| [1] Sun YC,Teng MM,Yuan WS,et al.Risk of post-vertebroplasty fracture in adjacent vertebral bodies appears correlated with the morphologic extent of bone cement. J Chin Med Assoc. 2011;74(8):357-362.
[2] Frankel BM,Monroe T,Wang C.Percutaneous vertebral augmentation: an elevation in adjacent-level fracture risk in kyphoplasty as compared with vertebroplasty. Spine J.2007; 7(5):575-582.
[3] Zou J,Mei X,Zhu X,et al.The long-term incidence of subsequent vertebral body fracture after vertebral augmentation therapy: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2012;15(4):E515-522.
[4] Brodano GB,Amendola L,Martikos K,et al.Vertebroplasty: benefits are more than risks in selected and evidence-based informed patients. A retrospective study of 59 cases. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(8):1265-1271.
[5] Bula P,Lein T,Strassberger C,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: indications - treatment strategy-complications. Z Orthop Unfall.2010; 148(6): 646-656.
[6] 田斐,邑晓东,卢海霖,等.PVP与PKP术后邻近椎体继发骨折的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(6):503-506.
[7] Voormolen MH,Lohle PN,Juttmann JR,et al.The risk of new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the year after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Vasc Interv Radiol.2006;17(1): 71-76.
[8] Zuccari AG,Oshida Y,Moore BK. Reinforcement of acrylic resins for provisional fixed restorations.Part I: Mechanical properties.Biomed Mater Eng.1997;7(5):327-343.
[9] Kolb JP,Kueny RA,Püschel K,et al.Does the cement stiffness affect fatigue fracture strength of vertebrae after cement augmentation in osteoporotic patients? Eur Spine J.2013; 22(7):1650-1656.
[10] Lieberman IH,Togawa D,Kayanja MM. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: filler materials. Spine J. 2005;5(6 Suppl): 305S-316S.
[11] Ryu KS,Shim JH,Heo HY,et al.Therapeutic Efficacy of Injectable Calcium Phosphate Cement in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Prospective Nonrandomized Controlled Study at 6-Month Follow-up. World Neurosurg. 2010;73:408-411.
[12] Cherng A,Takagi S,Chow LC.Effects of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and other gelling agents on the handling properties of calcium phosphate cement. J Biomed Mater Res.1997;35(3):273-277.
[13] Chen L,Xiang H,Li XX,et al.Improvement of the anti-washout performance of calcium phosphate cement by use of modified starch.Key Eng Mater. 2007;336-338:1628-1631.
[14] Qian G,Dong Y,Yang W,et al.Injectable calcium phosphate cement and fibrin sealant recombined human bone morphogenetic protein-2 composite in vertebroplasty: an animal study.Bosn J Basic Med Sci.2012;12(4): 231-235.
[15] Schumacher M,Henß A,Rohnke M,et al.A novel and easy-to-prepare strontium(II) modified calcium phosphate bone cement with enhanced mechanical properties.Acta Biomater.2013;9(7):7536-7544.
[16] Christel T,Kuhlmann M,Vorndran E,et al.Dual setting α-tricalcium phosphate cements.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(3):573-581.
[17] Tarsuslugil SM,O'Hara RM,Dunne NJ,et al.Development of calcium phosphate cement for the augmentation of traumatically fractured porcine specimens using vertebroplasty. J Biomech.2013;46(4):711-715.
[18] 孙钰,吴乃庆,曹晓建,等.硅胶薄膜囊预防椎体后凸成形术中骨水泥渗漏的实验研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(11): 913-915.
[19] 周云,唐天驷,熊成东,等.可吸收球囊制作的实验研究[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2005,25(4):595-598.
[20] Sun G,Wei D,Liu X,et al.Novel biodegradable electrospun nanofibrous P(DLLA-CL) balloons for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures.Nanomedicine. 2013;9(6): 829-838.
[21] 刘训伟,魏岱旭,彭湘涛,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术在治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中恢复椎体高度局限性的观察及机制探讨[J].医学影像学杂志,2013,23(9):1457-1460.
[22] Kokubo T,Kushitani H,Sakka S,et al.Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface-structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic A-W.J Biomed Mater Res. 1990;24(6): 721-734.
[23] Lieberman IH,Dudeney S,Reinhardt MK,et al.Initial outcome and efficacy of "kyphoplasty" in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1631-1638.
[24] Galovich LA,Perez-Higueras A,Altonaga JR,et al.Biomechanical, histological and histomorphometric analyses of calcium phosphate cement compared to PMMA for vertebral augmentation in a validated animal model.Eur Spine J.2011;20(Suppl 3):S376-S382. |


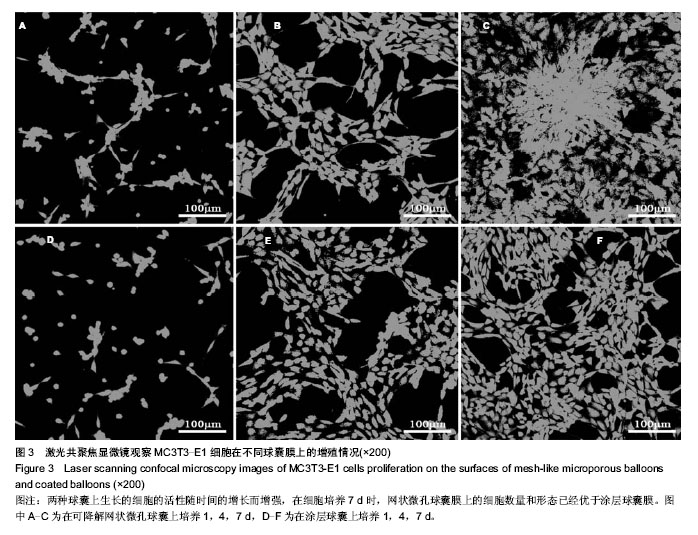

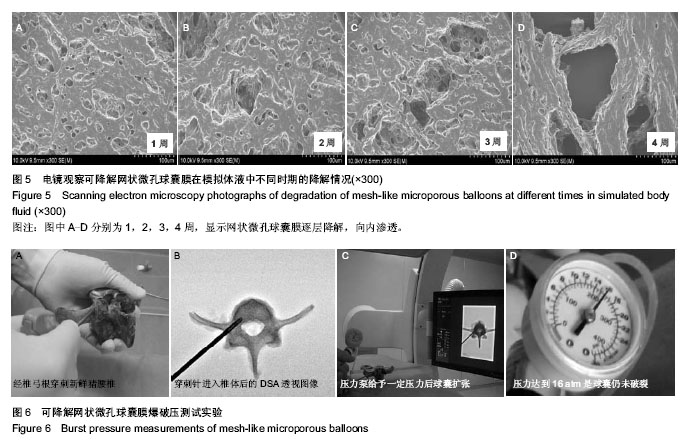

.jpg)