| [1]张颖,王富友,谭洪波,等.微骨折技术修复羊膝关节软骨缺损组织学观察[J].重庆医学,2010,39(19):2565-2569.
[2]Steadman JR, Briggs KK, Rodrigo JJ. Outcomes of microfracture for traumatic chondral defects of the knee: average 11 year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2003;19(6):477-484.
[3]Blevins FT, Steadman R, Rodrigo J. Treatment of articular cartilage defects in athletes: an analysis of functional outcome and lesion appearance. J Orthopedics. 1998;21(14):761-763.
[4]Elluru RG, Thompson F, Reece A. Fibroblast growth factor 18 gives growth and directional cues to airway cartilage. Laryngoscope. 2009;27(5):437-440.
[5]李成,王伟,等.软骨源性形态发生蛋白缓释系统对兔膝骨关节炎影响的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,12(34): 6293-6296.
[6]葛志强,冯传汉,吕厚山,等.不同孔径钻孔术对兔关节软骨缺损修复的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,1997,13(2):93-95.
[7]张春霞,孙磊,修忠标,等.鹿茸多肽对实验性膝骨性关节炎关节软骨中糖胺多糖和Ⅱ型胶原水平的影响[J].中国骨伤, 2012,25(2): 138-142.
[8]Kenneth J, Livak TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△Ct method. Schmittgen Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.
[9]孟丽,崔芳,龚淼等.透射电镜电子染色方法的改良[J].电子显微学报,2010,29(2):189-190.
[10]倪磊,吕厚山.修复膝关节软骨缺损的关节镜技术—微骨折技术[J].中国微创外科杂志,2005,5(7):350-354.
[11]付昌马,钱春生,章有才,等.微骨折术联合玻璃酸钠注射修复膝关节软骨损伤[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,2(2):109-111.
[12]林松,吴昌新,何和与,等.微骨折术修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(2):168-169.
[13]Li XD, Leo BM, Beck G, et al. Collagen and proteoglycan abnormalities in the GDF-5-deficient mice and molecular changes when treating disk cells with recombinant growth factor. Spine. 2004;38(7):720-729.
[14]Everman DB, Bartels CF, Yang Y, et al. The mutational spectrum of brachydactyly type C. Am J Med Genet. 2002; 112(3):291-296.
[15]Erlacher L, Ng CK, Ullrich R, et al. Presence of cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage and enhancement of matrix replacement in vitro. Arthritis Rheuma.1998;41(17):263-273.
[16]李成,王伟.软骨组织工程中相关生长因子理论研究的最新资讯[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(28):5260-5263.
[17]Coleman CM, Tuan RS. Growth/differentiation factor 5 enhances chondrocyte maturation. Developmental Dynamics. 2003;25(9):74-77.
[18]Feng G, Wan Y, Balian G, et al. Adenovirus-mediated expression of growth and differentiation factor-5 promotes chondrogenesis of adipose stem cells. Growth Factors. 2008; 13(6):857-861.
[19]Guo CA, Liu XG, Huo JZ, et al. Novel gene-modified-tissue engineering of cartilage using stable transforming growth factor-beta1-transfected mesenchymal stem cells grown on chitosan scaffolds. J Biosci Bioeng. 2007;34(24):59-63.
[20]穆长征,马云胜,王征,等.软骨源形态发生蛋白基因转染自体骨髓间充质细胞修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(49):9185-9188.
[21]韩敏,孙秀霞,李仲谨,等.载药微球制剂的研究进展[J].应用化工, 2007,5(36):493-495.
[22]Prestwich GD, Marecak DM. Chemical modification of hyaluronic acid for drugdelive biomaterials, and bioehemieal Probes. 1998.
[23]Fraser JR, Brown TJ, Laureni TC. Catabolismof aluronan. The chemistry biology,and medical applications of hyaluronan and medical applications of hyaluronan and its derivatives. 1998.
[24]张丽娜,凌沛学,娄红祥,等.关节腔注射玻璃酸钠治疗兔膝骨关节炎的研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2007,28(6):391-394.
[25]胡炯,杜宁,代岭辉,等.建立膝骨性关节炎关节软骨缺损的动物模型的研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2009,32(11):13-16.
