设计:细胞学体外对比观察实验。
时间及地点:实验于2010年6月至2011年7月在哈尔滨医科大学附属第二医院实验室完成。
材料:
实验动物与分组:选取2,4,6,8,12周龄和10,12月龄纯系SD大鼠各15只。实验动物由哈尔滨医科大学实验动物中心提供,实验过程中对动物处理均符合动物伦理学标准。
主要仪器:SW-CJ-2FD洁净工作台(苏净安泰),研究级倒置显微镜(Olympus公司),冷冻离心机(Eppendorf公司),二氧化碳孵箱(Nuaire公司),冷冻离心机(Eppendorf公司)。
主要试剂:DMEM低糖、DMEM高糖培养基、胎牛血清(Hyclone公司),Hanks液、胰酶细胞消化液(Beyotime公司),带滤膜25 cm2培养瓶(Greiner公司),成骨诱导分化完全培养基、成软骨诱导分化完全培养基(Cyagen公司)。
实验方法:
骨髓间充质干细胞的体外分离:颈椎脱臼法处死SD大鼠,无菌条件下切开皮肤、皮下,分离股骨,置于体积分数为75%乙醇中浸泡约1 min,Hank’s液洗涤,除去软组织,咬骨钳咬去股骨近远端骨骺,用大号针头在骨端的生长面开一个小孔,换干净针头,用注射器吸10 mL DMEM-LG培养基,插入小孔冲出骨髓于离心管中,吹打成骨髓细胞悬液。将骨髓细胞悬液离心(1 500 r/min离心5 min),弃上清及脂肪层。加入5 mL含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM-LG培养液,混匀。按照1∶1的比例将上述细胞悬液缓慢滴加到密度为1.073 g/mL的Percoll分离液中,1 500 r/min离心30 min。离心后管内容物分为3层:上层为血小板,中间为Percoll分离液,底层为红细胞和多核白细胞。在上、中层液体界面处可见到乳白色云雾状的单个核细胞层。
骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养:
原代培养:将分离后收获的有核细胞加入DMEM培养液5 mL(含体积分数为15%胎牛血清),制成单细胞悬液,以3×105/cm2接种于25 cm2培养瓶内,置于37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2,饱和湿度条件下的培养箱中培养,3 d后首次半量换液,将未贴壁的细胞全部弃掉,以后每3-5 d全量换液1次。
传代培养:待原代培养细胞生长铺满至瓶底约80%融合时,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化液消化贴壁细胞1 min,见细胞回缩,形态变圆,间隙增大时,立即倒掉消化液终止消化。加入DMEM培养液5 mL(含体积分数为15%胎牛血清),吹打制成细胞悬液,按1∶2传代培养(即1瓶细胞消化后分装2瓶继续培养),第1次传代后的细胞称为P1代细胞。以后传代的细胞依次称为P2、P3……代细胞。
细胞形态观察:每天在倒置显微镜下观察原代和传代骨髓间充质干细胞的生长情况及形态特征,并适时拍照。
流式细胞仪检测骨髓间充质干细胞的表面标志:取P3代骨髓间充质干细胞用胰酶消化,PBS重新悬浮后,调整细胞浓度为1×106/cm2,取100 μL细胞悬液与CD34 APC、CD44FITC、CD45PE-Cy5、CD29FITC、CD90PE单抗室温避光孵育20 min后,用流式细胞仪检测。
骨髓间充质干细胞的诱导分化:细胞于P10代进行分化诱导。待细胞达到80%-90%融合时,消化。一部分细胞用于软骨分化,另一部分细胞接种至6孔板。将细胞接种于6孔板中,加入2 mL/孔的鼠骨髓间充质干细胞完全培养基,放入37 ℃,体积分数为5% CO2孵箱中培养。待细胞贴壁生长至适宜密度时再进行成骨成软骨诱导。
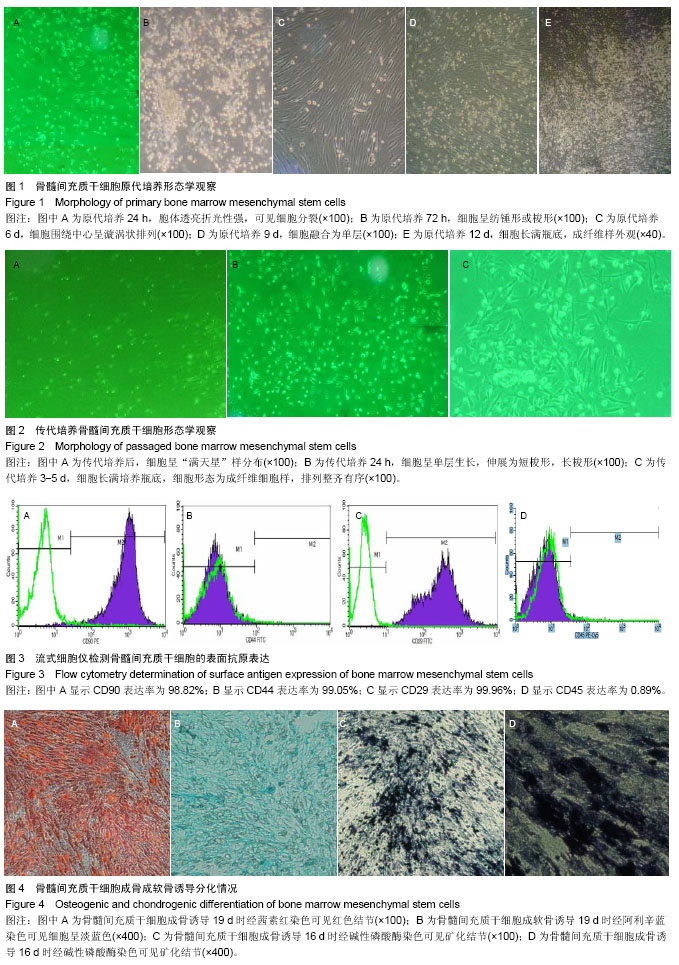
