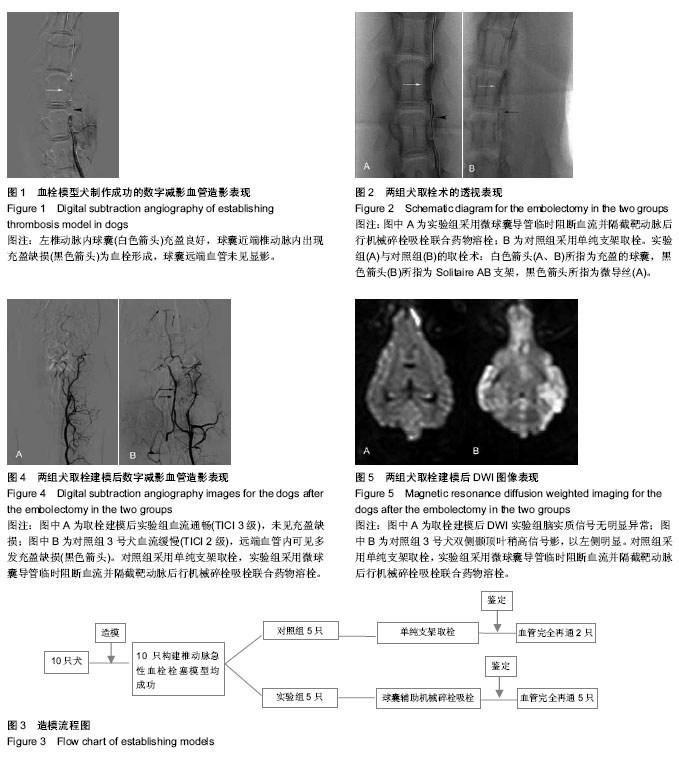
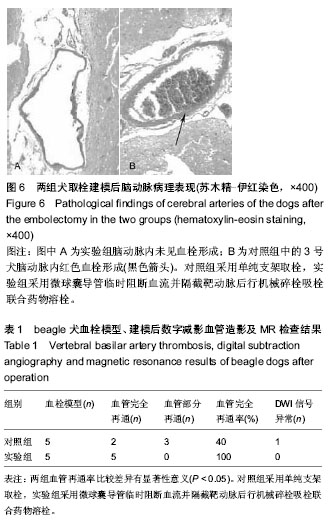
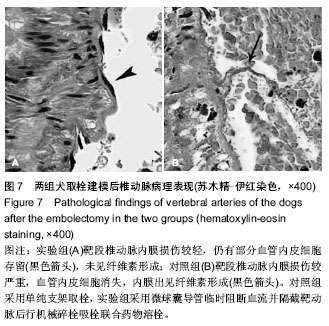
| [1] Hayakawa M. Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: past, present and future. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014; 54(12):1197-1199.
[2] Zhai YK, Zhu WJ, Hou HL, et al. Efficacy of telemedicine for thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. J Telemed Telecare. 2015.
[3] Hlavica M, Diepers M, Garcia-Esperon C, et al. Pharmacological recanalization therapy in acute ischemic stroke-Evolution, current state and perspectives of intravenous and intra-arterial thrombolysis. J Neuroradiol. 2015.
[4] Friedricn B, Gawlitza M, Schob S, et al. Distance to thrombus in acute middle cerebral artery occlusion: a predictor of outcome after intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2015.
[5] Turc G, Isabel C, Calvet D. Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2014;95(12): 1129-1133.
[6] Lin C, Li N, Wang K, et al. Efficacy and safety of endovascular treatment versus intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77849.
[7] Singh B, Parsaik AK, Prokop LJ, et al. Endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013;88(10):1056-1065.
[8] Bae GS, Kwon HJ, Kang CW, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy using a solitaire stent in acute ischemic stroke; initial experience in 40 patients. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2012;14(3):164-169.
[9] Serrone JC, Jimenez L, Ringer AJ. The role of endovascular therapy in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Neurosurgery. 2014;74 Suppl 1:S133-S141.
[10] Turk AR, Campbell JM, Spiotta A, et al. An investigation of the cost and benefit of mechanical thrombectomy for endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6(1):77-80.
