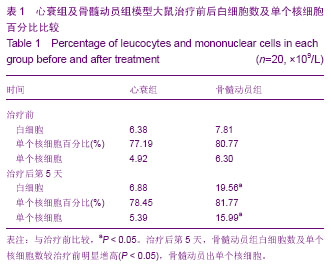
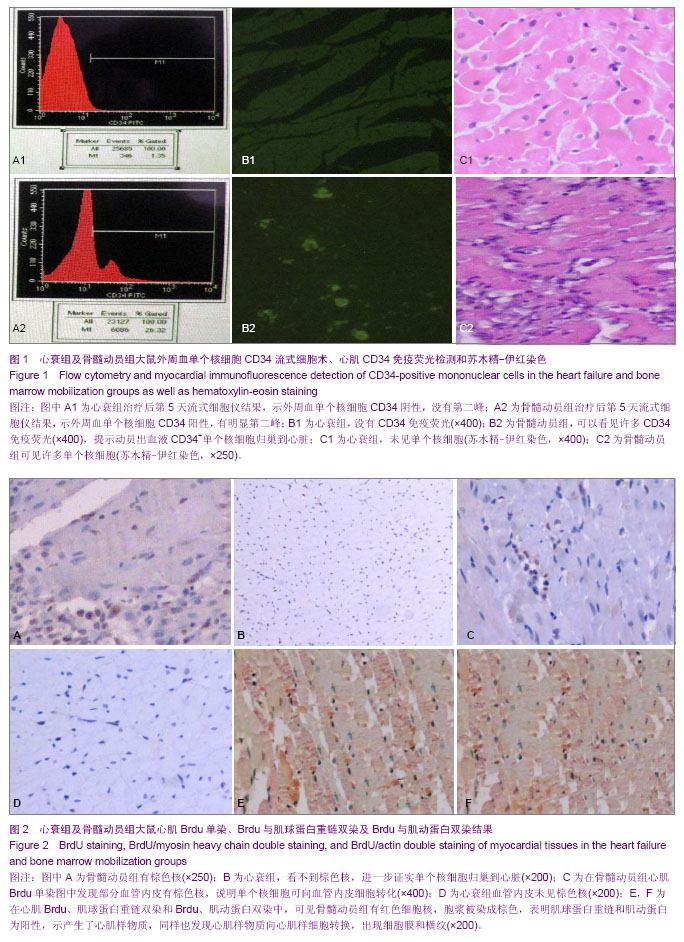
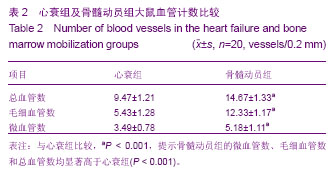
| [1] 肖文涛,高丽君,高传玉,等.不同类型骨髓干细胞治疗扩张型心肌病的疗效对比[J].中华心血管病杂志,2012,40(7):575-577.[2] Arnous S, Mozid A, Mathur A. The Bone Marrow Derived Adult Stem Cells for Dilated Cardiomyopathy (REGENERATE-DCM) trial: study design. Regen Med. 2011;6(4):525-533.[3] Yeo C, Mathur A. Autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells for ischemic heart failure: REGENERATE-IHD trial. Regen Med. 2009;4(1):119-127.[4] Möbius-Winkler S, Höllriegel R, Schuler G, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells: implications for cardiovascular disease. Cytometry A.2009;75(1):25-37.[5] Brunner S, Engelmann MG, Franz WM. Stem cell mobilisation for myocardial repair. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008;8(11): 1675-1690.[6] Li TS, Takahashi M, Ohshima M, et al. Myocardial repair achieved by the intramyocardial implantation of adult cardiomyocytes in combination with bone marrow cells. Cell Transplant. 2008;7(6):695-703.[7] Cheng Z, Liu X, Ou L,et al. Mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008; 22(5):363-371. [8] De Silva R, Raval AN, Hadi M, et al. Intracoronary infusion of autologous mononuclear cells from bone marrow or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized apheresis product may not improve remodelling, contractile function, perfusion, or infarct size in a swine model of large myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(14):1772-1782.[9] Ripa RS, Kastrup J. G-CSF therapy with mobilization of bone marrow stem cells for myocardial recovery after acute myocardial infarction --a relevant treatment? Exp Hematol. 2008;36(6):681-686.[10] Brunner S, Huber BC, Fischer R, et al.G-CSF treatment after myocardial infarction: impact on bone marrow-derived vs cardiac progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(6):695-702. [11] Inoue T, Sata M, Hikichi Y,et al. Mobilization of CD34-positive bone marrow-derived cells after coronary stent implantation: impact on restenosis. Circulation. 2007;115(5):553-561.[12] Liu KQ, Qi X, Du JP,et al. Treatment of acute myocardial infarction with autologous bone marrow stem cells mobilization combined with recombinant growth factor in rat. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2006;18(8):494-497.[13] Nikol S, Kuhlmann M. Mobilization of stem cells in cardiovascular disease. Improvement of vascularization, cardiac function and arrhythmias.Med Klin (Munich). 2006; 22:190-192.[14] Kanellakis P, Slater NJ, Du XJ, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and stem cell factor improve endogenous repair after myocardial infarction .Cardiovasc Res. 2006;70(1):117-125. [15] Jakob P, Landmesser U. Current status of cell-based therapy or heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2013;10(2):165-176.[16] Koninckx R, Daniëls A, Windmolders S, et al. The cardiac atrial appendage stem cell: a new and promising candidate for myocardial repair. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;97(3):413-423.[17] Honold J, Fischer-Rasokat U, Lehmann R,et al. G-CSF stimulation and coronary reinfusion of mobilized circulating mononuclear proangiogenic cells in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease:five-year results of the TOPCARE-G-CSF trial. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(11): 2325-2337.[18] Mozid AM, Jones D, Arnous S, et al. The effects of age, disease state, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on progenitor cell count and function in patients undergoing cell therapy for cardiac disease. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(2): 216-223.[19] Konenkov VI, Pokushalov EA, Poveshchenko OV, et al. Phenotype of peripheral blood cells mobilized by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with chronicheart failure. