中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (30): 4878-4888.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.30.020
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
冠状动脉生物可降解支架设计与应用:材料学的进一步革新将带来什么?
陈佳慧,沈 雳,王齐兵,葛均波
- 复旦大学附属中山医院心内科,上海市心血管病研究所,上海市 200032
-
修回日期:2014-05-12出版日期:2014-07-16发布日期:2014-08-08 -
通讯作者:王齐兵,主任医师,教授,硕士生导师,复旦大学附属中山医院心内科,上海市心血管病研究所,上海市 200032 -
作者简介:陈佳慧,女,1990年生,江苏省南通市人,汉族,复旦大学在读硕士,主要从事冠状动脉性心脏病的基础和临床研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81370323),上海市科学技术委员会科研计划项目(12DZ1940604)
Design and application of biodegradable coronary stents: what will be brought by further innovations in materials science?
Chen Jia-hui, Shen Li, Wang Qi-bing, Ge Jun-bo
- Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
-
Revised:2014-05-12Online:2014-07-16Published:2014-08-08 -
Contact:Wang Qi-bing, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China -
About author:Chen Jia-hui, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81370323; the Research Project of the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, No. 12DZ1940604
摘要:
背景:随着社会经济的发展和老龄化的加剧,冠状动脉性心脏病成为危害人类生命健康的首要致死病因,与此同时,心血管介入治疗(尤其是支架植入)在当今心血管疾病治疗中的地位与日俱增。 目的:阐述心脏介入材料的发展历程、研究进展以及最新临床应用试验,可降解支架的优点以及弊端,同时展望其未来的发展趋势和改进方向。 方法:应用计算机检索PubMed数据库1999年1月至2014年4月间相关文献,检索词为“stent, scaffold, bioabsorbable, bioresorbable, biodegradable, biocompatibility, material properties”,并限定文章语言种类为英语,对资料进行初审。 结果与结论:新型完全生物可降解支架是心脏介入治疗中的又一重大进展,为冠状动脉性心脏病患者带来新的福音。在植入初始阶段表现出与金属裸支架相同的机械支撑力,植入后释放抗增殖药物,预防血栓形成及再狭窄,同时在特定的时间内完全降解,明显减少了晚期及极晚期血栓形成及支架内再狭窄的风险。但可降解支架的长期安全性及有效性有待进一步研究来证明。支架设计及材料学革新是克服当前可降解支架缺点研究与应用的重点。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈佳慧,沈 雳,王齐兵,葛均波. 冠状动脉生物可降解支架设计与应用:材料学的进一步革新将带来什么?[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(30): 4878-4888.
Chen Jia-hui, Shen Li, Wang Qi-bing, Ge Jun-bo. Design and application of biodegradable coronary stents: what will be brought by further innovations in materials science?[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(30): 4878-4888.
In addition, other three clinical trials are underway: the ABSORB Physiology, the ABSORB II, and the ABSORB EXTEND. The ABSORB Physiology setting focuses on estimating the short- and long-term effects of an Absorb BVS and a Xience V® (Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, USA) stent. The ABSORB II study is the first randomized trial designed to compare the safety and efficacy of the Absorb BVS and Xience prime (Abbott Laboratories) in 500 patients with de novo coronary artery disease. The ABSORB EXTEND trial is a large-scale, single-arm trial that enrolls 1 000 patients with complex coronary artery disease which aims to evaluate the occurrence of side branch blockage after the implantation of bioresorbable vascular scaffold. The results show that bioresorbable vascular scaffolds can provide durable support force, allow persistent drug release and have no late in-stent restenosis. However, the research results also show that the bioresorbable vascular scaffold posses a higher rate of small side branch blockage compared with XIENCE V® which calls for further improvement of stent design strategy[35]. Data from this trial may be used to support approval in various markets around the world[36] (Figures 2, 3).
