| [1] Ozin GA, Varaksa N, Coombs N, et al. Bone mimetics: a composite of hydroxyapatite and calciumdodecylphosphate lamellar phase. J Mater Chem. 1997;7:1601-1607.
[2] Doremus RH. Bioceramics. J Mater Sci. 1992;27(2):285-297.
[3] Suchanek W, Yoshimura M. Processing and properties of hydroxyapatite-based biomaterials for use as hard tissue replacement implants. J Mater Res. 1998;13(1):94-117.
[4] Burstein FD, Cohen SR, Hudgins R, et al. The use of porous granular hydroxyapatite in secondary orbitocranial reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100(4):869-874.
[5] Choi SH, Levy ML, McComb JG. A method of cranioplasty using coralline hydroxyapatite. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1998; 29(6): 324-327.
[6] Boden SD, Martin GJ Jr, Morone M, et al. The use of coralline hydroxyapatite with bone marrow, autogenous bone graft, or osteoinductive bone protein extract for posterolateral lumbar spine fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(4):320-327.
[7] Wasielewski RC, Sheridan KC, Lubbers MA. Coralline hydroxyapatite in complex acetabular reconstruction. Orthopedics. 2008;31(4):367.
[8] Thalgott JS, Giuffre JM, Fritts K, et al. Instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion using coralline hydroxyapatite with or without demineralized bone matrix, as an adjunct to autologous bone. Spine J. 2001;1(2):131-137.
[9] Ono I, Gunji H, Kaneko F, et al. Treatment of extensive cranial bone defects using computer-designed hydroxyapatite ceramics and periosteal flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 92(5): 819-830.
[10] Fu K, Meng ZB, Li J, et al. Repairing the defect of benign bone tumor with the coralline hydroxyapatite. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008;33(5):421-424.
[11] Wolfe SW, Pike L, Slade JF 3rd, et al. Augmentation of distal radius fracture fixation with coralline hydroxyapatite bone graft substitute. J Hand Surg Am. 1999;24(4):816-827.
[12] Thalgott JS, Klezl Z, Timlin M, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion with processed sea coral (coralline hydroxyapatite) as part of a circumferential fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(24):E518-527.
[13] Gosain AK, Riordan PA, Song L, et al. A 1-year study of osteoinduction in hydroxyapatite-derived biomaterials in an adult sheep model: part II. Bioengineering implants to optimize bone replacement in reconstruction of cranial defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114(5):1155-1165.
[14] Ning Y, Wei T, Defu C, et al. The research of degradability of a novel biodegradable coralline hydroxyapatite after implanted into rabbit. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;88(3):741-746.
[15] Cohen AJ, Dickerman RD, Schneider SJ. New method of pediatric cranioplasty for skull defect utilizing polylactic acid absorbable plates and carbonated apatite bone cement. J Craniofac Surg. 2004;15(3):469-472.
[16] Roy DM, Linnehan SK. Hydroxyapatite formed from coral skeletal carbonate by hydrothermal exchange. Nature. 1974; 247(5438):220-222.
[17] Hollinger JO, Brekke J, Gruskin E, et al. Role of bone substitutes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(324):55-65.
[18] Lane JM, Tomin E, Bostrom MP. Biosynthetic bone grafting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(367 Suppl):S107-117.
[19] Voor MJ, Arts JJ, Klein SA, et al. Is hydroxyapatite cement an alternative for allograft bone chips in bone grafting procedures? A mechanical and histological study in a rabbit cancellous bone defect model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004; 71(2):398-407.
[20] Chen F, Mao T, Tao K, et al. Bone graft in the shape of human mandibular condyle reconstruction via seeding marrow-derived osteoblasts into porous coral in a nude mice model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60(10):1155-1159.
[21] Sivakumar M, Kumar TS, Shantha KL, et al. Development of hydroxyapatite derived from Indian coral. Biomaterials. 1996; 17(17):1709-1714.
[22] Birchall JD, Thomas NL. On the architecture and function of cuttlefish bone. J Mater Sci. 1983;18(7):2081-2086.
[23] Kumar GS, Girija EK, Thamizhavel A, et al. Synthesis and characterization of bioactive hydroxyapatite-calcite nanocomposite for biomedical applications. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;349(1):56-62.
[24] Battistella E, Mele S, Foltran I, et al. Cuttlefish bone scaffold for tissue engineering: a novel hydrothermal transformation, chemical-physical, and biological characterization. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2012;10(2):99-106.
[25] Kannan S, Rocha JH, Agathopoulos S, et al. Fluorine-substituted hydroxyapatite scaffolds hydrothermally grown from aragonitic cuttlefish bones. Acta Biomater. 2007;3(2):243-249.
[26] Jia X, Qian W, Wu D, et al. Cuttlebone-derived organic matrix as a scaffold for assembly of silver nanoparticles and application of the composite films in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009;68(2): 231-237.
[27] Milovac D, Gallego Ferrer G, Ivankovic M, et al. PCL-coated hydroxyapatite scaffold derived from cuttlefish bone: morphology, mechanical properties and bioactivity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;34:437-445.
