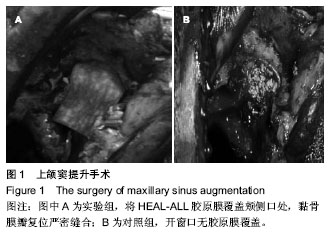
骨移植材料在上颌窦提升后新生骨高度的长期稳定性是种植体成功的关键因素
[28],而种植体与新生骨的良好骨性整合是种植体成功的标准之一
[29]。力学实验是检测种植体-骨界面强度的一种有效及简便的方法。Haas等
[30]研究表明颌窦提升后种植体的牵出力随着时间的延长而增加,使用羟基磷灰石作为移植材料时,12,26周时分别达到325.1及521.8 N。本研究中实验组及对照组的种植体牵出力亦随着时间的延长而增加。这表明种植体与骨的结合强度随着时间的延长而增强。实验组在24周时即达到
547.2 N,大于Haas的结果。这可能与移植材料的种类及种植体的类型有一定关系。实验组与对照组在4,12周时牵出力无明显差异,而在24周时差异有显著性意义。这应该与Bio-oss骨粉成骨及吸收较慢有关;同时种植体顶部骨的吸收亦有一定的影响。
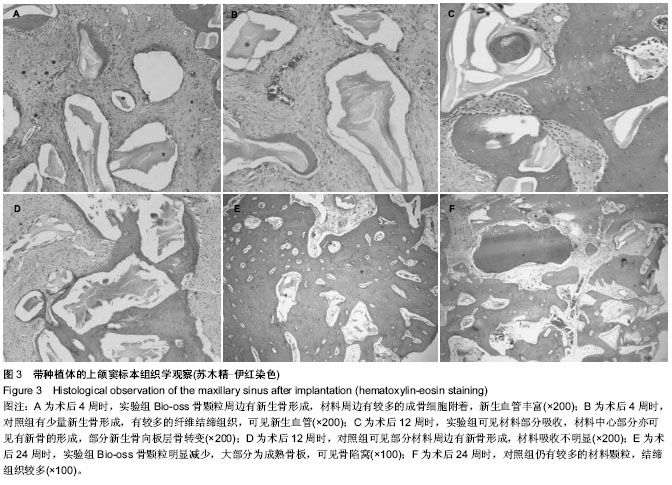
组织形态学的分析在一定程度上解释牵出力与时间的相关性。研究结果显示,实验组与对照组中新生骨的面积随着观察时间的延长而增加,并且成熟的束状骨也增多。这与种植体牵出力的变化具有一致性。但在Haas的研究中出现了组织形态学与力学测试相反的现象,即自体骨移植后组织学显示远好于对照及羟基磷灰石组,但种植体牵出力却小于后者。作者认为虽然新生骨比例的增加、成熟骨增多并不必然代表种植体与骨的结合强度更好,但至少是提供了二者良好结合的基础,有关其中的相关性有待于进一步的研究。
种植体在上颌窦提升后顶部的骨吸收一直是学者们关注的现象。Kahnberg等[31]发现上颌窦外提升同期牙种植体的总体失败率高达39%,骨移植材料第1年的吸收率为21%,3年内为30%。在Miyajima的动物实验中,6个月时移植的自体骨块体积减少约50%[32]。Choi等[33]临床研究中发现无膜覆盖的上颌窦外提升患者,6个月后再开窗处仍可见大量的骨粉颗粒,并且骨粉颗粒有“逸出”上颌窦颊侧骨窗的现象,这说明有移植骨材料移位的现象。种植体顶部骨吸收的原因尚不清楚,Hatano等[28]认为压力诱导的移植后上颌窦底黏膜的塌陷下降及骨吸收可导致骨垂直高度的降低。本研究中可以发现对照组种植体顶部有明显的骨吸收发生,导致种植体顶部暴露。而实验组则骨吸收不明显。其可能的原因是种植体的顶部接近上颌窦的黏膜远离周边的骨壁,无骨性的支持,基于重力、空气压力、头部的运动等因素移植骨材料的移位是可能发生的。本研究证实了骨移植材料的移位。因此骨移植材料的移位是种植体顶部骨吸收的原因之一。
在上颌窦提升中是否使用覆盖膜目前仍有争议。林野等[34]对9例患者进行上颌窦提升植入自体骨与Bio-Oss的混合物,没有使用覆盖膜,仍取得了满意的效果。Fugazzotto[35]对各类骨量不足使用引导骨再生技术,达到种植义齿的修复目的。但王宏青等[36]的研究中在有钛膜覆盖的情况下的骨吸收量明显大于无膜覆盖的各组。
目前用于上颌窦外提升的覆盖膜主要有可吸收膜和不可吸收膜,也有使用局部组织瓣如颊脂垫瓣覆盖达到人工膜的目的[37]。不可吸收膜的缺点是创口易开裂,膜早期暴露概率高,暴露后成骨的效果受影响大。另外由于膜不能在体内降解,需二次手术取出;目前临床已很少使用。可吸收膜的最大优点是无需二次手术取出;另外暴露后有一定的抗感染能力,所以即使暴露,感染的机会也较不可吸收膜少,对成骨效率的影响较小[38-39],因此在临床应用的范围越来越广泛[40]。
目前国内使用的可吸收膜主要以Bio-Gide为主。该生物膜为进口产品,价格较贵,增加患者负担。 HEAL-ALL生物膜是国内生产的一种异种脱细胞真皮基质,采用特殊工艺将真皮内可能被宿主识别而引起排斥反应的各种细胞及其成分脱除,只保留真皮中含胶原网架的细胞外基质及真皮层与表皮层之间的基底膜。由于完全清除了细胞成分及Ⅰ、Ⅱ型细胞相容性抗原,所以其免疫活性很低,不会诱发排斥反应,表现出良好的生物相容性。该研究显示在上颌窦提升中,使用HEEAL-ALL生物膜的引导骨再生技术可以促进上颌窦提升后新生骨的形成、移植骨材料的改建、骨成熟的过程,同时可以减少新生骨的吸收;提高种植体与新生骨的结合强度。由于本研究观察时间较短,无法预测长期的骨改变情况,有待于更进一步的研究。