The ReZolve stent has a spiral slide-and-lock mechanism and carries the anti-proliferative drug sirolimus. Currently, this new scaffold is undergoing evaluation in the RESTORE (ReZolve sirolimus-eluting bioresorbable coronary scaffold) clinical trial, which aims to pilot investigate its safety and efficacy in 50 patients. Clinical data from the RESTORE trial will become available throughout 2012 as patients pass the 1- and 6-month clinical evaluation stages. Furthermore, the RESTORE II clinical trial which aims to assess the safety and performance of the ReZolve2 Bioresorbable Coronary Scaffold in native coronary arteries started in April 2013. Totally 125 patients are estimated to enrolled in this trial. The preliminary outcomes are supposed to publish in 2014.
The metallic alloys mainly utilized for BRSs are iron and magnesium alloyed with some rare metals[51]. Metal bioabsorbable stents are intuitively attractive since they have the potential to perform similarly to stainless steel metal stents[52].
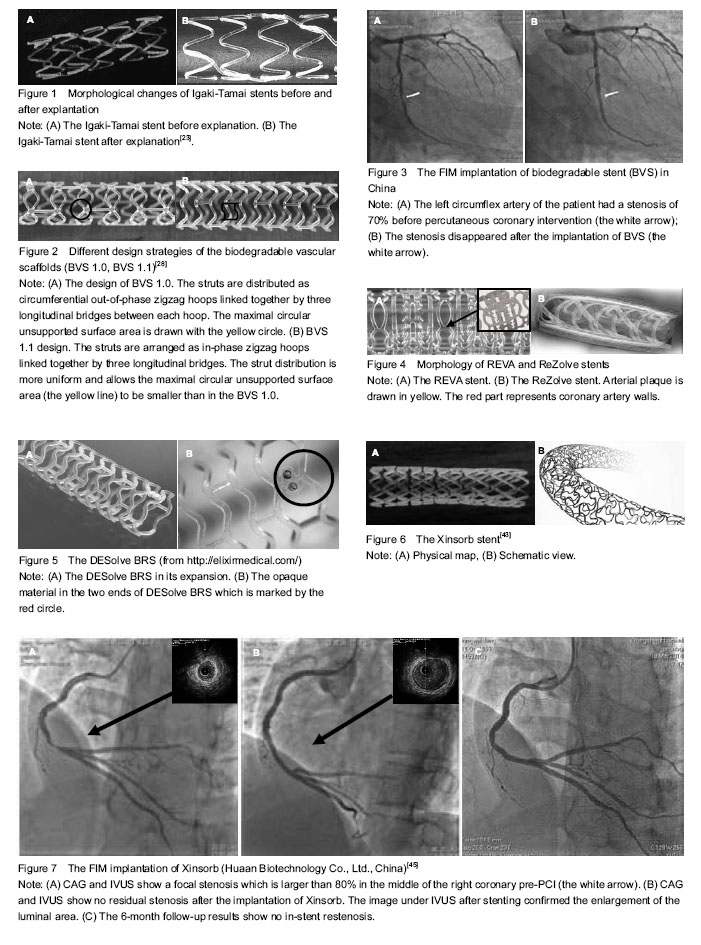
Other BRSs: Other technologies using polymer other than poly-lactide, as well as using other resorbable metal alloys, are also being investigated. These BRSs are currently undergoing testing, such as Avatar BRS, Sahajanand BRS, MeRes BRS, Zorion BRS.
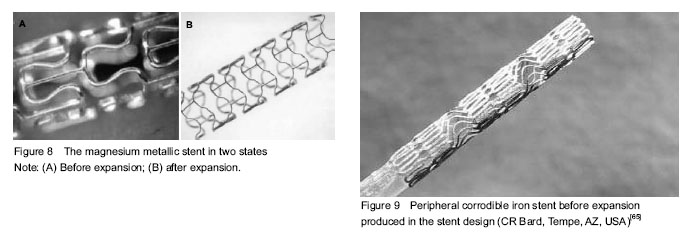
An appropriate degradation rate of scaffold backbone is essential for BRS. The BRSs are supposed to exist for a certain period of time and then completely disappear. Two dominant factors influencing the degradation rate are inherent properties of materials and implanted environment (Table 1).
