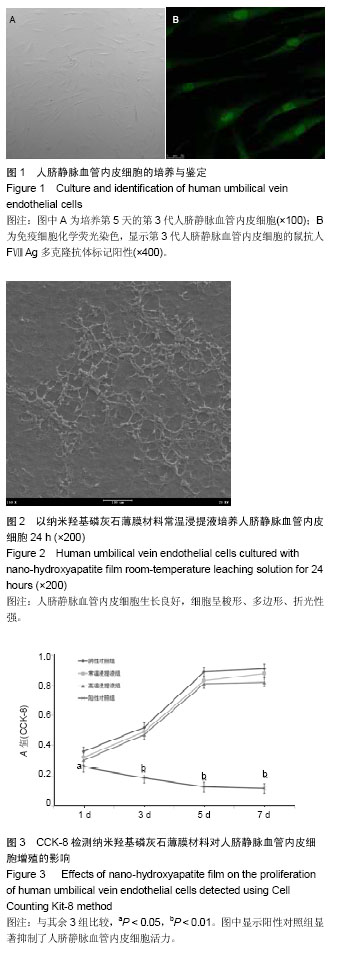
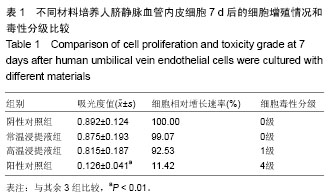
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (16): 2534-2539.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.16.014
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米羟基磷灰石对人脐带静脉血管内皮细胞的毒性评价
程光存,严中亚,李春生,严 宇,韦晓勇
- 安徽医科大学附属省立医院胸心外科,安徽省心血管病研究所,安徽省合肥市 230001
Nano-hydroxyapatite is non-toxic to human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells
Cheng Guang-cun, Yan Zhong-ya, Li Chun-sheng, Yan Yu, Wei Xiao-yong
- Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, the Affiliated Provincial Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Anhui Provincial Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, Hefei 230001, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
背景:有研究应用脉冲激光沉积合成技术在人工心脏机械瓣膜上沉积胶原制备了新型纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜涂层。 目的:观察此种新型纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜对人脐带静脉血管内皮细胞的毒性。 方法:分别采用纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜常温浸提液、纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜高温浸提液、高密度聚乙烯及苯酚溶液培养人脐静脉血管内皮细胞,72 h内倒置相差显微镜下观察细胞生长状况;培养7 d时采用CCK-8法检测细胞增殖与毒性分级。 结果与结论:培养24 h,纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜常温浸提液组、纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜高温浸提液组和高密度聚乙烯组细胞生长良好,呈梭形,折光性强,3组细胞形态、数量无明显差异;苯酚溶液组细胞多为悬浮、圆形、固缩的死细胞;48 h时,除了苯酚溶液组外,其余3组细胞数量明显增加,细胞生长密集,至72 h时细胞生长旺盛,间隙显著减小。培养7 d内,纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜常温浸提液组、纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜高温浸提液组和高密度聚乙烯组细胞增殖活性无差异,均高于苯酚溶液组(P < 0.05),纳米羟基磷灰石薄膜毒性级别为0至1级,表明纳米羟基磷灰石人工心脏机械瓣膜有良好的组织细胞相容性,无毒性作用。
中图分类号: