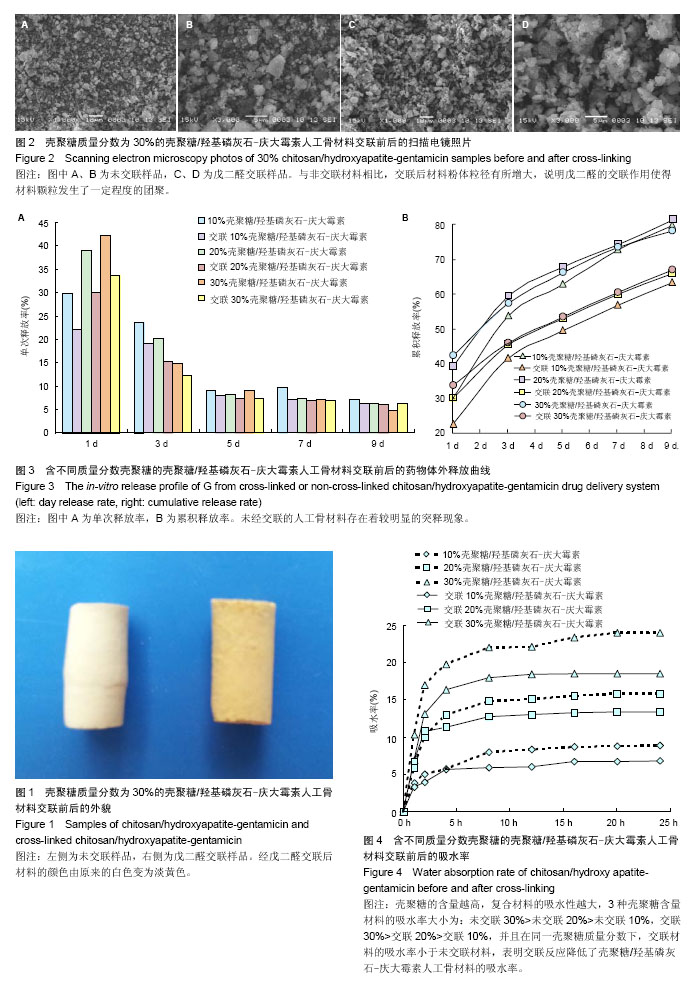
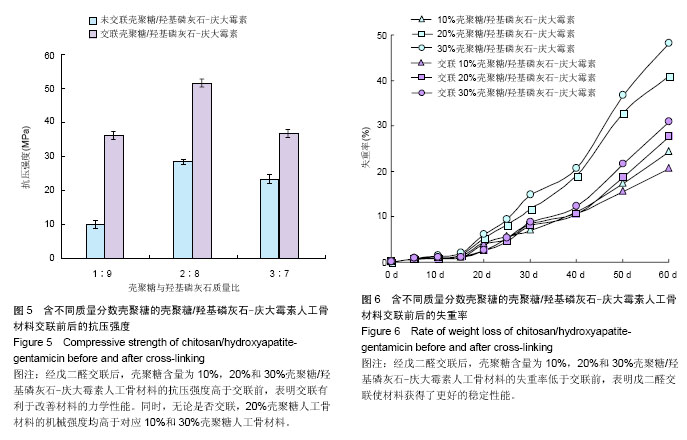
| [1] Netz DJ,Sepulveda P,Pandolfelli VC,et al.Potential use of gelcasting hydroxyapatite porous ceramic as an implantable drug delivery system.Int J Pharm.2001;213(1-2):117-125.
[2] Santos C,Rovath CF,Franke RP,et al.Spray-dried hydroxyapatite-5-Fluorouracil granules as a chemotherapeutic delivery system.Ceram Int. 2009;35(1): 509-513.
[3] 邹琴,张利,左奕,等.载黄芪多糖骨水泥的理化性能及体外细胞相容性研究[J].功能材料, 2008,39(9):1515-1521.
[4] Ginebra MP,Traykova T,Planell JA.Calcium phosphate cements as bone drug delivery systems: A review.J Control Release.2006;113(2):102-110.