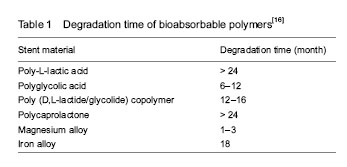
In brief, the ideal biomaterial is expected to overcome all the drawbacks shown as follow (Table 2).
| [1] Yazdani SK, Farb A, Nakano M, et al. Pathology of drug-eluting versus bare-metal stents in saphenous vein bypass graft lesions. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2012; 5(6):666-674. [2] Gruntzig A. Transluminal dilatation of coronary-artery stenosis. Lancet. 1978;1(8058):263. [3] Roubin GS, Cannon AD, Agrawal SK, et al. Intracoronary stenting for acute and threatened closure complicating percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation. 1992;85(3):916-927. [4] Serruys PW, de Jaegere P, Kiemeneij F, et al. A comparison of balloon-expandable-stent implantation with balloon angioplasty in patients with coronary artery disease. Benestent Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(8): 489-495. [5] Fischman DL, Leon MB, Baim DS, et al. A randomized comparison of coronary-stent placement and balloon angioplasty in the treatment of coronary artery disease. Stent Restenosis Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331(8):496-501. [6] Serruys PW, Keane D. The bailout stent. Is a friend in need always a friend indeed? Circulation. 1993;88(5 Pt 1): 2455-2457. [7] Serruys PW, Strauss BH, Beatt KJ, et al. Angiographic follow-up after placement of a self-expanding coronary-artery stent. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(1):13-17. [8] Rensing BJ, Vos J, Smits PC, et al. Coronary restenosis elimination with a sirolimus eluting stent: first European human experience with 6-month angiographic and intravascular ultrasonic follow-up. Eur Heart J. 2001;22(22):2125-2130. [9] Serruys PW, Daemen J. Are drug-eluting stents associated with a higher rate of late thrombosis than bare metal stents? Late stent thrombosis: a nuisance in both bare metal and drug-eluting stents. Circulation. 2007;115(11):1433-1439. [10] Colombo A, Karvouni E. Biodegradable stents: "fulfilling the mission and stepping away". Circulation. 2000;102(4): 371-373. [11] Stack RS, Califf RM, Phillips HR, et al. Interventional cardiac catheterization at Duke Medical Center. Am J Cardiol. 1988;62(10 Pt 2):3F-24F. [12] Karrillon GJ, Morice MC, Benveniste E, et al. Intracoronary stent implantation without ultrasound guidance and with replacement of conventional anticoagulation by antiplatelet therapy. 30-day clinical outcome of the French Multicenter Registry. Circulation. 1996;94(7):1519-1527. [13] Hassell ME, van de Hoef TP, Damman P, et al. The bioresorbable coronary scaffold. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2012;156(36):A4994. [14] Heublein B, Rohde R, Kaese V, et al. Biocorrosion of magnesium alloys: a new principle in cardiovascular implant technology? Heart. 2003;89(6):651-656. [15] Bourantas CV, Zhang Y, Farooq V, et al. Bioresorbable scaffolds: current evidence and ongoing clinical trials. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2012;14(5):626-634. [16] Waksman R. Update on bioabsorbable stents: from bench to clinical. J Interv Cardiol. 2006;19(5):414-421. [17] Vert M. Bioabsorbable polymers in medicine: an overview. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F:F9-F14. [18] Onuma Y, Serruys PW. Bioresorbable scaffold: the advent of a new era in percutaneous coronary and peripheral revascularization? Circulation. 2011;123(7):779-797. [19] Zidar JP, Lincoff A, Stack R. Biodegradable stents. In: Topol EJ, ed. Textbook of Interventional Cardiology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saundars,1994. [20] van der Giessen WJ, Slager CJ, van Beusekom HM, et al. Development of a polymer endovascular prosthesis and its implantation in porcine arteries. J Interv Cardiol. 1992;5(3): 175-185. [21] van der Giessen WJ, Lincoff AM, Schwartz RS, et al. Marked inflammatory sequelae to implantation of biodegradable and nonbiodegradable polymers in porcine coronary arteries. Circulation. 1996;94(7):1690-1697. [22] Tamai H, Igaki K, Kyo E, et al. Initial and 6-month results of biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents in humans. Circulation. 