋锐沅, 付 彬, 洪晓华, 莫春梅. 中药复方制剂抑制CD133+肝癌干细胞增殖及干性转录因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | 戴雅玲, 陈乐文, 何肖君, 林华伟, 贾微微, 陈立典, 陶 静, 柳维林. miR-146b过表达慢病毒载体构建及对海马神经干细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
时间及地点:实验于2011年9月至2012年8月在陕西师范大学运动生物学研究所和国家211工程大学重点建设实验室完成。
材料:
实验动物:3月龄雄性SD大鼠49只,购于西安交通大学医学院实验动物管理中心,动物质量合格证号:陕医动证字08-004号,体质量180-220 g,动物室内温度20- 29 ℃,相对湿度40%-50%,实验各组大鼠均用干燥饲料喂养,严格按照国家啮齿类动物标准执行,自由饮水和进食,分笼饲养,每笼7只。
实验方法:
心肌梗死动物模型制备:用生理盐水配置5%的戊巴比妥钠麻醉剂,按照大鼠体质量(30 μg/kg)腹腔注射,采用电子呼吸机连接呼吸面罩正压通气辅助其规律呼吸,待大鼠呼吸变得缓慢正常后,剪刀去胸部毛,手术刀开胸暴露心脏,整个手术过程均用心电图和血压仪监测是否有异常变化,同时观察结扎处心肌颜色变化。在左心耳和肺动脉圆锥间下缘2 mm处结扎左冠状动脉前降支,进针深度为0.3-0.5 mm。以心电图ST段弓背抬高,出现Q波或T波倒置现象,心肌颜色变白判断为结扎成功标志,手术成功后用7号针逐层缝合,缝合处滴入适当80×104 U的抗生素,防治皮肤感染,正常对照组不做任何手术处理[10]。
|
有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员心肌梗死大鼠的心电图和血流动力学实验
所用主要试剂和仪器:
|
|
|
试剂和仪器
|
来源
|
|
重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子注射液
|
哈药集团生物工程有限公司
|
|
戊巴比妥钠
|
美国Sigma公司
|
|
动物电子辅助呼吸机
|
浙江大学医学院医学仪器实验厂
|
|
实验动物用3.0 kg电子称
|
浙江余姚市金诺天平有限公司
|
|
大鼠笼式电刺激5道实验跑台
|
安徽正华生物仪器设备有限公司
|
|
实验用6 mm聚乙烯导管
|
西安交通大学实验仪器与设备中心
|
|
RM6240多道生理信号采集处理系统
|
四川省成都仪器厂
|
|
ECG型小动物心电图机
|
深圳市凯沃尔电子有限公司
|
|
电子分析天平
|
上海奥豪斯国际贸易有限公司
|
有氧运动训练方案:心肌梗死运动组和心肌梗死运动动员剂组SD大鼠共18只,运动强度和时间严格按照Xu等[11-12]文献所报道的标准执行。训练具体方案为:大鼠在进行心肌梗死手术后1周开始训练,为了能使大鼠更好的适应跑台的训练强度和时间,起始训练速度为10 m/min,跑台坡度为5%,训练时间为10 min,速度逐渐增加至 16 m/min,运动时间持续至50 min(含起始训练时间10 min);1周后起始训练时间缩短为5 min,其他参数均不变,以上训练方案每周5 d,训练至8周结束。大鼠在有氧运动过程中偶尔会出现与电动跑台不同步现象,及时采用小于< 1 mA的电刺激仪促使其与训练节奏同步,每天观察大鼠的一般状况,每4 d测量体质量以监控运动强度是否合理。