[28] Fernandez JM, Molinuevo MS, Cortizo MS, et al. Development of an osteoconductive PCL-PDIPF-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(6): e126-135.
[29] Arafat MT, Lam CX, Ekaputra AK, et al. Biomimetic composite coating on rapid prototyped scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(2):809-820.
[30] Kim BS, Yang SS, Lee J. A polycaprolactone/cuttlefish bone-derived hydroxyapatite composite porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013. in press.
[31] Li X, Zhao Y, Bing Y, et al. Biotemplated syntheses of macroporous materials for bone tissue engineering scaffolds and experiments in vitro and vivo. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(12):5557-5562.
[32] Jia X, Qian W. Simultaneous synthesis and assembly of gold nanoparticles in cuttlebone-derived organic matrix: a "green" pathway for gold nanocomposite. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2008; 8(9):4370-4376.
[33] Ogasawara W, Shenton W, Davis SA, et al. Template mineralization of ordered macroporous chitin−silica composites using a cuttlebone-derived organic matrix. Chem Mater. 2000;12(10):2835-2837.
[34] Taves DR. Similarity of octacalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite structures. Nature. 1963;200:1312-1313.
[35] 刘金华,王大志.乌贼骨及其水热改性制备羟基磷灰石的研究[J].无机材料学报,2006,21(2):433-438.
[36] 胡浩,朱胜利,崔振铎,等.TiZrCuPd金属玻璃表面沉积钙磷层的研究[J].功能材料,2010,41(10):1845-1847.
[37] 杨浩,王春婷,吴玉梅,等.MTT试验中细胞特性状态及细胞数与OD值的关系探讨[J].动物医学进展,2002,23(5):49-53.
[38] 国家药品监督管理局.GB/T 16886.5-2003 医疗器械生物学评价 第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2003 |
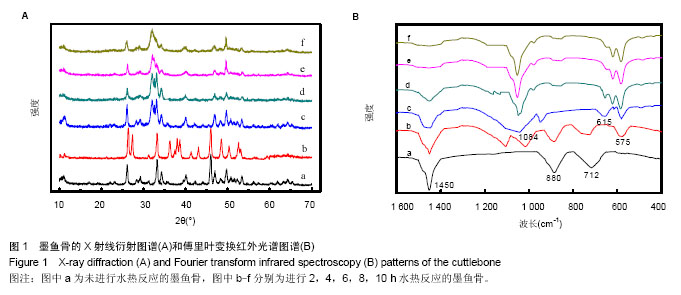
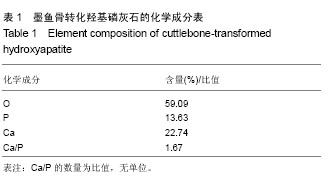
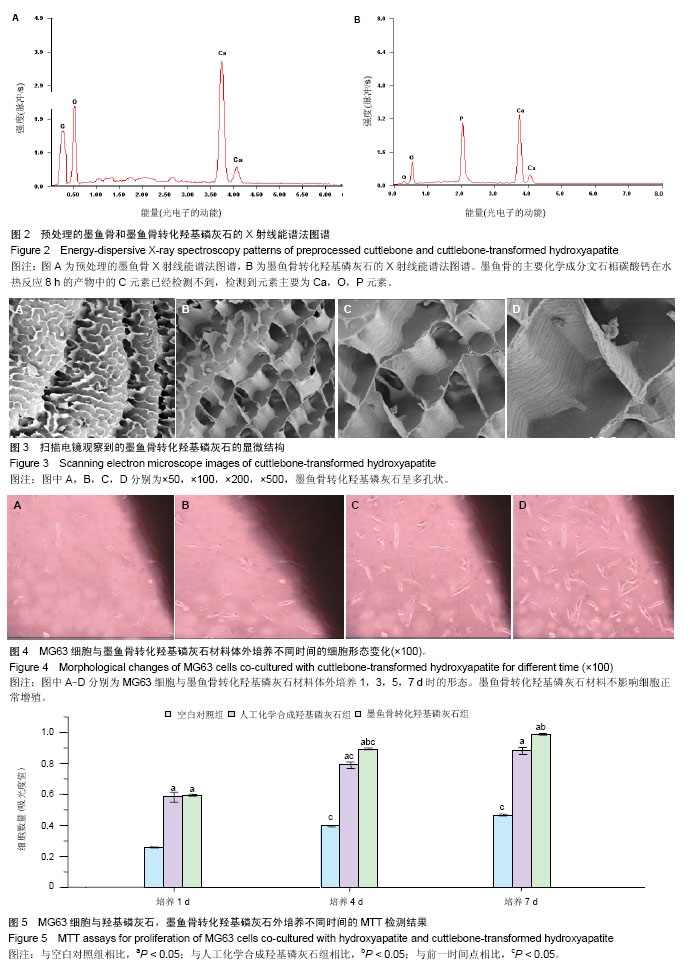
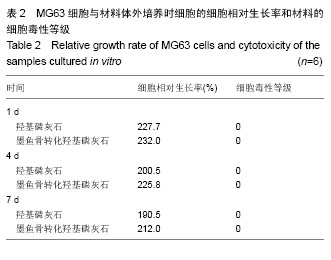
.jpg)