| [1] Getgood A, Brooks R, Fortier L, et al. Articular cartilage tissue engineering. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2009; 91-B:565-576.
[2] Hoemann C, Sun J, McKee M, et al.Chitosan-glycerol phosphate/blood implants elicit hyaline cartilage repair integrated with porous subchondral bone in microdrilled rabbit defects. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.2007; 15:78-89.
[3] Jaklenec A, Hinckfuss A, Bilgen B, et al. Sequential release of bioactive IGF-I and TGF-β1 from PLGA microsphere-based scaffolds.Biomaterials. 2008;29:1518-1525.
[4] Nixon A, Fortier L, Williams J, et al. Enhanced repair of extensive articular defects by insulin-like growth factor-I-laden fibrin composites. J Orthop Res. 1999; 17:475-487.
[5] Hwang NS, Elisseeff JP. Application of Stem Cells for Articular Cartilage Regeneration. J Knee Surg. 2009; 22:60-71.
[6] Re'em T, Witte F, Willbold E, et al. Simultaneous regeneration of articular cartilage and subchondral bone induced by spatially presented TGF-beta and BMP-4 in a bilayer affinity binding system.Acta Biomater. 2012 ;8(9):3283-3293.
[7] Frisbie D, Bowman S, Colhoun H, et al. Evaluation of autologous chondrocyte transplantation via a collagen membrane in equine articular defects-results at 12 and 18 months. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.2008; 16:667-679.
[8] Elisseeff J, McIntosh W, Fu K, et al. Controlled-release of IGF-1 and TGF-β1 in a photopolymerizing hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J Orthop Res. 2001; 19: 1098-1104.
[9] Kim K, Lam J, Lu S, et al. Osteochondral tissue regeneration using a bilayered composite hydrogel with modulating dual growth factor release kinetics in a rabbit model.J Control Release.2013;168(2):166-178.
[10] Aulin C, Jensen-Waern M, Ekman S, et al.Cartilage repair of experimentally 11 induced osteochondral defects in New Zealand White rabbits.Lab Anim. 2013;47(1):58-65.
[11] Lee CS, Watkins E, Burnsed OA, et al. Tailoring adipose stem cell trophic factor production with differentiation medium components to regenerate chondral defects.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(11-12):1451-1464.
[12] Davis ME, Hsieh PCH, Takahashi T, et al. Local myocardial insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) delivery with biotinylated peptide nanofibers improves cell therapy for myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2006; 103:8155-8160.
[13] Ahearne M, Liu Y, Kelly DJ.Combining freshly isolated chondroprogenitor cells from the infrapatellar fat pad with a growth factor delivery hydrogel as a putative single stage therapy for articular cartilage repair.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(5-6):930-939.
[14] Unterman SA, Gibson M, Lee JH, et al.Hyaluronic acid-binding scaffold for articular cartilage repair.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(23-24):2497-506.
[15] Kopesky P, Vanderploeg E, Kisiday J, et al.Controlled delivery of TGF-b1 by self-assembling peptide hydrogels induces chondrogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells and modulates Smad2/3 signaling. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(1-2):83-92.
[16] Park K-H, Park W, Na K. Synthetic matrix containing glucocorticoid and growth factor for chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009; 108: 168-173.
[17] Schmidt M, Chen E, Lynch S. A review of the effects of insulin-like growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor on in vivo cartilage healing and repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14:403-412.
[18] Hunziker E.Growth-factor-induced healing of partial-thickness defects in adult articular cartilage.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001; 9:22-32.
[19] Noth U, Steinert AF, Tuan RS. Technology Insight: adult mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis therapy.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2008; 4:371-380.
[20] Ikeda R, Fujioka H, Nagura I, et al. The effect of porosity and mechanical property of a synthetic polymer scaffold on repair of osteochondral defects. Int Orthop. 2009; 33:821-828.
[21] Holland TA,Bodde EW,Cuijpers VM et al. Degradable hydrogel scaffolds for in vivo delivery of single and dual growth factors in cartilage repair.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007; 15:187-197.
[22] Fortier LA, Mohammed HO, Lust G, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I enhances cell-based repair of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84-B:276-288.