骨髓干细胞动员剂的给药剂量和方法:国内外大量文献报道,心肌急性缺血后数小时到48 h内释放大量的炎症因子(白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8等),炎症因子可诱导少量干细胞动员,此时同时注入粒细胞集落刺激因子对骨髓干细胞的动员作用更强。目前研究证实皮下或肌肉注射粒细胞集落刺激因子动员骨髓干细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死,其有效的细胞成分基本相同[13-15]。本实验骨髓干细胞动员剂选择了粒细胞集落刺激因子。具体给药方法为:心肌梗死动员剂组和心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠在进行心肌梗死手术后3 h按剂量给予生理盐水稀释的重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子(rhG-CSF,质量浓度为2 mg/L)皮下注射10 μg/(kg•d),连续使用5 d;正常对照组同样在皮下注射等量生理盐水,共5 d,心肌梗死组大鼠则于左冠状动脉结扎手术后不作任何处理。
心功能评价指标的测定:实验结束后各组大鼠称质量经20%乌拉坦腹腔麻醉后,取仰卧位固定大鼠于手术台上,将心电图针电极插入四肢皮下,用肢体导联进行心电图检测。切开大鼠颈部皮肤,分离右颈总动脉,0.3%肝素抗凝(2 mL/kg),用聚乙烯导管(内充盈生理盐水)经右颈总动脉逆行插管并记录颈总动脉血压,然后将插管送至左心室,另一端经压力传感器输入RM-6240多导生理记录仪,等左心室曲线波出现后,将导管连同右颈总动脉一并固定结扎,稳定10 min后测量各项指标。
主要观察指标:采用生理多导记录仪通过测试血流动力学指标评定心脏功能,血流动力学常用的指标有心率、左心室收缩压、左室舒张末压、左室内压最大上升速率、左室内压最大下降速率;ECG型小动物心电图机检测大鼠心电图各波段变化。
统计学分析:所有数据运用SPSS 17.0统计软件包进行处理。实验结果中所有数据以x(_)±s表示,多组间均数比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用t 检验,显著性差异选择P < 0.05和P < 0.01水平。
3.2 实验各组大鼠血流动力学变化分析 基础研究和临床上常采用血流动力学生理学指标的变化直接反映心脏功能的强弱。一般有左心室收缩压、左心室舒张末压、左心室内压力最大上升速率和左心室内压最大下降速率4个经典评价指标。左心室收缩压上升是心肌收缩力增强或外周阻力过大(血管弹性下降和高血压等),由心脏后负荷引起室内压过大,是评价心功能最重要的指标。左室舒张末压是在左心室收缩功能减弱或容量负荷过度时升高,一般是由左心室前负荷引起,是病理性心脏的临床表现。左室内压最大上升速率变化是评价心肌收缩性能的金指标,此值下降一般代表心肌收缩力明显减弱。左室内压最大下降速率是评价心肌舒张功能的金指标,此值下降代表心肌舒张功能减弱[17]。
3.2.1 骨髓干细胞动员对心肌梗死大鼠血流动力学指标的影响 近年来关于骨髓干细胞动员对心肌梗死大鼠心功能的影响文献报道越来越多。Duran等[18]采用药物自体动员骨髓干细胞或将培养的骨髓干细胞直接移植到实验动物梗死区,观察修复受损心肌的效果,结果表明,骨髓干细胞在心肌梗死与非梗死交界区表现出横向分化能力,伴随大量新生肌组织出现的同时,广泛建立与未损心肌间微循环,显著减小心肌梗死面积,心室舒张末压力得到改善,心室扩张程度减轻,实验动物病死率显著降低;同时心室射血分数逐渐提高,血流动力学测试指标明显改善,提示粒细胞集落刺激因子促进心肌细胞再生对心功能有很大影响,粒细胞集落刺激因子联合干细胞因子与单独应用比较对心肌梗死小鼠病死率影响接近,但是梗死面积减少了40%,室壁扩张程度下降了26%,左心室舒张末压下降了70%,实验证明左心室射血分数及血流动力学指标明显改善[19]。分析原因可能是急性心肌梗死后粒细胞集落刺激因子激活了机体的补体系统,促使中性粒细胞及淋巴细胞快速向梗死区聚集,释放活性氧介质,诱导细胞因子释放,增强内皮的细胞黏附分子1与中性粒细胞黏附,诱发细胞因子的级联反应,包括白细胞介素6、人粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、干细胞因子等细胞生长因子的分泌动员并趋化骨髓干细胞归巢到梗死心肌组织[20]。