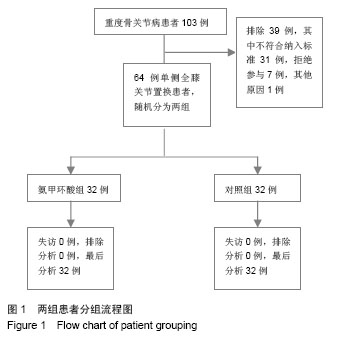
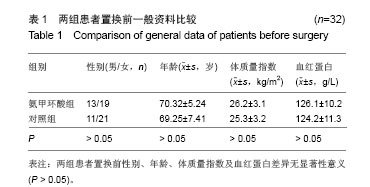
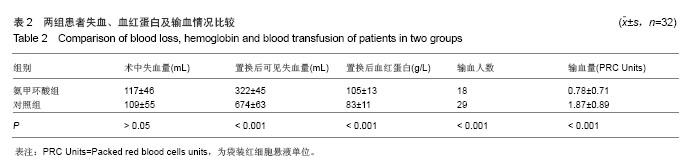
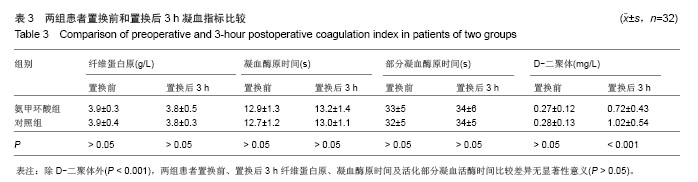
| [1]Listed NA. National Joint Registry for England and Wales. Summary of annual statistics (England and Wales), 2011.
[2]罗吉伟,金大地,黄美贤,等.全膝关节置换术围手术期失血量的评估[J].南方医科大学学报,2006,26(11):1606-1608.
[3]Ferraris VA, Brown JR, Despotis GJ, et al. 2011 Update to the society of thoracic surgeons and the society of cardiovascular anesthesiologists blood conservation clinical practice guidelines. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91(3): 944-982.
[4]Fiebig E. Safety of the blood supply. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;357:6-18.
[5]Maniar RN, Kumar G, Singhi T, et al. Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty:a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:2605.
[6]Sabatini L, Atzori F, Revello S, et al. Intravenous use of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134: 1609-1614.
[7]Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth .2003;90:596-599.
[8]Janssens M, Joris J, David JL, et al. High-dose aprotinin reduces blood loss in patients undergoing total hip replacement surgery. Anesthesiology. 1994;80:23-29.
[9]Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, et al. Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:169-177.
[10]Camarasa MA, Olle G, Serra-Prat M, et al. Efficacy of aminocaproic, tranexamic acids in the control of bleeding during total knee replacement: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96:576-582.
[11]Ponnusamy KE, Kim TJ, Khanuja HS. Perioperative blood transfusions in orthopaedic surgery.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(21):1836-1844.
[12]Slover J, Bosco J. Cost analysis of use of tranexamic Acid to prevent major bleeding complications in hip and knee arthroplasty surgery.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014; 43(10):E217-220.
[13]Samujh C,Falls TD,Wessel R, et al. Decreased blood transfusion following revision total knee arthroplasty using tranexamic acid.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(9):182-185.
[14]Veien M, Sorensen JV, Madsen F, et al. Tranexamic acid given intraoperatively reduces blood loss after total knee replacement: a randomized, controlled study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002;46:1206-1211.
[15]Hynes M, Calder P, Scott G. The use of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2003; 10:375-377.
[16]Orpen NM, Little C, Walker G, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces early post-operative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled trial of 29 patients.Knee. 2006;13:106-110.
[17]Engel JM, Hohaus T, Ruwoldt R, et al. Regional hemostatic status and blood requirements after total knee arthroplasty with and without tranexamic acid or aprotinin. Anesth Analg. 2001;92:775-780.
[18]Tanaka N, Sakahashi H, Sato E, et al. Timing of the administration of tranexamic acid for maximum reduction in blood loss in arthroplasty of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:702-705.
[19]Tan J, Chen H, Liu Q, et al. A meta-analysis of the effectiveness and safety of using tranexamic acid in primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Surg Res. 2013;184(2): 880-887.
[20]Huang Z,Ma J,Shen B,et al.Combination of intravenous and topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12):2342-2346.
[21]Yang Y,Lv YM,Ding PJ,et al. The reduction in blood loss with intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in unilateral total knee arthroplasty without operative drains: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(1): 135-139.
[22]Schreiber GB, Busch MP, Kleinman SH, et al. The risk of transfusion transmitted viral infections: the Retrovirus Epidemiology Donor Study.N Engl J Med.1996; 334: 1685-1690.
[23]Gascon P, Zoumbos NC, Young NS. Immunologic abnormalities in patients receiving multiple blood transfusions. Ann Intern Med.1984;100:173-177.
[24]Singh J, Ballal M S, Mitchell P, et al.Effects of tranexamic acid on blood loss during total hip arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg. 2010; 18(3):282-286.
[25]Ishida K,Tsumura N,Kitagawa A, et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(11):1639-1645
[26]Alshryda S, Mason J, Vaghela M, et al. Topical (intra-articular) tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following total knee replacement: a randomized controlled trial (TRANX-K). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(21):1961-1968.
[27]Kazemi SM, Mosaffa F, Eajazi A, et al.The effect of tranexamic acid on reducing blood loss in cementless total hip arthroplasty under epidural anesthesia. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1):17.
[28]MacGillivray RG, Tarabichi SB, Hawari MF, et al. Tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss after bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized double blind study. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(1):24-28.
[29]McConnell JS, Shewale S, Munro NA, et al. Reducing blood loss in primary knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled trial of tranexamic acid and fibrin spray.Knee. 2012; 19(4):295-298.
[30]Roy SP, Tanki UF, Dutta A, et al. Efficacy of intra-articular tranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12):2494-2501.
[31]Alipour M, Tabari M, Keramati M, et al. Effectiveness of oral Tranexamic acid administration on blood loss after knee artroplasty: a randomized clinical trial.Transfus Apher Sci. 2013;49(3):574-577.
[32]Lin PC,Hsu CH,Chen WS, et al. Does tranexamic acid save blood in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(7):1995-2002.
[33]Soni A, Saini R, Gulati A, et al. Comparison between intravenous and intra-articular regimens of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1525-1527.
[34]Sarzaeem MM, Razi M, Kazemian G, et al.Comparing efficacy of three methods of tranexamic acid administrationin reducing hemoglobin drop following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1521-1524.
[35]Alipour M, Tabari M, Keramati M, et al. Effectiveness of oral Tranexamic acid administration on blood loss after knee artroplasty: a randomized clinical trial.Transfus Apher Sci. 2013;49(3):574-577.
[36]Sano M, Hakusui H, Kojima C, et al. Absorption and excretion of tranexamic acid following intravenous, intramuscular and oral administrations in healthy volunteers. Jpn J Clin Pharmacol Therapeutics.1976;7:375-382.
[37]Benoni G, Fredin H. Fibrinolytic inhibition with tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusion after knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomised, double-blind study of 86 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1996;78:434-440.
[38]Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(13):1153-1159.
[39]Alshryda S, Sarda P, Sukeik M, et al.Tranexamic acid and the reduction of blood loss in total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(12):1577-1585.
[40]Zhang H, Chen J, Chen F, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and use of blood products in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(9):1742-1752.
[41]连鸿凯,王少华,白玉,等.髋膝关节置换术后血浆D-二聚体浓度变化特点的临床观察[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(11): 1090-1092. |