中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (40): 7054-7060.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.40.006
• 脂肪干细胞 adipose-derived stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
脂肪源性干细胞的体外分离培养与鉴定
杜郭佳,陈小红,朱国华,范雁东,王 昀,党木仁
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院神经外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
-
出版日期:2013-10-01发布日期:2013-10-31 -
通讯作者:党木仁,博士,主任医师,博士生导师,新疆医科大学第一附属医院神经外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054 -
作者简介:杜郭佳★,男,1979年生,新疆维吾尔自治区昭苏县人,蒙古族,2008年新疆医科大学毕业,硕士,主治医师,主要从事颅底外科、神经内镜及干细胞方面的研究。 -
基金资助:新疆维吾尔自治区青年科学基金资助项目(2011211B31)*
In vitro isolation, culture and identification of adipose-derived stem cells
Du Guo-jia, Chen Xiao-hong, Zhu Guo-hua, Fan Yan-dong, Wang Yun, Dang Mu-ren
- Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2013-10-01Published:2013-10-31 -
Contact:Dang Mu-ren, M.D., Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China damrjab@163.com -
About author:Du Guo-jia★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China dgrjav@163.com -
Supported by:the Youth Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2011211B31*
摘要:
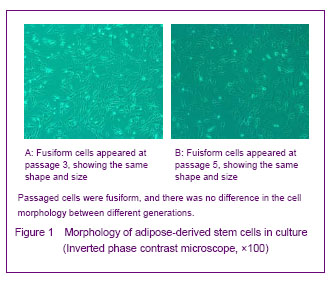
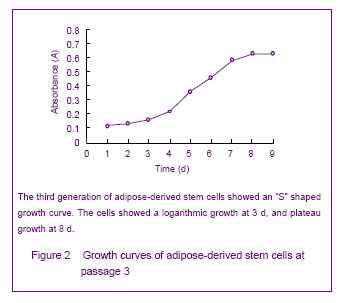
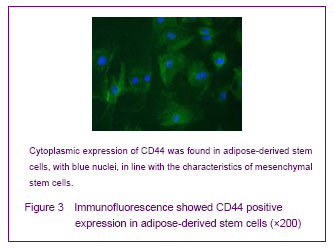
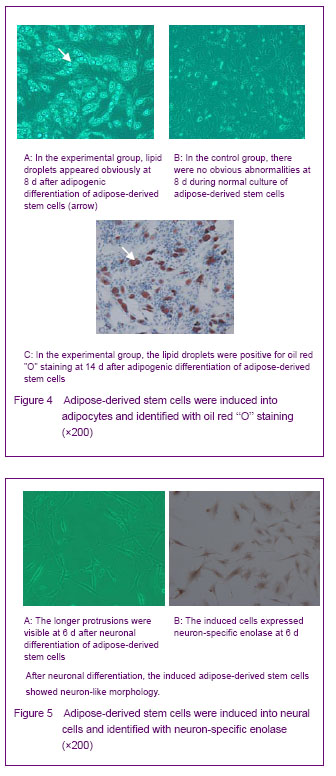
背景:脂肪间充质干细胞来源丰富、取材方便、体外有较强增殖能力并具有多向分化的潜能,有望成为组织工程的种子细胞。 目的:体外分离培养SD大鼠脂肪干细胞并进行鉴定。 方法:取SD大鼠腹股沟区皮下脂肪组织,0.075%I型胶原酶消化分离、培养脂肪源性干细胞,倒置相差显微镜下观察脂肪源性干细胞的细胞形态和增殖特征。取第3代细胞用MTT比色法描绘生长曲线,免疫荧光法鉴定干细胞标志物CD44,含有体积分数10%胎牛血清、地塞米松和胰岛素的DMEM/F12定向诱导成脂分化,油红“O”染色成脂分化鉴定。免疫组化法鉴定向神经细胞诱导分化的结果。 结果与结论:分离出的大鼠脂肪源性干细胞生长曲线呈“S”形,强烈表达干细胞标志物CD44。成脂诱导分化经油红“O”染色呈橘红色。向神经细胞诱导分化后表达神经元标志物神经元特异性烯醇化酶。说明SD大鼠脂肪源性干细胞在体外具有易于分离培养和扩增,表达间充质干细胞相关表型,特定条件下可诱导分化的特点。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杜郭佳,陈小红,朱国华,范雁东,王 昀,党木仁. 脂肪源性干细胞的体外分离培养与鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(40): 7054-7060.