诸多实验显示,急性心肌梗死后外周血干细胞在炎症因子的诱导下显著升高,峰值出现在心肌梗死后第5-7天,尽管组织或器官缺血缺氧引起的炎症反应,使得机体自身存在着骨髓干细胞的“归巢”现象,进而表现为损伤后出现修复反应,但远不足以达到修复组织的目的。研究发现,大鼠心肌梗死后及时予以粒细胞集落刺激因子动员,外周血干细胞是原来的4倍左右[21-22],粒细胞集落刺激因子于用药5 d左右能使外周血干细胞达到峰值,心肌梗死后骨髓自体动员可以显著增加外周血中骨髓来源的干细胞数量,有利于骨髓干细胞归巢至受损心肌和周围区域参与心肌组织恢复,有效改善心功能。
目前,关于自体骨髓干细胞动员或定向培养后移植治疗缺血性心脏病的文献较多,干细胞疗法有效改善心脏功能的喜人效果已得到医学领域的广泛认可,其主要机制主要涉及到几个方面[23]:①骨髓干细胞动员了血液中内皮祖细胞的数量,使其归巢到心肌缺血边缘区域,增殖分化为新的毛细血管和小动脉,促使侧支血管循环形成,达到了血管再生目的,而再生的血管又改善了心肌梗死周边和梗死区尚存活心肌细胞的血液供应,心肌组织实质成分得到修复,从而改善心脏收缩功能,心脏功能显著提升。②骨髓干细胞分化为特有的心肌细胞,梗死心肌组织出现良性重塑,心肌实质成分和间质成分比例适当,心功能得到进一步明显提升。③骨髓间充质干细胞“归巢”至缺血心肌中分裂、增殖和分化为心肌间质成分,使心室壁弹性增强,减缓梗死区瘢痕继续硬化,缩小心肌梗死面积,从而限制心室过度扩张。④骨髓干细胞动员能更好地保护梗死边缘区心肌的组织结构,缩小梗死面积,改善左心室功能,从而降低大鼠死亡率。⑤基质金属蛋白酶在粒细胞集落刺激因子动员骨髓干细胞修复心肌组织,促进血管新生,改善心脏功能的过程中扮演着极其重要的角色,其机制主要是通过显著降解骨髓细胞外基质发挥控制细胞和组织有限增生,防治过度增殖的作用。外源性注入粒细胞集落刺激因子后骨髓和循环血液中炎症因子、中性粒细胞数量明显增多,活性增强;活化的中性粒细胞成为第二信使激活心肌细胞增殖的信号转导通路,促使细胞因子释放增多,心肌组织修复能力显著增强,同时细胞外间质成分过度增多,通过基质金属蛋白酶降解细胞外基质,达到细胞和组织修复的稳态。另一方面,骨髓干细胞动员可使循环血液中白细胞介素8水平升高,进一步刺激中性粒细胞释放基质金属蛋白酶9和基质金属蛋白酶2,降解细胞外基质,打破正常的髓血屏障,促使造血祖细胞向循环系统释放[24]。
本文实验结果显示,心肌梗死组大鼠心脏血流动力学出现明显变化,与正常对照组相比,左心室收缩压值急剧下降,左心室舒张末压值显著升高,左心室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率显著下降,提示心肌梗死大鼠的血流动力学指标急剧下降,心功能严重损害。可能是冠状动脉左前降支结扎手术后导致心肌组织缺血缺氧,心肌细胞大量坏死,心肌胶原增加,心肌间质成分异常增生,病理性心脏肥大,心肌产生恶性重塑,出现心功能代偿现象。心肌梗死动员剂组大鼠左心室收缩压、左心室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率值显著上升,左心室舒张末压值显著下降,说明骨髓干细胞动员使心功能显著提升,病理性心肌重塑显著得到改善,可能是骨髓干细胞通过旁分泌和自分泌一些细胞因子促使梗死区固有干细胞增殖分化为心肌细胞,另外骨髓干细胞归巢到心肌梗死炎症区分化心肌细胞,以修复或维持受损的心肌组织,提高心功能。