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2012;153(1):124-128.[20] Ripa RS. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor therapy to induce neovascularization in ischemic heart disease. Dan Med J. 2012;59(3):B4411. [21] Zimmet H, Porapakkham P, Porapakkham P, et al. Short- and long-term outcomes of intracoronary and endogenously mobilized bone marrow stem cells in the treatment of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(1): 91-105.[22] Zhao Q, Sun C, Xu X, et al. CD34+ cell mobilization and upregulation of myocardial cytokines in a rabbit model of myocardial ischemia. Int J Cardiol. 2011;152(1):18-23.[23] Ichim TE, Solano F, Lara F, et al. Combination stem cell therapy for heart failure. Int Arch Med. 2010;3(1):5. [24] Hou M, Hu SS, Wei YJ, et al. Effects of mobilization of bone marrow stem cells on regenerative potential of cardiac tissues after myocardial infarction. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009; 89(17):1192-1196.[25] 姚巍,王凤芝.骨髓间充质细胞静脉移植联合自体骨髓干细胞动员对心肌病心力衰竭大鼠的心功能影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(29):5645-5648.[26] 姚巍,王凤芝.重组人生长激素联合骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植对心力衰竭大鼠心功能的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2007,7(11): 825-827.[27] Helmuth L. Stem cell shear call of injured tissue.Science. 2000; 290: 1479-1481.[28] Dotsenko O, Xiao Q, Xu Q, et al. Bone marrow resident and circulating progenitor cells in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90(6):1944-1951.[29] Habeeb NM, Youssef OI, El Hadidi ES. Therapeutic role of mobilized bone marrow cells in children with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. ISRN Pediatr. 2012;2012:927-968.[30] Druka?a J, Paczkowska E, Kucia M, et al.. Stem cells, including a population of very small embryonic-like stem cells, are mobilized into peripheral blood in patients after skin burn injury. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(1):184-194.[31] Wright DE, Wagers AJ, Gulati AP, et al.Physiological migration of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Science. 2001;294: 1933-1936.[32] OrlicD,Kajstura J,Chimenti S,et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infracted myocardium. Nature. 2001;410(6829): 701-705.[33] Stroncek DF, Clay ME, Herr G, et al. The kinetics of G-CSF mobilization of CD34+ cells in healthy people. Transfus Med. 1997;7:19-24.[34] Harada M, Nagafuji K, Fujisaki T, et al. G-CSF-induced mobilization of peripheral blood stem cells from healthy adults for allogeneic transplantation. J Hematother. 1996;5(1):63-71.[35] Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, et al. Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioblasts preventscardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med. 2001;7: 430-436.[36] Ciulla MM, Lazzari L, Pacchiana R, et al. Homing of peripherally injected bone marrow cells in the rat after experimental myocardial injury. Haematologica. 2003;88: 614-621.[37] Stroncek DF, Clay ME, Herr G, et al. The kinetics of G-CSF mobilization of CD34+ cells in healthy people. Transfus Med. 1997;7:19-24.[38] Kajstura J, Zhang X, Reiss K, et al. Myocyte cellular hyperplasia and Myocyte cellular hypertrophy contribute to chronic ventricular remodeling in coronary artery narrowing -induced cardiommyopathy in rats. Circ Res. 1994; 74(3): 383-400.[39] 欧瑞明,陈运贤,钟雪云,等.粒细胞集落刺激因子对大鼠实验性心肌梗死治疗作用[J].广东医学,2002,23(11):1131-1133.[40] 刘宏伟,盖鲁粤,张端珍,等.粒细胞集落刺激因子骨髓干细胞动员治疗免心肌梗死的实验研究[J].军医进修学院学报,2005, 26(2): 132-134.[41] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Mobilized bone marrow cells repair the Infracted heart, improving function and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2001;98:10344-10349. |
.jpg)