Du Guo-jia, Chen Xiao-hong, Zhu Guo-hua, Fan Yan-dong, Wang Yun, Dang Mu-ren. In vitro isolation, culture and identification of adipose-derived stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(40): 7054-7060.
Growth curve of cultured adipose-derived stem cells
Cultured adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells possess stem cell properties
Adipogenic differentiation of cultured adipose-derived stem cells
| [1]Rodbell M. Metabolism of isolated fat cells. I. Effects of hormones on glucose metabolism and lipolysis. J Biol Chem. 1964;239:375-380. [2]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [3]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295. [4]Lin XH, Liu N, Xiao YC, et al. Effects of adipose-derived stem cells transplantation on the neuronal apoptosis and the expression of Bcl-2 and caspase-12 in the brain post focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;27(1):40-43. [5]Graham SH, Chen J, Clark RS. Bcl-2 family gene products in cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17(10):831-841. [6]Plesnila N. Role of mitochondrial proteins for neuronal cell death after focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2004;89:15-19. [7]Ferrer I, Planas AM. Signaling of cell death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemia: life and death struggle in the penumbra. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003;62(4): 329-339. [8]Cai YN, Yuan XD, Ou Y, et al. Apoptosis duringβ-mercaptoethanol-induced differentiation of adult adipose-derived stromal cells into neurons. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(10):750-755. [9]Gao X, Dong T, Li Z Q, et al. Survival of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplanted via the tail vein in rat brain with cerebral ischemia. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongchang Yanjiu. 2012;16(27):5067-5071. [10]The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [11]Stanford WL, Caruana G, Vallis KA, et al. Expression trapping: identification of novel genes expressed in hematopoietic and endothelial lineages by gene trapping in ES cells. Blood. 1998;92(12):4622-4631. [12]Forrai A, Robb L. The gene trap resource: a treasure trove for hemopoiesis research. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(8): 845-856. [13]Stanford WL, Cohn JB, Cordes SP. Gene-trap mutagenesis: past, present and beyond. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(10): 756-768. [14]Joyner AL, Auerbach A, Skarnes WC. The gene trap approach in embryonic stem cells: the potential for genetic screens in mice. Ciba Found Symp. 1992;165:277-297. [15]Clay TM, Custer MC, Spiess PJ, et al. Potential use of T cell receptor genes to modify hematopoietic stem cells for the gene therapy of cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 1999;5(1):3-15. [16]Filippi MD, Sainteny F. Hematopoietic differentiation of embryonic stem cells in mice: a model to study the biology of hematopoiesis. Transfus Clin Biol. 2001;8(1):6-16. [17]Kitajima K, Takeuchi T. Mouse gene trap approach: identification of novel genes and characterization of their biological functions. Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;76(6): 1029-1037. [18]Conquet F. Inactivation in vivo of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 by specific chromosomal insertion of reporter gene lacZ. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34(8):865-870. [19]Guan C, Ye C, Yang X, et al. A review of current large-scale mouse knockout efforts. Genesis. 2010;48(2):73-85. [20]Araki K, Yamamura K. Genetic screening for novel genes by insertional mutagenesis with gene trap method in ES cells. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1995;40(14): 2017- 2024. [21]Vasileiskii SS. Fetal and embryonic hemoglobins. Sov J Dev Biol. 1972;3(1):27-32. [22]Schnütgen F. Generation of multipurpose alleles for the functional analysis of the mouse genome. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2006;5(1):15-18. [23]Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18(4):399-404. [24]Kørbling M, Estrov Z. Adult stem cells for tissue repair - a new therapeutic concept? N Engl J Med. 2003;349(6): 570-582. [25]Mitchell JB, McIntosh K, Zvonic S, et al. Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell-associated markers. Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):376-385. [26]Qin YW, Zhao JM, Su W, et al. Isolation, culture and identification of rat adipose-derived stem cells. