| [1]樊明文.牙体牙髓病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012:51-52.
[2]史俊男.现代口腔内科学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2004: 267-279.
[3]阙克华,郭斌,王博,等.中药五倍子对不同根面龋损提取非胶原蛋白后再矿化的影响[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2012,43(3): 358-361.
[4]黄彬,陈黄琴.绿茶提取物EGCG阻止牙本质龋进展的初步研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(15):1670-1671.
[5]Jackson JK,Zhao J,Wong W,et al.The inhibition of collagenase induced degradation of collagen by the galloyl-containing polyphenols tannic acid. epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin gallate.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010; 21(5):1435-1443.
[6]Roomi MW,Monterrey JC,Kalinovsky T,et al.Comparative effects of EGCG, green tea and a nutrient mixture on the patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in cancer cell lines.Oncol Rep.2010;24(3):747-757.
[7]李娜.五倍子单宁酸对变异链球菌作用的初步研究[D].西安第四军医大学,2013.
[8]赵今,李艳,孙玉亮,等.没食子鞣质及有效提取物对致龋细菌粘附抑制的作用[J].新疆医科大学学报,2009,32(1):6-8.
[9]林静,朱明,李新尚,等.没食子鞣质及联合氟化钠对不同状态下变形链球菌乳酸脱氢酶活性影响的研究[J].口腔医学,2011, 31(5):257-260.
[10]Hirasawa M,Takada K,Otake S.Inhibition of acid production in dental plaque bacteria by green tea catechins.Caries Res.2006;40(3):265-270.
[11]黄彬,陈黄琴.绿茶提取物EGCG对牙龈卟啉单胞菌体外抑菌作用的研究[J].医药前沿, 2012,2(20):182-183.
[12]阮金云,陈鲲,李娇,等.没食子和五倍子对牛切牙脱矿与再矿化的动力学研究[J].安徽农业科学,2012,52(27):13319-13320.
[13]郑翼,邹玲,李伟.五倍子化学组分对脱矿牙釉质再矿化的影响[J].广东牙病预防,2013,21(7):359-363.
[14]严维,王洋,周璇,等.五倍子促进正畸白垩斑再矿化的体外研究[J].宜春学院学报,2013,35(3):93-95.
[15]陈鲲,阮金云,易多宗,等.五倍子与没食子提取物对人工脱矿釉质再矿化的研究[J].大理学院学报:综合版,2012,11(9):22-24.
[16]邓盟,黎红,董孝立,等.中药五倍子提取物对牙本质表面性能的强化作用[J].上海口腔医学, 2013,22(2):164-168.
[17]李淑慧,吴佩玲.CPP—ACP与氟化钠促进脱矿釉质再矿化的显微硬度研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2011,34(3):323-325.
[18]楚金普,李继遥,郝玉庆,等.中药五倍子化学成分对早期龋显微硬度的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2006,41(10):616-617.
[19]王丽梅,易多宗,杨发,等.三种天然药物对脱矿牛切牙釉质显微硬度的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013,23(9):551-553.
[20]Park SY,Jeong YJ,Kim SH,et al.Epigallocatechin gallate protects against nitric oxide-induced apoptosis via scavenging ROS and modulating the Bcl-2 family in human dental pulp cells.J Toxicol Sci.2013;38(3):371-378.
[21]Kato MT,Leite AL,Hannas AR,et al.Gels containing MMP inhibitors prevent dental erosion in situation.J Dent Res. 2013; 89(5):468.
[22]Chen HQ,Huang B. Effect of EGCG Application on Collagen Degradation in Dentine Caries.Appl Mech Mater. 2013; 455:112-116.
[23]李艳君,唐荣银,吕昕,等.五倍子提取液对牙本质龋损时胶原蛋白分解的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2002,12(5): 252-254.
[24]徐琚,葛丽华,宿颖,等.基质金属蛋白酶2、8、9在乳牙牙本质中的表达及含量分析[J]. 北京口腔医学,2011,19(2):67-69.
[25]黄冠伟,邹琳.人工龋模型的建立方法[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2010, 37(5):537-540.
[26]郭靖.五倍子鞣质促进早期釉质龋再矿化作用的HRTEM研究[D].河南:郑州大学,2014.
[27]汪大照,余志芬,张向宇.五倍子提取物对牙釉质脱矿和再矿化作用的影响[J].江苏中医药, 2011,43(4):85-87.
[28]李艳君,吕昕.牙本质生物人工龋的实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志, 2009,38(8):988-990.
[29]蔡晨星,朱玲,闫智奇,等.奥威尔牙齿脱敏剂对早期牙本质龋再矿化及抑制脱矿作用体外研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2010, 26(3):349-352.
[30]赵今,李新尚,林静,等.天然药物没食子对早期釉质龋再矿化作用的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(4):469-473.
[31]牛巧丽,哈木拉提•吾甫尔,赵今,等.天然药物没食子和联合氟制剂预防龋病的动物实验研究[J].科技导报,2009,27(24):61-66.
[32]黄彬,陈黄琴.绿茶提取物EGCG对牙本质抗酸蚀作用的初步研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(9):928-929.
[33]徐帅.表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯保护脱矿牙本质基质的相关作用研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2014.
[34]Du X,Huang X,Huang C,et al.Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) enhances the therapeutic activity of a dental adhesive.J Dent.2012;40(6):485-492. |
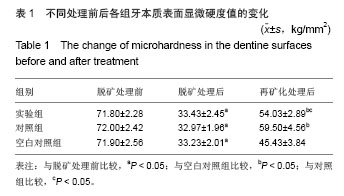
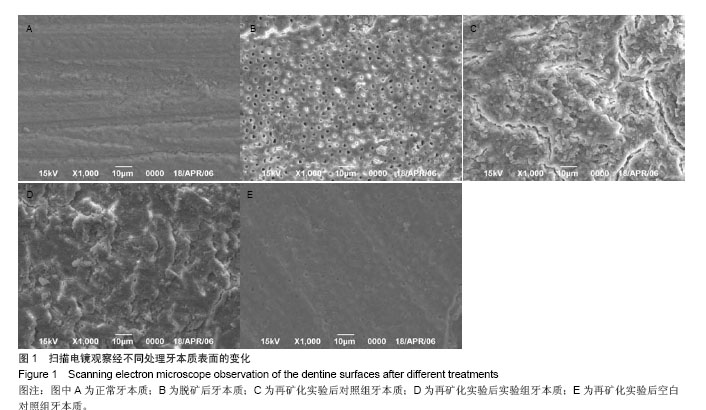
.jpg)