[26]DoréD, de Hoog J, Giles G, et al. A longitudinal study of the association between dietary factors, serum lipids, and bone marrow lesions of the knee. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;17(4): 236-240.
[27]Caplan AL, Elyaderani M. Principles of cartilage repair and regeneration. Clin Orthop. 1997;342(16):254-269.
[28]魏泓.医学实验动物学[M]四川:四川科学技术出版社,2001.
[29]Toivanen AT, Heliovaara M, Inpivaara O, et al. Obesity, physically demanding work and traumatic knee injury are major risk factors for knee osteoarthritis-a population--based study with a follow-up of 22 years. Rheumatology. 2010;18(5): 147-150.
[30]Rehan Youssef A, Longino D, Seerattan R, et al. Muscle weakness causes joint degeneration in rabbits. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;23(3):246-249. |
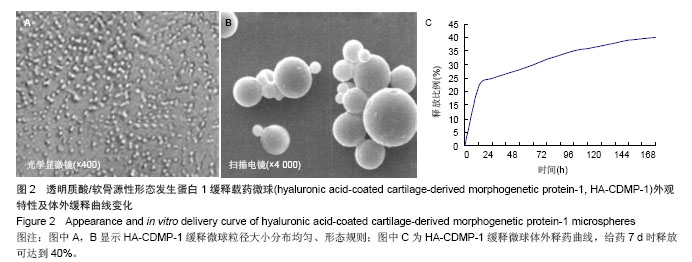
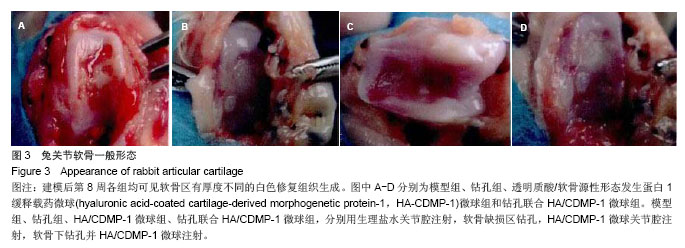
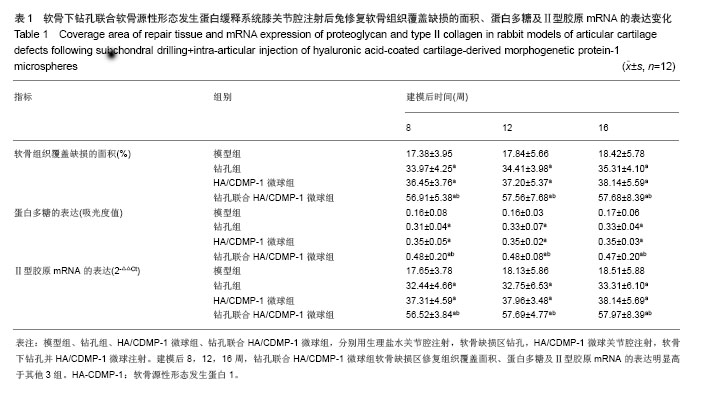
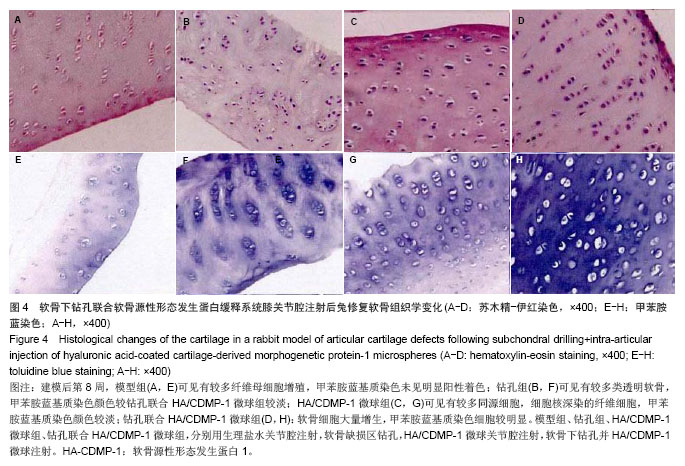
.jpg)
.jpg)