3.2.2 有氧运动对心肌梗死大鼠血流动力学指标的影响 在动物实验中,Leosco等[25]对心肌梗死后心力衰竭的Wister大鼠进行为期10周的有氧运动训练。结果发现,心力衰竭安静对照组大鼠左心室胶原过度增生,左心室内径明显增大,射血分数显著降低,左心室舒张末压增大,且肺部出现严重的充血性堵塞现象,心肌细胞对外源性肾上腺素刺激的收缩反应变得迟钝,与心衰对照组相比,心力衰竭运动组大鼠心肌组织内血管内皮生长因子表达逐渐增加,同时梗死区动脉生成增多,冠脉血流明显提高,左心室内径减小,心肌细胞对外源性肾上腺素刺激的收缩反应增强。提示运动改善心力衰竭大鼠的心脏功能可能与肾上腺素受体(β1-AR)的上调有关。关于运动对心肌梗死后大鼠心室重构的影响,Waard等[26]在实验中得到了相类似的结果,同时发现,心肌梗死运动组大鼠心肌组织内cAMP和β1-AR水平显著性升高,而且发现心肌细胞内Na+/Ca2+交换水平也得到了明显加强。更进一步证实了运动对心肌梗死大鼠心功能改善与β1-AR水平关系密切。
在临床试验中,Zheng等[27]对患有急性心肌梗死的30例患者长达6个月的康复锻炼计划,其中有3例患者由于身体不适没完成规定的康复计划,其余27例患者6个月后进行超声心动图检测。结果发现,运动组最大吸氧量VOmax的峰值获得了较大提高(P < 0.01);左心室舒张末期的内径与对照组比较显著较少(P < 0.01);左心室射血分数显著提高(P < 0.05),而左心室收缩末期内径和左心室质量指数均没有显著差异。提示6个月的康复运动能够在一定程度上防治急性心肌梗死后早期的心室重构,有利于逐渐改善心功能。
本文研究结果显示,有氧运动后左心室收缩压、左室内压最大上升速率和左室内压最大下降速率有一定程度的回升,左室舒张末压有所下降,心脏收缩舒张功能得到改善。有氧运动能够适度改善心肌梗死大鼠的心功能,维持心脏的功能完整性和协调性;心肌梗死运动动员剂组大鼠心功能的各项指标变化几乎接近于正常对照组大鼠,表明有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员后显著降低了心肌梗死大鼠左室舒张末压,明显升高了左心室收缩压,使心肌收缩/舒张功能都得到显著改善。
1 心肌梗死后心功能下降是其临床上重要的表现,心电图和血流动力学是评价心功能的科学有效指标,因此,心肌梗死后心电图和血流动力学的变化可判断患者的预后效果和未来的发展趋势。 2 已有研究证实有氧运动或者自体骨髓干细胞动员单一因素干预可有效改善心肌梗死动物和患者心功能,血流动力学指标趋于良好的方向发展,但两因素同时干预效果尚未见文献报道。实验证实了8周有氧运动联合自体骨髓干细胞动员的心肌梗死大鼠心功能指标较单一干预因素更佳,更趋于正常状态。
近十几年来经济快速发展和自然环境的改变使人们的生活方式发生了巨大的变化。很多研究显示不良的生活方式可导致多种慢性疾病发病率显著升高,其中心脑血管疾病的发病率和死亡率一直居高不下。有学者据预测到2020年我国心脑血管疾病人数将达到3亿人,每年约有250万人死于此疾病,心肌梗死是死亡率最高的心脑血管疾病之一,因此,积极探索有效的治疗方法和手段对心血管疾病患者而言具有主要的现实意义。以往临床上采用药物延缓心肌梗死患者的寿命,可药物不良反应大,长期服用带来一系列问题。随着干细胞技术的快速发展,自体干细胞动员疗法改善心肌梗死心功能取得了较好的临床效果,正在越来越多的应用。传统认为心肌梗死患者不适合运动或锻炼,由于运动存高风险,患者常采用静养方式,但新近的研究报道心肌梗死可以进行康复运动,田振军等研究团队对心肌梗死动物运动方式、运动强度等多了大量具有开创性的基础研究工作。上述都是一种治疗方式或干预因素对心肌梗死功能的影响,两种或多种干预方式效果是否更好,需要实验验证,本文采用运动联合药物动员干细胞对心肌梗死心电图和血流动力学的影响,探讨多途径联合干预对心肌梗死大鼠心功能的改善情况,为心脏病康复提供基础实验依据。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||