| [1] Bischof G,Silbernagl A,Probst M,et al.Quantum Chemical Study of the Molecular Dynamics of Hydrated Li+ and Be2+ Cations.Int J Quantum Chem. 1997;65:803-816.
[2] Rana SV.Metals and apoptosis: Recent developments.J Trace Elem Med Biol.2008;22(4):262-284.
[3] Ross GC,Adrian PH.The uses and adverse effects of beryllium on health. Indian J Occupy Environ Med. 2009; 13(2):65-76.
[4] Dave J.Lessons learned from beryllium exposures.Industrial Safety & Hygiene News.2005;39(11):20.
[5] Powers JM,Sakaguchi RL.Craig's restorative dental materials.Philadelphia, PA : Elsevier/Mosby,2012.
[6] Lin HY, Bowers B, Wolan JT, et al. Metallurgical, surface, and corrosion analysis of Ni-Cr dental casting alloys before and after porcelain firing.Dent Mater. 2008;24(3):378-385.
[7] Hajishengallis G,Lamont RJ.Breaking bad: Manipulation of the host response by Porphyromonas gingivalis.Eur J Immunol. 2014;44(2):328-338.
[8] Nagano K,Hasegawa Y,Abiko Y, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis FimA Fimbriae: Fimbrial Assembly by fimA Alone in the fim Gene Cluster and Differential Antigenicity among fimA Genotypes.PLoS ONE.2012;7(9):e43722.
[9] Masuda T,Murakami Y,Noguchi T,et al.Effects of various growth conditions in a chemostat on expression of virulence factors in Porphyromonas gingivalis . Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:3458-3467.
[10] Gunsalus IC,Stanier RY.The bacteria : a treatise on structure and function, v.1 : Structure.New York : Academic Press,1960.
[11] Madigan MT,Martinko JM,Parker J.Brock Biology of Microorganisms. edn.9, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2000.
[12] E.Enger.生物学原理[M].北京:科学出版社,2004.
[13] Nakagawa I,Amano A,Kuboniwa M,et al.Functional differences among FimA variants of Porphyromonas gingivalis and their effects on adhesion to and invasion of human epithelial cells.Infect Immun.2002;70(1):277-285.
[14] Walter C,Zahlten J,Schmeck B,et al.Porphyromonas gingivalisstrain-dependent activation of human endothelial cells.InfectImmun.2004;72(10):5910-5918.
[15] Aoki Y,Tabeta K,Murakami Y,et al.Analysis of immunostimulatory activity of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae conferred by Toll-like receptor 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2010;398:86-91.
[16] Shoji M,Yoshimura A,Yoshioka H,et al.Recombinant Porphyromonas gingivalis FimA preproprotein expressed in Escherichia coli is lipidated and the mature or processed recombinant FimA protein forms a short filament in vitro.Can J Microbiol.2010;56:959-967.
[17] Moorefield B.DNA break repair goes live.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014;21(2):117.
[18] 印木泉.遗传毒理学[M].北京:科学出版社,2002.
[19] 袁丽红.微生物学实验[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2010.
[20] Kazimierz SK,William SJr F,Konstantin S.Nickel carcinogenesis.Mutat Res.2003;533:67-97.
[21] Katarzyna W, Janusz B. Free radicals-mediated induction of oxidized DNA bases and DNA−protein cross-links by nickel chloride. Mutat Res.2002;514:233-243.
[22] Yong-Woo L,Limor B,Max C.Effects of nickel on DNA methyltransferase activity and genomic DNA methylation levels.Mutat Res.1998;415:213-218.
[23] 袁跃,胡晶,王友如.Pfu酶原核的高效表达及其活性分析[J].生物技术,2012,22(5):29-31.
[24] J.莎姆布鲁克.分子克隆实验指南[M].黄培堂译.3版.北京:科学出版社,2005.
[25] Summers AO,Wireman J,Vimy MJ,et al.Mercury released from dental "silver" fillings provokes an increase in mercury- and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in oral and intestinal floras of primates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37(4):825-834.
[26] 佘朝晖,邱著文,林幼敏,等.口腔修复常用合金耐腐蚀性能评价[J].海南医学,2010, 21(19):58-60. |
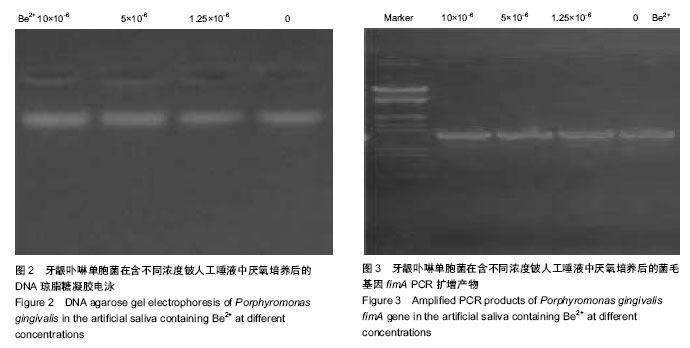

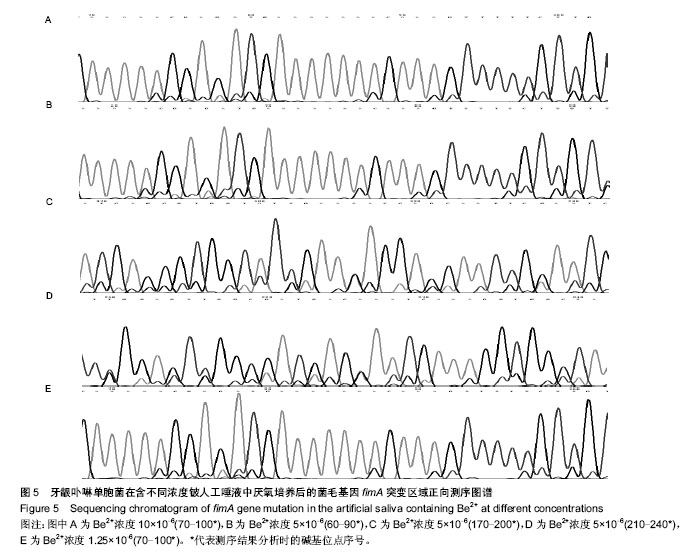
.jpg)