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011; 15(23):4242-4246. [27]Choi YS, Dusting GJ, Stubbs S, et al. Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into beating cardiomyocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(4):878-889. [28]Fang B, Song Y, Lin Q, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells as salvage therapy for treatment of severe refractory acute graft-vs.-host disease in two children. Pediatr Transplant. 2007;11(7):814-817. [29]Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S, et al. Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood. 2001;98(8): 2396-2402. [30]Schieker M, Pautke C, Haasters F, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells at the single-cell level: simultaneous seven-colour immunofluorescence. J Anat. 2007;210(5):592-599. [31]Zhou MH, Zhang XW, Li L. Research of rat's adipose-derived stem cells induced differentiation into adipogenic cells. Shiyong Fuchan Ke Zazhi. 2011;27(7): 515-518. [32]Cheng WD, Zhao Y, He JS, et al. Adipogenic and osteogenic potential of rat adipose tissue-derived stromal cells in vitro. Anhui Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2007;42(5): 501-504. [33]Yang XF, HE X, He J, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells into adipocytes directed differentiation. Jilin Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban. 2009;35(6):987-991. [34]Kirchner S, Kieu T, Chow C, et al. Prenatal exposure to the environmental obesogen tributyltin predisposes multipotent stem cells to become adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 2010; 24(3):526-539. [35]Li HX, Luo X, Liu RX, et al. Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;291(1-2):116-124. [36]Liu Q, Cen L, Zhou H, et al. The role of the extracellular signal-related kinase signaling pathway in osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells and in adipogenic transition initiated by dexamethasone. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(11):3487-3497. [37]Ashjian PH, Elbarbary AS, Edmonds B, et al. In vitro differentiation of human processed lipoaspirate cells into early neural progenitors. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(6): 1922-1931. |
| [1] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | 肖 豪, 刘 静, 周 君. 脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | 惠小珊, 白 京, 周思远, 王 阶, 张金生, 何庆勇, 孟培培. 中医药调控干细胞诱导分化的理论机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [4] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [5] | 范一鸣, 刘方煜, 张洪宇, 李 帅, 王岩松. 脊髓损伤后室管膜区内源性神经干细胞反应的系列问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [6] | 侯婧瑛, 郭天柱, 于萌蕾, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理通过激活MALAT1靶向抑制miR-195促进骨髓间充质干细胞的生存和血管形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [7] | 周 颖, 张 幻, 廖 松, 胡凡琦, 易 静, 刘玉斌, 靳继德. 去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理对人牙髓干细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [8] | 梁学振, 杨 曦, 李嘉程, 骆 帝, 许 波, 李 刚. 补肾活血胶囊介导Hedgehog信号通路调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨成脂分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [9] | 王继芳, 鲍 祯, 乔亚红. miR-206调控小细胞肺癌干细胞EVI1基因表达及细胞生物学行为[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [10] | 刘 峰, 彭宇环, 罗良平, 吴本清. 植物源性碱性成纤维细胞生长因子维持人胚胎干细胞的生长与分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [11] | 闻丹丹, 李 强, 沈才齐, 纪 哲, 金培生. 外用红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架提高脂肪间充质干细胞活性修复糖尿病创面[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [12] | 朱兵兵, 邓江华, 陈晶晶, 慕晓玲. 白细胞介素8受体可提高脐带间充质干细胞迁移和向损伤内皮的黏附[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [13] | 罗小玲, 张 丽, 杨茂桦, 徐 洁, 徐晓梅. 柚皮素干预人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [14] | 熊挺淋, 应梦慧, 张丽莎, 张晓刚, 杨 燕. 诱导多能干细胞分化的心肌细胞电生理特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1063-1067. |
| [15] | 王新民, 刘 飞, 许 杰, 白玉玺, 吕 剑. 髓芯减压联合牙髓干细胞治疗兔早期激素性股骨头坏死[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
Design
Main reagents and instruments for isolation, culture and identification of adipose-derived stem cells are as follows.
.jpg)
1 文章特点在于成功运用胶原酶Ⅰ消化法从脂肪组织中分离培养出数量多、纯度高、活力强的大鼠脂肪源性干细胞,此方法克服了其他方法容易导致的细胞活力低下、易分化、纯度不高等缺点。 2 对成脂诱导过程中发现,体外成脂诱导培养基DMEM/F12里含有体积分数10%胎牛血清、地塞米松和胰岛素就能刺激脂肪源性干细胞向脂肪分化,无需添加其他成份,既往研究往往需要添加吲哚美辛等。 3 文章创新点在于获取的体外分离培养的脂肪源性干细胞性状稳定,易于体外扩增,可行性高。
基金项目:
新疆维吾尔自治区青年科学基金资助项目(2011211B31)*
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||