[5] Gao C,Cai Y,Kong X,et al.Development and characterization of injectable chitosan-based hydrogels containing dexamethasone/rhBMP-2 loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Mat Lett.2013;93(1):312-315.
[6] 蓝琳,智伟,黄晶,等.丹酚酸B缓释羟基磷灰石颗粒与成骨细胞的活性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(51): 9501-9506.
[7] Teng SH,Lee EJ,Wang P,et al.Functionally gradient chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for controlled drug release.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009; 90(1):275-282.
[8] Mahmoodi S,Sorkhi L,Farrokhi-Rad M,et al.Electrophoretic deposition of hydroxyapatite–chitosan nanocomposite coatings in different alcohols. Surf Coat Technol. 2013;216: 106114.
[9] 王新,刘玲蓉,张其清.纳米羟基磷灰石-壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(2):120-124.
[10] Kong L,Gao Y,Cao W,et al.Preparation and characterization of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite with enhanced compressive strength by urease-catalyzed method.J Biomed Mater Res A.2005;75(2):275-295.
[11] Baskar D,Balu R,Kumar TS.Mineralization of pristine chitosan film through biomimetic process.Int J Biol Macromol. 2011; 49(3):385-389.
[12] 杨洪,傅山岗.尿素共沉淀法制备纤维状羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合粉料[J].应用化学, 2005,22(1):87-90.
[13] Liu C,Wang W,Shen W,et al.Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a nonceramic hydroxyapatite.J. Endodontics. 1997;23(8): 490-493.
[14] Lawton DM,Lamaletie MDJ,Gardner DL.Biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite ceramic: response of chondrocytes in a test system using low temperature scanning electron microscopy. J Dent.1989;17(1):21-27.
[15] Craig GT,Brook IM,Lamb DJ.Tissue response to subperiosteal implantation of dense hydroxyapatite: case report.Biomaterials.1989;10(2):133-135.
[16] Martin L,Søren O,Cody B,et al.Improved bone anchorage of hydroxyapatite coated implants compared with tricalcium-phosphate coated implants in trabecular bone in dogs.Biomaterials.1999;20(9):803-808.
[17] Matsumoto T,Okazaki M,Inoue M,et al.Hydroxyapatite particles as a controlled release carrier of protein. Biomaterials.2004;25(17):3807-3812.
[18] Ravi Kumar MNV.A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React Funct Polym.2000;46(1):1-27.
[19] Britto DD,Campana-Filho SP.Kinetics of the thermal degradation of chitosan.Thermochimica Acta. 2007;465(1-2): 73-82.
[20] Kong M,Chen XG,Xing K,et al.Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review.Int J Food Microbiol. 2010;144(1):51-63.
[21] Hong Y, Song H, Gong Y,et al.Covalently crosslinked chitosan hydrogel: Properties of in vitro degradation and chondrocyte encapsulation.Acta Biomaterialia.2007;3(1):23-31.
[22] Klokkevold PR,Lew DS,Ellis DG,et al.Effect of chitosan on lingual hemostasis in rabbits.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 49(8):858-863.
[23] Kang PL,Chang SJ,Manousakas I,et al.Development and assessment of hemostasis chitosan dressings.Carbohydr Polym.2011;85(3): 565-570.
[24] 陈黄琴,黄彬.复合蟾毒灵的壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石人工骨对骨肉瘤细胞增殖的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2011,20(25): 3143-3146.
[25] Liu TY,Chen SY,Li JH,et al.Study on drug release behavior of CDHA/chitosan nanocomposites—Effect of CDHA nanoparticles.J Control Release. 2006;112(1):88-95.
[26] Sivakumar M,Panduranga Rao K.Preparation, characterization and in vitro release of gentamicin from coralline hydroxyapatite-gelatin composite microspheres. Biomaterials.2002;23(15):3175-3181.
[27] 朱华跃,肖玲.戊二醛交联对壳聚糖/PVA共混膜结构和性能的影响[J].浙江海洋学院学报:自然科学版,2005,24(2):126-142.