[11] Kang DH, Hwang YH, Kim YS, et al. Direct thrombus retrieval using the reperfusion catheter of the penumbra system: forced-suction thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(2):283-287.
[12] Kappelhof M, Marquering HA, Berkhemer OA, et al. Intra-arterial treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke and internal carotid artery occlusion: a literature review. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7(1):8-15.
[13] Castano C, Dorado L, Guerrero C, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire AB device in large artery occlusions of the anterior circulation: a pilot study. Stroke. 2010;41(8):1836-1840.
[14] Pi Y, Zhang L, Yang Q, et al. Neurothrombectomy for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in 1530 patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2012;19(10):1363-1368.
[15] Walcott BP, Boehm KM, Stapleton CJ, et al. Retrievable stent thrombectomy in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: analysis of a revolutionizing treatment technique. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(10):1346-1349.
[16] Davalos A, Pereira VM, Chapot R, et al. Retrospective multicenter study of Solitaire FR for revascularization in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2012;43(10): 2699-2705.
[17] Yin NS, Benavides S, Starkman S, et al. Autopsy findings after intracranial thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: a clinicopathologic study of 5 patients. Stroke. 2010;41(5): 938-947.
[18] Mokin M, Khalessi AA, Mocco J, et al. Endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke: the end or just the beginning? Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36(1):E5.
[19] 罗中华,宦怡,贺洪德,等.急性缺血性脑卒中介入取栓器血栓模型的机械特性比较[J].介入放射学杂志,2013,22(4):317-321.
[20] Lee SH, Kim SY, Woo DC, et al. Differential neurochemical responses of the canine striatum with pentobarbital or ketamine anesthesia: a 3T proton MRS study. J Vet Med Sci. 2010;72(5):583-587.
[21] Rink C, Christoforidis G, Abduljalil A, et al. Minimally invasive neuroradiologic model of preclinical transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in canines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(37):14100-14105.
[22] Christoforidis GA, Rink C, Kontzialis MS, et al. An endovascular canine middle cerebral artery occlusion model for the study of leptomeningeal collateral recruitment. Invest Radiol. 2011;46(1):34-40.
[23] Gifford E, Drazin D, Dalfino JC, et al. The effectiveness of microballoon angioplasty in treating middle cerebral artery occlusion beyond the bifurcation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(8):1541-1548.
[24] 李克,吉训明,凌锋,等.急性脑动脉闭塞的血管造影分级及溶栓治疗疗效评估系统[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2006,3(12):573-576.
[25] 李贵福,马朝晖,罗望池,等.Solitaire AB型支架用于急性脑动脉闭塞取栓术31例[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(2):98-102.
[26] Roth C, Papanagiotou P, Behnke S, et al. Stent-assisted mechanical recanalization for treatment of acute intracerebral artery occlusions. Stroke. 2010;41(11):2559-2567.
[27] Papanagiotou P, Roth C, Walter S, et al. Treatment of acute cerebral artery occlusion with a fully recoverable intracranial stent: a new technique. Circulation. 2010;121(23):2605-2606.
[28] Shindo A, Kawanishi M, Kawakita K, et al. Treatment of acute cerebral artery occlusion using the penumbra system: our early experience. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(6): 441-449.
[29] Nayak S, Ladurner G, Killer M. Treatment of acute middle cerebral artery occlusion with a Solitaire AB stent: preliminary experience. Br J Radiol, 2010;83(996): 1017-1022.
[30] Mokin M, Kass-Hout T, Levy EI. Solitaire FR-a promising new device for acute ischemic stroke treatment. World Neurosurg. 2012;78(6):557-558.
[31] Humphries W, Hoit D, Doss V T, et al. Distal aspiration with retrievable stent assisted thrombectomy for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7(2):90-94.
[32] Mccabe JJ, Phillips TJ, Phatouros C, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire AB device in large intracerebral artery occlusions. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013;57(2):149-155.
[33] Miteff F, Faulder KC, Goh AC, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with a self-expanding retrievable intracranial stent (Solitaire AB): experience in 26 patients with acute cerebral artery occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(6): 1078-1081 |