2000;102(4):399-404. [23] Nishio S, Kosuga K, Igaki K, et al. Long-Term (>10 Years) clinical outcomes of first-in-human biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents: Igaki-Tamai stents. Circulation. 2012;125(19):234323-53. [24] Onuma Y, Garg S, Okamura T, et al. Ten-year follow-up of the IGAKI-TAMAI stent. A posthumous tribute to the scientific work of Dr. Hideo Tamai. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F:F109-111. [25] Zhang Y, Bourantas CV, Farooq V, et al. Bioresorbable scaffolds in the treatment of coronary artery disease. Med Devices (Auckl). 2013;6:37-48. [26] Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Regar E, et al. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): a prospective open-label trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9616): 899-907. [27] Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Regar E, et al. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): a prospective open-label trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9616): 899-907. [28] Serruys PW, Ormiston JA, Onuma Y, et al. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system (ABSORB): 2-year outcomes and results from multiple imaging methods. Lancet. 2009;373(9667):897-910. [29] Onuma Y, Serruys PW, Gomez J, et al. Comparison of in vivo acute stent recoil between the bioresorbable everolimus-eluting coronary scaffolds (revision 1.0 and 1.1) and the metallic everolimus-eluting stent. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;78(1):3-12. [30] Gomez-Lara J, Brugaletta S, Diletti R, et al. A comparative assessment by optical coherence tomography of the performance of the first and second generation of the everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds. Eur Heart J. 2011;32(3):294-304. [31] Brugaletta S, Gomez-Lara J, Serruys PW, et al. Serial in vivo intravascular ultrasound-based echogenicity changes of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold during the first 12 months after implantation insights from the ABSORB B trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(12):1281-1289. [32] Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Onuma Y, et al. First serial assessment at 6 months and 2 years of the second generation of absorb everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold: a multi-imaging modality study. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5(5):620-632. [33] Serruys PW, Onuma Y, Ormiston JA, et al. Evaluation of the second generation of a bioresorbable everolimus drug-eluting vascular scaffold for treatment of de novo coronary artery stenosis: six-month clinical and imaging outcomes. Circulation. 2010;122(22):2301-2312. [34] Serruys PW, Onuma Y, Dudek D, et al. Evaluation of the second generation of a bioresorbable everolimus-eluting vascular scaffold for the treatment of de novo coronary artery stenosis: 12-month clinical and imaging outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(15):1578-1588. [35] Tearney GJ, Bouma BE. Shedding light on bioabsorbable stent struts seen by optical coherence tomography in the ABSORB trial. Circulation. 2010;122(22):2234-2235. [36] Muramatsu T, Onuma Y, van Geuns RJ, et al. One-Year Clinical Outcomes of Diabetic Patients Treated With Everolimus-Eluting Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds: A Pooled Analysis of the ABSORB and the SPIRIT Trials. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014. in press. [37] Farooq V, Gomez-Lara J, Brugaletta S, et al. Proximal and distal maximal luminal diameters as a guide to appropriate deployment of the ABSORB everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold: a sub-study of the ABSORB Cohort B and the on-going ABSORB EXTEND Single Arm Study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;79(6): 880-888. [38] Pollman MJ. Engineering a bioresorbable stent: REVA programme update. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F: F54-57. [39] Stefan V. Desolve First in Man Study–Preliminary Results. Rotterdam: EuroPCR, 2012. [40] Yan J, Bhat VD. Elixir Medical's bioresorbable drug eluting stent (BDES) programme: an overview. