| [1]Helmy N, Hintermann B.New trends in the treatment of proximal humerus fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 442:100-108.[2]Konrad GG, Mehlhorn A, Kühle J,et al.Proximal humerus fractures - current treatment options.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2008;75(6):413-421.[3]姜保国, 陈建海.肱骨近端骨折的治疗[J].北京大学学报:医学版, 2012,44(6): 821-823.[4]Popescu D, Fernandez-Valencia JA, Rios M,et al.Internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the T2-proximal humeral nail.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(9): 1239- 1244.[5]Blum J, Hansen M, Rommens PM.Angle-stable intramedullary nailing of proximal humerus fractures with the PHN (proximal humeral nail).Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2009; 21(3):296-311.[6]曲志国,崔玉玲,崔正宏.肱骨近端锁定钢板与传统钢板及交叉针治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(2):248-250. [7]陈福海,安百章,高加智.肩部前外侧小切口入路肱骨近端锁定钢板治疗老年性肱骨近端骨折的临床应用[J].中国当代医药, 2013, 20(2): 48-49.[8]高礼层,秦涛,麻文谦.肩峰下前外侧入路治疗老年肱骨近端骨折疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2013,22(1): 61-62.[9]王永强.两种不同手术入路治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].中外健康文摘,2013,15: 67-68.[10]王鸥, 张道坤,毕雷鸣,等.经改良三角肌+肱肌分离入路锁定钢板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折[J].临床骨科杂志, 2013,16(4): 457.[11]张立兴,吴海龙,张斌,等.改良手术入路治疗老年肱骨近端骨折36例疗效观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(05): 448-450.[12]冯万文, 陈天年,刘海涛,等.应用锁定钢板经三角肌劈开入路治疗NeerⅡ型肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(1): 77-79.[13]Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS,et al.The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(434):123-129.[14]Röderer G, Abouelsoud M, Gebhard F,et al.Minimally invasive application of the non-contact-bridging (NCB) plate to the proximal humerus: an anatomical study.J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(9):621-627.[15]Neer CS 2nd.Displaced proximal humeral fractures. I. Classification and evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52(6):1077-1089.[16]Hawkins RJ, Angelo RL.Displaced proximal humeral fractures. Selecting treatment, avoiding pitfalls.Orthop Clin North Am. 1987;18(3):421-431.[17]Constant CR, Murley AH.A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (214):160-164.[18]Doorenbosch CA, Harlaar J, Veeger DH.The globe system: an unambiguous description of shoulder positions in daily life movements.J Rehabil Res Dev. 2003;40(2):147-155.[19]Rab GT.Shoulder motion description: the ISB and Globe methods are identical.Gait Posture. 2008;27(4):702-705.[20]Bonnefoy-Mazure A, Slawinski J,et al.Rotation sequence is an important factor in shoulder kinematics. Application to the elite players' flat serves.J Biomech. 2010;43(10):2022-2025.[21]Ellenbecker TS, Roetert EP, Bailie DS,et al.Glenohumeral joint total rotation range of motion in elite tennis players and baseball pitchers.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(12):2052- 2056.[22]Kibler WB, Sciascia A, Thomas SJ.Glenohumeral internal rotation deficit: pathogenesis and response to acute throwing.Sports Med Arthrosc. 2012;20(1):34-38.[23]郑和平,林建华,许卫红.胸肩峰动脉肩峰支逆行锁骨骨膜(骨)瓣移位术的应用解剖[J].中国解剖与临床,2001,5(2):76-78.[24]苗华,周建生.骨科手术入路解剖学[M].合肥:安徽科学技术出版社,1999:19-38. |
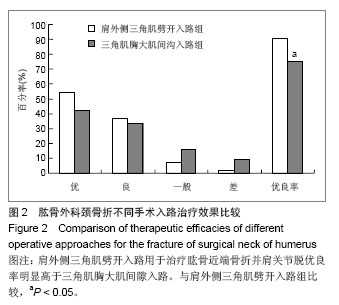
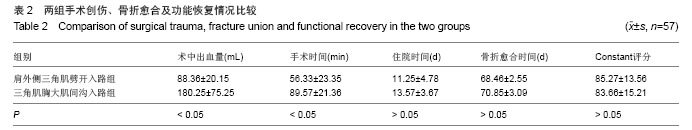
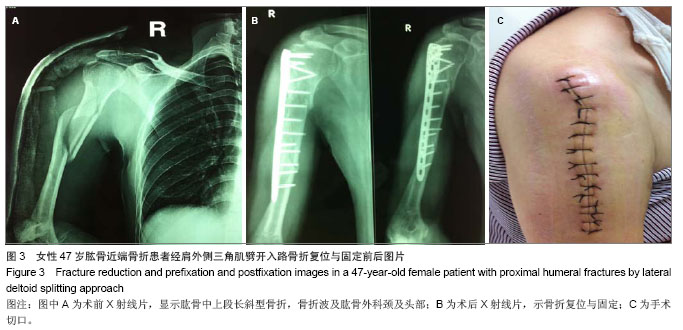
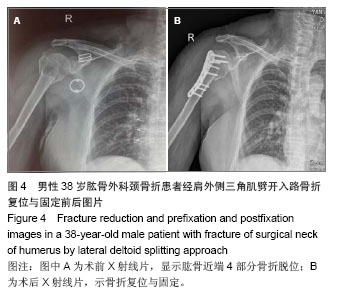
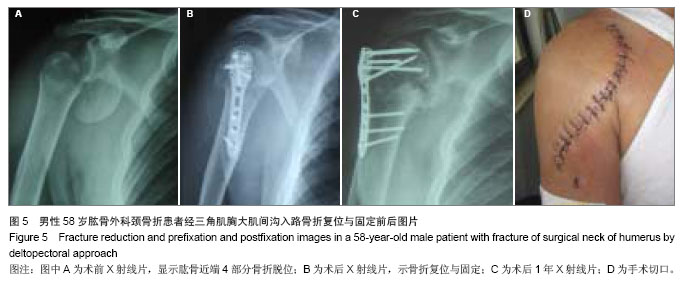
.jpg)
.jpg)