| [1]Wrobleewski A, Mejia H, Wright A.Application of platelet-rich plasma to enhance tissue repair. Operative Techniques in Orthopaedics.2010;20(2):98-105.
[2]de Leon JM, Driver VR, Fylling CP, et al.The clinical relevance of treating chronic wounds with an enhanced near-physiological concentration of platelet-rich plasma gel. Adv Skin Wound Care.2011;24(8): 357-368.
[3]Akingboye AA, Giddins S, Gamston P,et al.Application of autologous derived-platelet rich plasma gel in the treatment of chronic wound ulcer: diabetic foot ulcer. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2010;42(1):20-29.
[4]Sakata J, Sasaki S, Handa K,et al.A retrospective, longitudinal study to evaluate healing lower extremity wounds in patients with diabetes mellitus and ischemia using standard protocols of care and platelet-rich plasma gel in a Japanese wound care program. Ostomy Wound Manage.2012; 58(4): 36-49.
[5]Falanga V.Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet. 2005; 366(9498): 1736-1743.
[6]Greenhalgh DG.Wound healing and diabetes mellitus. Clin Plast Surg.2003; 30(1): 37-45.
[7]Gary Sibbald R, Woo KY. The biology of chronic foot ulcers in persons with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008; 24 Suppl 1: S25-30.
[8]Stadelmann WK, AG Digenis,Tobin GR. Physiology and healing dynamics of chronic cutaneous wounds. Am J Surg. 1998; 176(2A Suppl): 26S-38S.
[9]Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet, 2005;366(9498): 1736-1743.
[10]Onodera H, Ikeuchi D, Nagayama S, et al.Weakness of anastomotic site in diabetic rats is caused by changes in the integrity of newly formed collagen. Dig Surg. 2004; 21(2): 146-151.
[11]李萍,李光善,盛巡,等.糖尿病大鼠创面愈合过程中成纤维细胞增殖及Ⅰ型胶原合成减少[J].中国病理生理杂志,2005,21(9): 1807-1810.
[12]Martin P. Wound healing--aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science, 1997;276(5309): 75-81.
[13]Medina Abelardo, Scott Paul G,Ghahary Aziz,et al. Pathophysiology of chronic nonhealing wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2005;26(4): 306-319.
[14]Diegelmann RF, Evans MC. Wound healing: an overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front Biosci. 2004;9: 283-9.
[15]Lerman OZ, Galiano RD, Armour M, et al. Cellular dysfunction in the diabetic fibroblast: impairment in migration, vascular endothelial growth factor production, and response to hypoxia. Am J Pathol. 2003;162(1):303-12.
[16]Loot MA, Kenter SB, Au FL, et al. Fibroblasts derived from chronic diabetic ulcers differ in their response to stimulation with EGF, IGF-I, bFGF and PDGF-AB compared to controls. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002;81(3):153-60.
[17]Kushida S, Kakudo N, Suzuki K, et al. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Proliferation and Myofibroblastic Differentiation in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Ann Plast Surg.2013; 71(2): 219-224.
[18]Cáceres M, Hidalgo R, Sanz A, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on cell adhesion, cell migration, and myofibroblastic differentiation in human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 2008;79(4):714-20.
[19]Sandra S Scherer, Mickael Tobalem, Enrico Vigato, et al. Nonactivated versus Thrombin-Activated Platelets on Wound Healing and Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Differentiation In Vivo and In Vitro.Plast Reconstr Surg.2012;129: 46e.
[20]Cho JW, Kim SA, Lee KS. Platelet-rich plasma induces increased expression of G1 cell cycle regulators, type I collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human skin fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med.2012;29(1): 32-36.
[21]El-Sharkawy H, Alpdogan Kantarci, Jennifer Desdy, et al.Platelet-rich plasma: growth factors and pro- and anti-inflammatory properties.J Periodontol.2007;78(4): 661-669.
[22]Leshem-Lev D, Omelchenko A, Perl L,et al.Exposure to platelets promotes functional properties of endothelial progenitor cells. J Thromb Thrombolysis.2010;30:398-403.
[23]Lev EI, Aboulfatova K, Harris D, et al.Potential role of activated platelets in homing of human endothelial progenitor cells to subendothelial matrix. Thromb Haemost. 2006;96:498-504.
[24]Langer H, May AE, Daub K, et al.Adherent platelets recruit and induce differentiation of murine embryonic endothelial progenitor cells to mature endothelial cells in vitro. Circ Res. 2006;98:289.
[25]Laitiff AA, Teoh SL, Das S. Wound healing in diabetes mellitus: traditional treatment modalities. Clin Ter.2010; 161(4): 359-364.
[26]Steed DL, Attinger C, Colaizzi T, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of diabetic ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2006; 14(6):680-692.
[27]Gariani K, Uçkay I, Lipsky BA. Managing diabetic foot infections: a review of the new guidelines. Acta Chir Belg. 2014;114(1):7-16. |
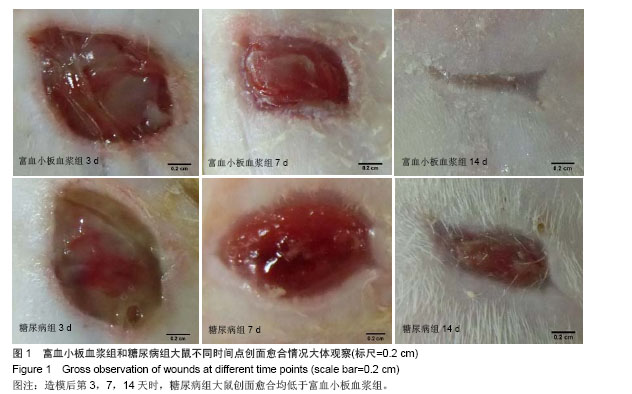
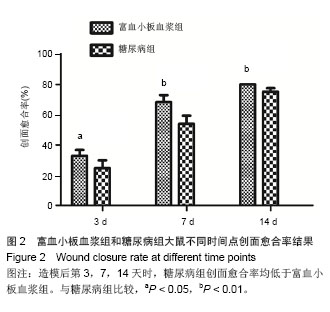
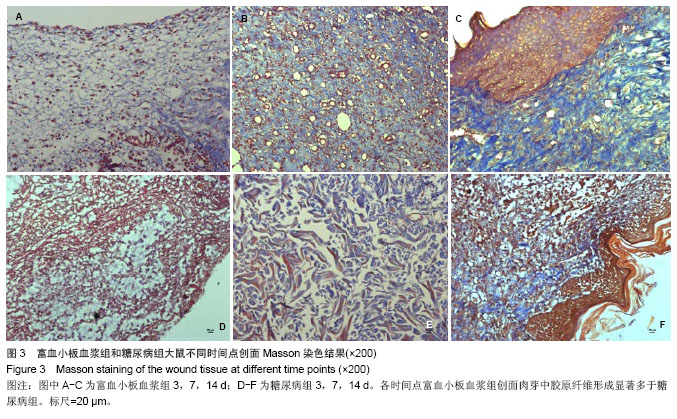
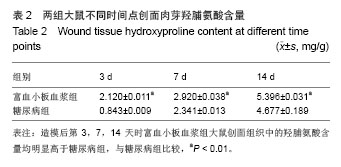
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)