[23] Davidson EN, van der Kraan P, van den Berg W. TGF-b and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15:597-604.
[24] Diao H, Wang J, Shen C, et al. Improved cartilage regeneration utilizing mesenchymal stem cells in TGF-β1 gene-activated scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A.2009; 15: 2687-2698.
[25] Guo X,Park H, Young S,et al. Repair of osteochondral defects with biodegradeable hydrogel composites encapsulating marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010; 6:39-47.
[26] Mi Z, Ghivizzani S, Lechman E, et al. Adverse effects of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human TGF-β1 into rabbit knees. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5:R132-R139.
[27] Fan H, Hu Y, Qin L, et al. Porous gelatin-chondroitin- hyaluronate tri-copolymer scaffold containing microspheres loaded with TGF-β1 induces differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vivo for enhancing cartilage repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 77:785-794.
[28] Miller RE, Grodzinsky AJ, Barrett MF,et al. Effects of the combination of microfracture and self-assembling Peptide filling on the repair of a clinically relevant trochlear defect in an equine model.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(19): 1601-1609.
[29] Chen P, Zhu S, Wang Y, et al. The amelioration of cartilage degeneration by ADAMTS-5 inhibitor delivered in a hyaluronic acid hydrogel.Biomaterials. 2014;35(9):2827-2836. |
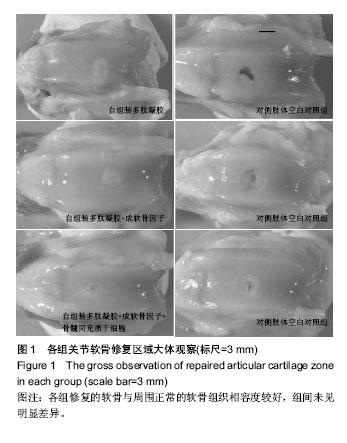
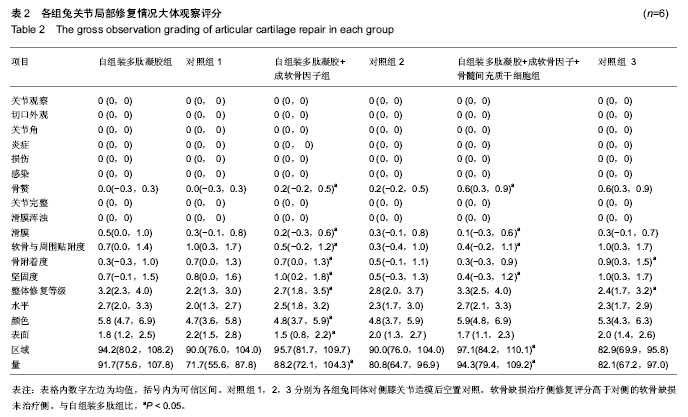
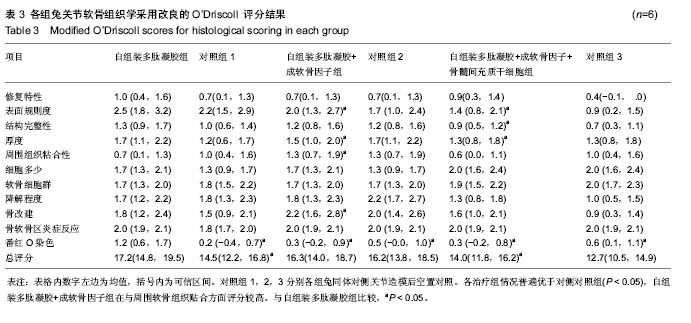
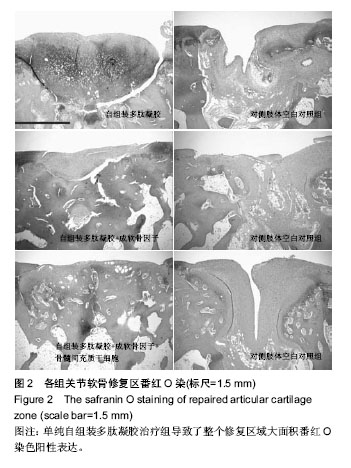
.jpg)
.jpg)