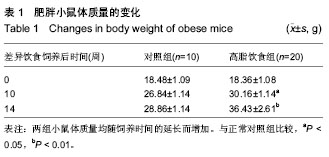
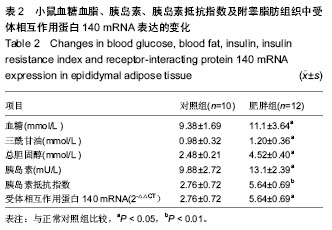
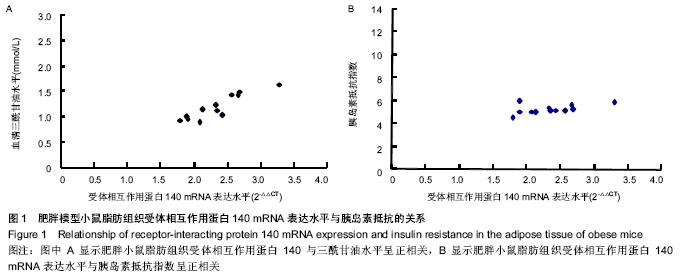
| [1] Guyenet SJ, Schwartz MW. Clinical review: Regulation of food intake, energy balance, and body fat mass: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(3):745-755.
[2] Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ. Targeting fat to prevent diabetes. Cell Metab. 2007;5(5):323-325.
[3] Badman MK, Flier JS. The adipocyte as an active participant in energy balance and metabolism. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132(6):2103-2115.
[4] Ahima RS, Lazar MA. Adipokines and the peripheral and neural control of energy balance. Mol Endocrinol. 2008; 22(5):1023-1031.
[5] Francis GA, Fayard E, Picard F, et al. Nuclear receptors and the control of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol. 2003;65: 261-311.
[6] Desvergne B, Michalik L, Wahli W. Transcriptional regulation of metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2006;86(2):465-514.
[7] Feige JN, Auwerx J. Transcriptional coregulators in the control of energy homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17(6): 292-301.
[8] Herzog B, Hallberg M, Seth A, et al. The nuclear receptor cofactor, receptor-interacting protein 140, is required for the regulation of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism by liver X receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(11):2687-2697.
[9] Rosell M, Jones MC, Parker MG. Role of nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140 in metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812(8):919-928.
[10] Hallberg M, Morganstein DL, Kiskinis E, et al. A functional interaction between RIP140 and PGC-1alpha regulates the expression of the lipid droplet protein CIDEA. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(22):6785-6795.
[11] Fritah A, Steel JH, Parker N, et al. Absence of RIP140 reveals a pathway regulating glut4-dependent glucose uptake in oxidative skeletal muscle through UCP1-mediated activation of AMPK. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32520.
[12] Powelka AM, Seth A, Virbasius JV, et al. Suppression of oxidative metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis by the transcriptional corepressor RIP140 in mouse adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(1):125-136.
[13] Ho PC, Lin YW, Tsui YC, et al. A negative regulatory pathway of GLUT4 trafficking in adipocyte: new function of RIP140 in the cytoplasm via AS160. Cell Metab. 2009;10(6):516-523.
[14] Ho PC, Wei LN. Biological activities of receptor-interacting protein 140 in adipocytes and metabolic diseases. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012;8(6):452-457.
[15] Fritah A, Christian M, Parker MG. The metabolic coregulator RIP140: an update. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 299(3):E335-340.
[16] O'Rahilly S. Human obesity and insulin resistance: lessons from experiments of nature. Novartis Found Symp. 2007;286: 13-23, 162-3, 196-203.
[17] 陈蕾,贾伟平,项坤三,等.肥胖者胰岛素抵抗与总体脂、局部体脂关系的研究[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2001,17(5):276-279.
[18] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[19] 杨爱君,崔雁,叶卉初,等.营养性肥胖动物模型的建立[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2005,4(3):156-157.
[20] 石国富,张洪德,王丽娟,等. ELISA检测胰岛素的进一步研究[J].标记免疫分析与临床,1996(4):234.
[21] Oliveira EP, Lima Md, Souza ML. Metabolic syndrome, its phenotypes, and insulin resistance by HOMA-IR. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2007;51(9):1506-1515.
[22] Duncan MH, Singh BM, Wise PH, et al. A simple measure of insulin resistance. Lancet. 1995;346(8967):120-121.
[23] 张宏山,许明,张阳,等.小鼠心肌组织3种总RNA提取方法比较[J].临床心血管病杂志,2010,26(2):149-150.
[24] 高海,李燕,周变华,等.动物脂肪代谢与肥胖基因调节研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2007,28(12):99-101.
[25] Fortuño A, Rodríguez A, Gómez-Ambrosi J, et al. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ: role of leptin and adiponectin in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. J Physiol Biochem. 2003;59(1):51-60.
[26] Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006;444(7121):840-846.
[27] Calle EE. Obesity and cancer. BMJ. 2007;335(7630): 1107-1108.
[28] Stefan N, Häring HU, Hu FB, et al. Metabolically healthy obesity: epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013;1(2):152-162.
[29] Cavaillès V, Dauvois S, L'Horset F, et al. Nuclear factor RIP140 modulates transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1995;14(15):3741-3751.
[30] Lee CH, Chinpaisal C, Wei LN. Cloning and characterization of mouse RIP140, a corepressor for nuclear orphan receptor TR2. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18(11):6745-6755.
[31] Chen WH. Turning down the heat: the potential role of RIP140 in inflammation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2012;9(3):195-196.
[32] Leonardsson G, Steel JH, Christian M, et al. Nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140 regulates fat accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(22):8437-8442.
[33] Christian M, Kiskinis E, Debevec D, et al. RIP140-targeted repression of gene expression in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(21):9383-9391.
[34] 查锡良.生物化学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008.
[35] 李光伟,李春梅,孙淑湘,等.胰岛素抵抗--遗传和环境因素致高血压的共同途径?[J].中华内科杂志,2003,42(1):11-15.
[36] 周鹏,陈南衡,王其民.高甘油三酯血症与胰岛素抵抗及糖代谢异常的关系[J].中华内科杂志,1998,37(7):447-450.
[37] 窦梅,马爱国.胰岛素抵抗主要原因及机制的研究进展[J].国外医学卫生学分册,2009,36(3):175-179.
[38] 李伶,杨刚毅.脂代谢紊乱和脂肪细胞因子与胰岛素抵抗[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2007,15(3):129-131.
[39] Kamon J, Yamauchi T, Terauchi Y, et al. The mechanisms by which PPARgamma and adiponectin regulate glucose and lipid metabolism. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003;122(4): 294-300.
[40] Yano W, Kubota N, Itoh S, et al. Molecular mechanism of moderate insulin resistance in adiponectin-knockout mice. Endocr J. 2008;55(3):515-522.
[41] Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med. 2002; 8(11):1288-1295.
[42] Gupta P, Ho PC, Huq MD, et al. PKCepsilon stimulated arginine methylation of RIP140 for its nuclear-cytoplasmic export in adipocyte differentiation. PLoS One. 2008;3(7): e2658.
[43] Christian M, White R, Parker MG. Metabolic regulation by the nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17(6):243-250.
[44] White R, Morganstein D, Christian M, et al. Role of RIP140 in metabolic tissues: connections to disease. FEBS Lett. 2008; 582(1):39-45. |