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F:F80-82. [41] Serruys PW, Garg S, Abizaid A, et al. A randomised comparison of novolimus-eluting and zotarolimus-eluting coronary stents: 9-month follow-up results of the EXCELLA II study. EuroIntervention. 2010;6(2):195-205. [42] Costa JR Jr, Abizaid A, Feres F, et al. EXCELLA First-in-Man (FIM) study: safety and efficacy of novolimus-eluting stent in de novo coronary lesions. EuroIntervention. 2008;4(1):53-58. [43] Shen L, Wang QB, Wu YZ, et al. Short-term effects of fully bioabsorbable PLLA coronary stents in a porcine model. Polymer Bulletin. 2012;68(4):1171-1181. [44] Wu Y, Shen L, Wang Q, et al. Comparison of acute recoil between bioabsorbable poly-L-lactic acid XINSORB stent and metallic stent in porcine model. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:413956. [45] Ge JB. The first case of independent bioresorbable stent (Xinsorb) implanted in China. 2013-10-09 . http://www.menzhen.org/. [46] Jabara R, Chronos N, Robinson K. Novel bioabsorbable salicylate-based polymer as a drug-eluting stent coating. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;72(2):186-194. [47] Jabara R, Pendyala L, Geva S, et al. Novel fully bioabsorbable salicylate-based sirolimus-eluting stent. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F:F58-64. [48] Lafont A, Durand E. A.R.T.: concept of a bioresorbable stent without drug elution. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F:F83-87. [49] cvPIPELINE. Santa Barbara: Market Monitors Inc. 2012. http://www.cvpipeline.com. [50] Cottone RJ, Thatcher GL, Parker SP, et al. OrbusNeich fully absorbable coronary stent platform incorporating dual partitioned coatings. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F: F65-71. [51] Vogt F, Stein A, Rettemeier G, et al. Long-term assessment of a novel biodegradable paclitaxel-eluting coronary polylactide stent. Eur Heart J. 2004;25(15):1330-1340. [52] Tsuji T, Tamai H, Igaki K, et al. Biodegradable stents as a platform to drug loading. Int J Cardiovasc Intervent. 2003;5(1):13-16. [53] Wittchow E, Adden N, Riedmüller J, et al. Bioresorbable drug-eluting magnesium-alloy scaffold: design and feasibility in a porcine coronary model. EuroIntervention. 2013;8(12):1441-1450. [54] Serruys PW, Garcia-Garcia HM, Onuma Y. From metallic cages to transient bioresorbable scaffolds: change in paradigm of coronary revascularization in the upcoming decade? Eur Heart J. 2012;33(1):16-25b. [55] Waksman R. Current state of the absorbable metallic (magnesium) stent. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F: F94-97. [56] Williams D. New interests in magnesium. Med Device Technol. 2006;17(3):9-10. [57] Heublein B, Rohde R, Kaese V, et al. Biocorrosion of magnesium alloys: a new principle in cardiovascular implant technology? Heart. 2003;89(6):651-656. [58] Zartner P, Cesnjevar R, Singer H, et al. First successful implantation of a biodegradable metal stent into the left pulmonary artery of a preterm baby. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2005;66(4):590-594. [59] Di Mario C, Griffiths H, Goktekin O, et al. Drug-eluting bioabsorbable magnesium stent. J Interv Cardiol. 2004; 17(6):391-395. [60] Erbel R, Di Mario C, Bartunek J, et al. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: a prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2007;369(9576):1869-1875. [61] Ghimire G, Spiro J, Kharbanda R, et al. Initial evidence for the return of coronary vasoreactivity following the absorption of bioabsorbable magnesium alloy coronary stents. EuroIntervention. 2009;4(4):481-484. [62] Haude M, Erbel R, Erne P, et al. Safety and performance of the drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold (DREAMS) in patients with de-novo coronary lesions: 12 month results of the prospective, multicentre, first-in-man BIOSOLVE-I trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9869):836-844. [63] Peuster M, Wohlsein P, Brügmann M, et al. A novel approach to temporary stenting: degradable cardiovascular stents produced from corrodible metal-results 6-18 months after implantation into New Zealand white rabbits. Heart. 