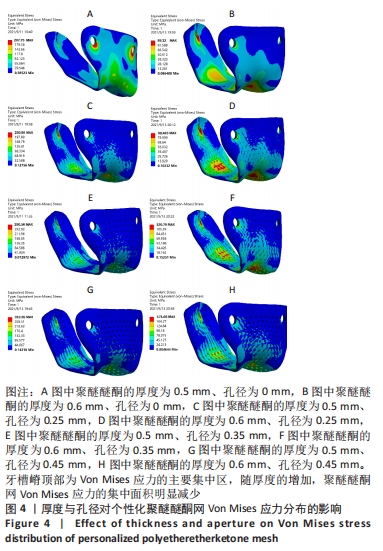
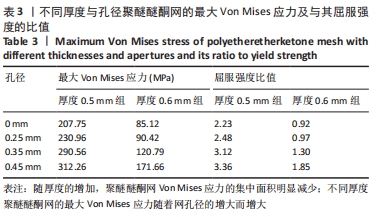
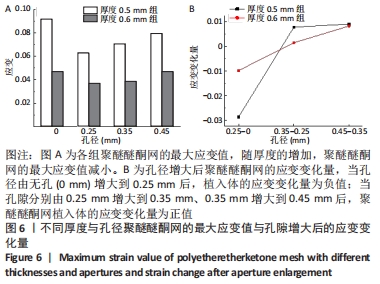
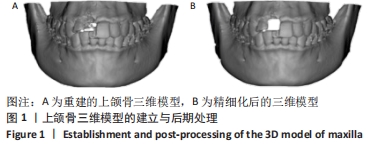
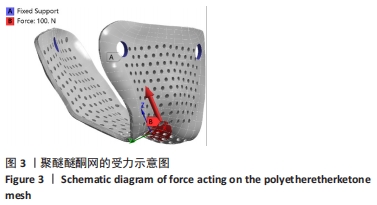
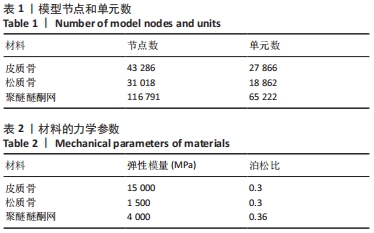
[1] 李安琳,谢方方.显微根尖外科手术中GBR应用的临床探究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(2):307-311.
[2] 田燕,钱若谷,张媛,等.牙槽骨缺损区引导骨再生后正畸牙移动的临床观察1例[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(1):132-133.
[3] WONJ Y, PARK CY, BAE JH, et al. Evaluation of 3D printed PCL/PLGA/β-TCP versus collagen membranes for guided bone regeneration in a beagle implant model. Biomed Mater. 2016;11(5):055013.
[4] ATEF M, TAREK A, SHAHEEN M, et al. Horizontal ridge augmentation using native collagen membrane vs titanium mesh in atrophic maxillary ridges: Randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2020; 22(2):156-166.
[5] TAN XP, TAN YJ, CHOW C, et al. Metallic powder-bed based 3D printing of cellular scaffolds for orthopaedic implants: A state-of-the-art review on manufacturing, topological design, mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;76:1328-1343.
[6] NAKAHARA I, TAKAO M, BANDOH S, et al. In vivo implant fixation of carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK hip prostheses in an ovine model. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(3):485-492.
[7] DEVINE DM, HAHN J, RICHARDS RG, et al. Coating of carbon fiber‐reinforced polyetheretherketone implants with titanium to improve bone apposition. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101B(4): 591-598.
[8] HENNESSY DW, CALLAGHAN JJ, LIU SS. Second-generation extensively porous-coated THA stems at minimum 10-year follow up. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(9):2290-2296.
[9] 谭国忠,涂欣冉,郭黎洋,等.3D打印明胶/海藻酸钠/58S生物玻璃骨缺损修复支架的生物安全性评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(4):521-527.
[10] 王宏,范海霞,程焕芝,等. 3D打印HAP-GEL支架复合BMSCs和HUVECs修复兔颅骨缺损的效果评价[J]. 上海口腔医学,2021,30(1): 28-32.
[11] 林柳兰,周建勇.3D打印聚醚醚酮及其复合材料修复骨缺损的应用现况[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10):1622-1628.
[12] TORSTRICKR FB, EVANS NT, STEVENS HY, et al. Do Surface Porosity and Pore Size Influence Mechanical Properties and Cellular Response to PEEK. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(11):2373-2383.
[13] KURTZ SM, DEVINE JN. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials. 2007;28(32):4845-4869.
[14] 陈东,汪涛,徐洲,等. 3D打印技术结合可塑形钛网在修复上颌骨缺损中的应用[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2020,55(3):200-204.
[15] 刘秉尧,曹罡,董震,等. 3-D打印技术用于钛网修复全上颌骨缺损6例报道[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2016(6):562-566.
[16] 袁帅,陈陶,李帝泽,等.三维打印个性化钛网在美学区牙槽骨缺损骨增量中应用的效果评估 [J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2020,55(11): 878-884
[17] SUMIDA T, OTAWA N, KAMATA YU, et al. Custom-made titanium devices as membranes for bone augmentation in implant treatment: Clinical application and the comparison with conventional titanium mesh. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43(10):2183-2188.