成骨诱导:待细胞达到70%-80%融合时,吸去旧培养液,加入2 mL/孔的成骨诱导分化完全培养基(L-DMEM培养液、体积分数为10%胎牛血清、0.1 μmol/L地塞米松、10 mmol/L β-磷酸甘油和50 μmol/L抗坏血酸磷酸钠)。每 3 d换液,直至可观察到明显钙结节。第1次换液后细胞活力下降,细胞状态变差,继续换液。第4次换液后细胞出现了较少的钙结节,细胞较为扁平。第5次换液后细胞钙结节变多,对其进行染色。19 d后,镜下观察分化情况已较为稳定,进行茜素红染色。
茜素红染色:小心轻缓倒去培养夜,加入PBS轻缓漂洗。加体积分数为10%中性甲醛固定30 min。加入约1 mL茜素红覆盖孔底,染色5 min左右。吸去染液,加入PBS轻缓漂洗。显微镜下观察,拍照。
成软骨诱导:细胞消化离心后,去上清液,按7.5×108 L-1的量加入软骨诱导基础液(含有转化生长因子β的无血清培养基)重悬细胞,然后1 500 r/min离心5 min。去上清,按5.0×108 L-1的量加入软骨诱导分化完全培养液(含体积分数为10%的胎牛血清、L-DMEM培养液、0.1 μmol/L地塞米松、110 μg/L转化生长因子β、50 μmol/L抗坏血酸磷酸钠)重悬细胞。吸取500 μL细胞悬液(既2.5×105个细胞)转入15 mL离心管中,1 500 r/min离心5 min。离心后不可摇动或吹打细胞团,小心地将离心管盖拧松,以便于气体交换。放入37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2中孵育(注意:24 h内不要摇动细胞团)。每两三天换新鲜的软骨诱导分化完全培养液,每管0.5 mL,换液后轻弹细胞团使其能脱壁漂浮。拧松管盖,放入37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中继续诱导。诱导过程中,细胞团直径会有所增大,表面会变得光滑并呈胶质状;诱导19 d后,细胞团直径已增至约2 mm,送做石蜡切片。
阿利辛蓝染色:按如下步骤脱蜡:二甲苯Ⅰ 10 min → 二甲苯Ⅱ 5 min →体积分数为100%乙醇Ⅰ 5 min→体积分数为100%乙醇Ⅱ 5 min→体积分数为95%乙醇Ⅰ 5 min →体积分数为95%乙醇Ⅱ 5 min→体积分数为85%乙醇 3 min→体积分数为75%乙醇 2 min→蒸馏水冲洗1 min。滴加1%阿利辛蓝染色液染色30 min。染色后用自来水轻轻冲洗2 min,然后用蒸馏水稍稍冲洗,晾干后在显微镜下观察染色情况。镜下可见细胞间有淡蓝色着色。
碱性磷酸酶染色:将细胞接种至6孔板,细胞贴壁约70%汇合后,加入间质干细胞成骨诱导液(包括地塞米松、β-磷酸甘油和抗坏血酸),分别于诱导1,3,7,10,16 d进行染色。用适当的洗涤液(1×PBS)洗涤3-5次,每次 3-5 min。用中性甲醇固定30 min,固定后用洗涤液洗涤3-5次。配制碱性磷酸酶染色工作液。洗涤最后一次后,去除洗涤液,加入适量染色液,确保能充分覆盖样品。室温避光5-30 min或更长时间(24 h),直至显色至预期深度。去除染色工作,用蒸馏水洗涤一两次终止显色反应。显色反应终止后,拍照。
放免骨钙素定量检测:取第3代骨髓间充质干细胞以1×106 L-1细胞浓度接种于6孔培养板,加入成骨诱导培养基,每两三天根据培养基颜色换液。分别于培养1,2,3周,取1×106 L-1细胞1 mL按大鼠骨钙素Elisa试剂盒操作步骤用免疫法定量检测骨钙素含量。
统计学分析:将原始数据录入Excel表后建立数据库,应用 SPSS 18.0医用统计软件包进行数据统计学处理。采用 ANOVA 方差分析并进行方差齐性检验;结果以x±s表示,并计算P 值,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。