2001;86(5):563-569. [64] Waksman R, Pakala R, Baffour R, et al. Short-term effects of biocorrodible iron stents in porcine coronary arteries. J Interv Cardiol. 2008;21(1):15-20. [65] Peuster M, Hesse C, Schloo T, et al. Long-term biocompatibility of a corrodible peripheral iron stent in the porcine descending aorta. Biomaterials. 2006;27(28): 4955-4962. [66] Pierson D, Edick J, Tauscher A, et al. A simplified in vivo approach for evaluating the bioabsorbable behavior of candidate stent materials. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(1):58-67. [67] Helmus MN, Gibbons DF, Cebon D. Biocompatibility: meeting a key functional requirement of next-generation medical devices. Toxicol Pathol. 2008;36(1):70-80. [68] Waksman R, Pakala R, Kuchulakanti PK, et al. Safety and efficacy of bioabsorbable magnesium alloy stents in porcine coronary arteries. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006;68(4): 607-619. [69] O'Brien B, Carroll W. The evolution of cardiovascular stent materials and surfaces in response to clinical drivers: a review. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(4):945-958. [70] Hermawan H, Dubé D, Mantovani D. Degradable metallic biomaterials: design and development of Fe-Mn alloys for stents. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(1):1-11. [71] Schinhammer M, Hänzi AC, Löffler JF, et al. Design strategy for biodegradable Fe-based alloys for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1705-1713. [72] Liu B, Zheng YF. Effects of alloying elements (Mn, Co, Al, W, Sn, B, C and S) on biodegradability and in vitro biocompatibility of pure iron. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(3): 1407-1420. [73] Peng T, Gibula P, Yao KD, et al. Role of polymers in improving the results of stenting in coronary arteries. Biomaterials. 1996;17(7):685-694. [74] Tanimoto S, Serruys PW, Thuesen L, et al. Comparison of in vivo acute stent recoil between the bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent and the everolimus-eluting cobalt chromium coronary stent: insights from the ABSORB and SPIRIT trials. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;70(4):515-523. [75] Zhu S1, Xu L, Huang N. Development of biodegradable magnesium-based biomaterial]. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2009;26(2):437-439, 451. [76] Acharya G, Park K. Mechanisms of controlled drug release from drug-eluting stents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58(3): 387-401. |
| [1] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 杨怡天, 王 璐, 姚 蔚, 赵 彬. 生物支架与巨噬细胞在骨再生中的相互影响及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [3] | 李 诚, 郑国爽, 蒯贤东, 于炜婷. 海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [4] | 徐 聪, 赵 赫, 孙 岩. 生物材料导管修复面神经损伤与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1089-1095. |
| [5] | 陈世崧, 刘晓红, 徐志云. 人工生物瓣膜的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [6] | 唐昊天, 廖荣东, 田 京. 压电材料修复骨缺损的应用及设计思路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [7] | 许其静, 杨伊春, 雷 微, 杨 莹, 余 江, 夏婷婷, 张 萌, 章 涛, 张 潜. 糖尿病皮肤慢性创面无细胞治疗的进展与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [8] | 刘 欢, 李 涵, 马云豪, 仲维剑, 马国武. 部分脱矿牙本质颗粒在上颌窦提升中的成骨性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [9] | 蒋海芳, 刘 融, 胡 鹏, 陈 伟, 魏在荣, 杨成兰, 聂开瑜. 3D打印技术在唇腭裂精准与个性化治疗中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(3): 413-419. |
| [10] | 王子扬, 左恩俊. 生物材料在活髓保存中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(3): 427-433. |
| [11] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李 佳, 蒋海越, 刘 霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(21): 3293-3299. |
| [12] | 徐 鑫, 刘曜玮, 穆云萍, 王建英, 李芳红, 赵子建. 脱细胞真皮基质水凝胶的制备及生物学评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(21): 3325-3331. |
| [13] | 黄森丽, 孙海港, 孙文全. 脱细胞、病毒灭活与灭菌组合工艺对猪真皮基质理化性能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(21): 3349-3355. |
| [14] | 刘卓冉, 李玉梅, 刘俊彦, 尹 彤, 姜 明, 李友瑞. 口腔抗菌领域中壳聚糖及其衍生物的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(21): 3361-3367. |
| [15] | 牛 林, 梅钰坤, 邹 蕊, 张雨薇, 张翼飞, 郝雅琪, 董少杰. 无机非金属生物材料在骨肉瘤治疗与伴发骨缺损再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(21): 3368-3374. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||