[18] JOHANSSON P, JIMBO R, NAITO Y, et al. Polyetheretherketone implants achieve increased bone fusion when coated with nano-sized hydroxyapatite: a histomorphometric study in rabbit bone. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;6(11):1435-1442.
[19] 秦胜男.CFR/PEEK复合材料的生物安全性评价[D].太原:山西医科大学,2018.
[20] 石峰,柴文文,曾理,等.125I辐照的聚醚醚酮粒子链的生物安全性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(38):5716-5721.
[21] 王克军,郭卫春,唐谨,等.短碳纤维增强聚醚醚酮为全髋假体材料的生物相容性及力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(34):6351-6354.
[22] 刘吕花,郑延延,张丽芳,等.硬组织植入聚醚醚酮表面生物活性改性研究[J].中国塑料,2018,32(11):7-18.
[23] 施张宇,李全,唐颂超,等.表面改性对介孔硅酸钙镁/聚醚醚酮复合材料性能的影响[J].无机材料学报,2018,33(1):67-74.
[24] 成沁雯,袁波,朱向东,等.不同磺化及碱处理聚醚醚酮的表面化学组成及体外生物活性评价[J].高等学校化学学报,2019,40(8): 1757-1765.
[25] 赵广宾,安超,秦勉,等.聚醚醚酮/羟基磷灰石复合植入物的制备及性能研究[J].西安交通大学学报,2019,53(4):72-78.
[26] 连克乾,张昕,周捷宇,等.骨髓间充质细胞在聚醚醚酮片和纯钛片表面的体外生物相容性比较[J].口腔疾病防治,2020,28(2):73-78.
[27] 魏星辉,范宏斌,付军,等.肩胛骨肿瘤切除3D打印聚醚醚酮个性化定制假体重建五例报告[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(2):122-127.
[28] 赵丙辉,李沅,李文娇.3D打印技术制备骨科植入材料聚醚醚酮的力学性能研究及氨基改性对材料成骨性能的影响[J].中国医疗器械信息,2021,27(13):10-12+74.
[29] 刘吕花,熊成东,张丽芳,等.聚醚醚酮表面接枝聚丙烯酸及其成骨细胞相容性[J].塑料工业,2021,49(7):159-163.
[30] TAKAHASHI N, KITAGAM T, KOMORI T. Behaviour of teeth under various loading conditions with finite element method. J Oral Rehabil. 1980; 7(6):453-461.
[31] 虎小毅,李立峰,史婧怡,等.不同程度骨吸收的下颌骨囊性病变治疗方式的选择及相关生物力学分析 [J].现代口腔医学杂志,2019, 33(4):193-196.
[32] WU S, LI Y, ZHANG YQ, et al. Porous Titanium-6 Aluminum-4 Vanadium Cage Has Better Osseointegration and Less Micromotion Than a Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone Cage in Sheep Vertebral Fusion. Artificial Organs. 2013;37(12):191-201.
[33] 喻缇,刘婷,黄元丁,等.不同材料多孔支架在即刻负载下修复兔股骨缺损的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(6):615-622.
[34] FROST HM. A 2003 Update of bone physiology and Wolff’s law for clinicians. Angle Orthod0 2004;74(1):3-15.
[35] EVANS NT, TORSTRICK FB, LEE C, et al. High-strength, surface-porous polyether-ether-ketone for load-bearing orthopedic implants. Acta Biomater. 2015;13:159-167.
[36] WONG KI, ZHONG Y, LI D, et al. Modified porous microstructure for improving bone compatibility of poly-ether-ether-ketone. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;120:104541.
[37] ATHANASOU NA, QUINN J, BULSTRODE CJ. Resorption of bone by inflammatory cells derived from the joint capsule of hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(1):57-62.
[38] GITTENS RA, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, SCHWARTZ Z, et al. Implant osseointegration and the role of microroughness and nanostructures: Lessons for spine implants. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(8):3363-3371.
[39] CHEAL EJ, SPECTOR M, HAYES WC. Role of loads and prosthesis material properties on the mechanics of the proximal femur after total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(3):405-422.
[40] PIERFRANCESCO ROBOTTI MS, GIANLUCA ZAPPINI MS. Thermal Plasma Spray Deposition of Titanium and Hydroxyapatite on Polyaryletheretherketone Implants. PEEK Biomater Handbook. 2012:119-143.
[41] WAZEN RM, CURREY JA, GUO H, et al. Micromotion-induced strain fields influence early stages of repair at bone–implant interfaces. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6663-6674.
[42] 陆伟,李涤尘,吴国锋.3D打印聚醚醚酮口腔修复体的初步临床报告[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(1):136-140.
[43] 段钢,陈宏亮,郭开今,等.3D打印β-磷酸三钙仿生骨支架修复兔股骨髁骨缺损[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(4):243-250.
[44] 陈宏亮,郭开今,陈向阳,等. 3D打印技术制备β-磷酸三钙仿生骨支架在兔股骨髁部骨缺损修复中的应用[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2021,26(5):571-577.
[45] SINGH S, UTREJA AK, SANDHU N, et al. An Innovative Miniature Bite Force Recorder. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2011;4(2):113-118.
[46] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:243-245.
[47] KARAGEORGIOU V, KAPLAN D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27):5474-5491.
|