| [1] Turpin YL,Tardivel RD,Tallec A,et al.Corrosion susceptibility of titanium covered by dental cements.Dent Mater. 2000;16(1): 57-61.
[2] Horasawa N,Takahashi A,Marek M.Galvanic interaction between titanium and gallium alloy or dental amalgam.Dent Mater.1999;15(5):318-322.
[3] Wu Z,Xu S,Li W,Teng J,et al.Study on corrosion resistance of three non-noble porcelain alloys.2011;29(5):485-487,493.
[4] Aberer W,Holub H,Strohal R,et al.Palladium in dental alloys--the dermatologists’ responsibility to warn.Contact Dermaiitis.1993;28(3):163-165.
[5] Hsu RWW,Yang CC,Huang CA,et al.Electrochemical corrosion properties of Ti-6Al-4V implant alloy in the biological environment.Mater Sci Eng A.2004;380(1-2):100-109.
[6] Ristic L, Vucevic D,Radovic L,et al. Corrosive and cytotoxic properties of compact specimens and microparticles of Ni-Cr dental alloy. J Prosthodont.2014;23(3):221-226.
[7] Reclaru L,Unger RE,Kirkpatrick CJ,et al.Ni-Cr based dental alloys; Ni release, corrosion and biological evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2012;32(6):1452-60.
[8] Yu J,Zhao F,Wen X,et al. Apoptosis mechanism of gingival fibroblasts induced by nickel ion contained in dental cast alloys.Biomed Mater Eng.2012;22(1-3):151-157.
[9] Robert GC.John MP.Restorative dental materials.11th edtion.Missouri.A Harcout Health Sciences Company. 2002:56-57.
[10] Grosgogeat B,Reclaru L,Lissac M,et al.Measurement and evaluation of galvanic corrosion between titanium/Ti6Al4V implants and dental alloys by electrochemical techniques and auger spectrometry.Biomaterials.1999; 20(10): 933-941.
[11] 刘肃,周延民,王晓容,等.镍铬合金、钛合金及金铂合金在人工唾液中的耐腐蚀性能[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2005,31(5): 774-777.
[12] 孙平,陆瑛,陈松.钴铬、镍铬、含钛镍铬烤瓷合金在人工唾液中耐腐蚀性能的比较[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(6):652-656.
[13] Manaranche C,Homberger H.A proposal for the classification of dental alloys according to their resistance to corrosion.Dent Mater.2007;23(11):1428-1437.
[14] Hodgson AW,Kurz S,Virtanen S,et al.Passive and transpassive behaviour of CoCrMo in simulated biological solutions.Electrochim Acta.2004; 49(13):2167-2178.
[15] Ozcelik TB,Yilmaz B.Galvanic gold plating for fixed dental prosthesis. Eur J Dent.2013;7(3):373-376.
[16] Jones SB,Taylor RL,Colligon JS,et al.Effect of element concentration on nickel release from dental alloys using a novel ion beam method.Dent Mater.2010;26(3):249-256.
[17] Williamson RS,Disegi J,Griggs JA,et al.Nanopore formation on the surface oxide of commercially pure titanium grade 4 using a pulsed anodization method in sulfuric acid.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2013;24(10):2327-2335.
[18] 刘秀晨,安成强.金属腐蚀学[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2002: 86-141.
[19] Ozkomur A,Erbil M,Akova T.Diamondlike carbon coating as a galvanic corrosion barrier between dental implant abutments and nickel-chromium superstructures. 2013; 28(4):1037-1047.
[20] 魏宝明.金属腐蚀理论及应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 1984: 145-146.
[21] Barão VA,Mathew MT,Assunção WG,et al.Stability of cp-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy for dental implants as a function of saliva pH - an electrochemical study.Clin Oral Implants Res.2012; 23(9):1055-1062.
[22] Geckili O,Bilhan H,Bilgin T,et al.The effect of urea on the corrosion behavior of different dental alloys.Indian J Dent Res.2012;23(1):75-79. |
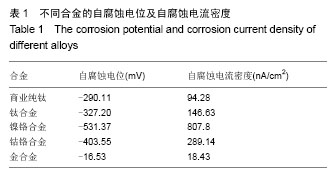
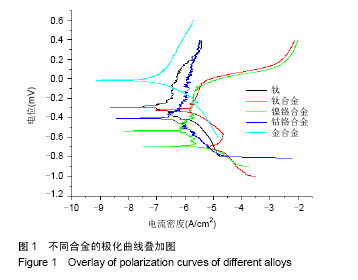
.jpg)