[28] Beppu MM,Vieira RS,Aimoli CG,et al.Crosslinking of chitosan membranes using glutaraldehyde: Effect on ion permeability and water absorption.J Membr Sci. 2007; 301(1-2):126-130.
[29] Kikuchi M,Matsumoto HN,Yamada T,et al.Glutaraldehyde cross-linked hydroxyapatite/collagen self-organized nanocomposites. Biomaterials.2004;25(1):63-69.
[30] 陈新,邵正中,黄郁芳,等.不同交联剂含量对戊二醛交联壳聚糖膜结构与性能影响的研究[J].化学学报, 2000,58(12): 1654-1659.
[31] 王襄平,梅兴国.多肽及蛋白类药物微球包封率和释放的研究进展[J].国外医学:药学分册,2006,33(3):219-223.
[32] 王丹.多肽及蛋白类药物微球的载体材料、制备以及突释现象[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(10):1931-1934.
[33] 李向荣.药剂学[M].杭州:浙江大学出版社,2010:456-460.
[34] 周建平.药剂学[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2004:216-218.
[35] 赵宏霞,黄才欢,金花,等.壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石-庆大霉素缓释材料的抗菌性能研究及AFM观察[J].功能材料,2009,40(3): 429-435.
[36] 赵宏霞,金花,蔡继业.庆大霉素对羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料性能的影响[J].无机化学学报,2010,26(1):106-111.
[37] 吴国杰,吴炜亮,崔英德.聚醚一壳聚糖水凝胶合成工艺条件对性能的影响研究[J].材料导报,2005,19(11):128-130.
[38] 杨旭东,吴国杰,林玩金.壳聚糖水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2005,33(12):48-50.
[39] 李雪洁,刘万顺,韩宝芹.戊二醛交联型羧甲基壳聚糖的制备和生物相容性的研究[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2007,37 (S2): 121-126.
[40] 肖海军,侯春林,薛锋.羧甲基壳聚糖-羧甲基纤维素防粘连膜的制备及其理化特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14 (38): 7069-7074.
[41] 许勇,洪华,钱颖,等.医用壳聚糖膜的制备和性能研究[J].功能高分子学报,2004,17(1): 55-60.
[42] 蒋柳云,李玉宝,张利,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖-羧甲基纤维素复合支架材料的研究[J].无机材料学报,2008,23(1): 135-140.
[43] Zou B,Li X,Zhuang H,et al.Degradation behaviors of electrospun fibrous composites of hydroxyapatite and chemically modified poly(DL-lactide). Polym Degrad Stabil. 2011;96:114-122.
[44] Li L,Li G,Jiang J,et al.Electrospun fibrous scaffold of hydroxyapatite/poly (ε-caprolactone) for bone regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(2):547-554.
[45] 宁思敏,王东,孙海钰,等.大鼠成骨细胞与壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架降解产物的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18 (12): 1846-1851.
[46] 楼维维,董伊雯,金逸凡,等.掺镧羟基磷灰石涂层的合成和性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(8):1224-1230.
[47] 王海霞,岳进.梯度掺锶羟基磷灰石骨水泥的体外细胞生物学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(47):8149-8154.
[48] 李斯日古楞,胡晓文,章超,等.珊瑚羟基磷灰石修复种植体周不同类型骨缺损的效果观察[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2011,5(2):192-204.
[49] Xia Y,Zhou P,Cheng X,et al.Selective laser sintering fabrication of nano-hydroxyapatite/poly-ε-caprolactone scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications.Int J Nanomedicine.2013;8:4197-4213.
[50] Wang H,Li Y,Zuo Y,et al.Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007; 28(22):3338-3348.
[51] Heo SJ, Kim SE, Wei J,et al.Fabrication and characterization of novel nano- and micro-HA/PCL composite scaffolds using a modified rapid prototyping process.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;89(1):108-116.
[52] Fu S,Ni P,Wang B,et al.In vivo biocompatibility and osteogenesis of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone)/nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold.Biomaterials. 2012;33(33):8363-8371. |