| [1]邵志敏,余科达.乳腺外科的发展趋势[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2007,14(3):252-254.
[2]马文浩.乳腺癌干细胞信号转导通路的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2011,17(18):2759-2762.
[3]Zardawi SJ, O'Toole SA, Sutherland RL,et al. Dysregulation of Hedgehog, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways in breast cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24(3):385-398.
[4]Wang Y, Zhou D, Phung S,et al.SGK3 is an estrogen- inducible kinase promoting estrogen-mediated survival of breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25(1):72-82.
[5]牛畅,叶棋浓.乳腺癌干细胞和乳腺癌[J].生物技术通讯,2010, 21(5):731-735.
[6]Moulder S. Intrinsic resistance to chemotherapy in breast cancer.Womens Health (Lond Engl). 2010;6(6):821-830.
[7]Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S.Tumour stem cells and drug resistance.Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(4):275-284.
[8]Cariati M, Naderi A, Brown JP,et al. Alpha-6 integrin is necessary for the tumourigenicity of a stem cell-like subpopulation within the MCF7 breast cancer cell line. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(2):298-304.
[9]Phillips TM, McBride WH, Pajonk F.The response of CD24(-/low)/CD44+ breast cancer-initiating cells to radiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(24):1777-1785.
[10]Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G,et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell. 2009;138(4):645-659.
[11]Lindeman GJ, Visvader JE. Insights into the cell of origin in breast cancer and breast cancer stem cells. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2010;6(2):89-97.
[12]Heerma van Voss MR, van der Groep P, Bart J, et al. Expression of the stem cell marker ALDH1 in BRCA1 related breast cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011;34(1):3-10.
[13]Mumcuoglu M, Bagislar S, Yuzugullu H,et al.The ability to generate senescent progeny as a mechanism underlying breast cancer cell heterogeneity. PLoS One. 2010;5(6): e11288.
[14]Huang M, Li Y, Zhang H,et al.Breast cancer stromal fibroblasts promote the generation of CD44+CD24- cells through SDF-1/CXCR4 interaction.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:80.
[15]Jordan CT, Guzman ML. Mechanisms controlling pathogenesis and survival of leukemic stem cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(43):7178-7187.
[16]Beug H.Breast cancer stem cells: eradication by differentiation therapy. Cell. 2009;138(4):623-625.
[17]Pece S, Serresi M, Santolini E, et al. Loss of negative regulation by Numb over Notch is relevant to human breast carcinogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2004;167(2):215-221.
[18]Zardawi SJ, O'Toole SA, Sutherland RL, et al. Dysregulation of Hedgehog, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways in breast cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24(3):385-398.
[19]Rizzo P, Osipo C, Foreman K, et al. Rational targeting of Notch signaling in cancer.Oncogene. 2008;27(38): 5124-5131.
[20]Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Burkadze G,et al. Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis.Pathobiology. 2006;73(5):213-223.
[21]于晓敏,王辰,王军.Wnt信号通路的生物学效应及其与肺部疾病的关系[J].首都医科大学学报,2009,30(2):182-184.
[22]徐新娟,丁文柏. Wnt信号转导通路与肺癌的研究近况[J].医学综述,2008,14(2):217-219.
[23]林叔陈,张凤春,张雁云,等.肿瘤干细胞的调控机制研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤学,2009,17(1):183-186.
[24]Boras-Granic K, Wysolmerski JJ.Wnt signaling in breast organogenesis.Organogenesis. 2008;4(2):116-122.
[25]Curtin JC, Lorenzi MV. Drug discovery approaches to target Wnt signaling in cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 2010;1(7): 563-577.
[26]Lindvall C, Evans NC, Zylstra CR,et al.The Wnt signaling receptor Lrp5 is required for mammary ductal stem cell activity and Wnt1-induced tumorigenesis.J Biol Chem. 2006; 281(46):35081-35087.
[27]Liu BY, McDermott SP, Khwaja SS,et al.The transforming activity of Wnt effectors correlates with their ability to induce the accumulation of mammary progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(12):4158-4163.
[28]Patrawala L, Calhoun T, Schneider-Broussard R,et al.Side population is enriched in tumorigenic, stem-like cancer cells, whereas ABCG2+ and ABCG2- cancer cells are similarly tumorigenic.Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6207-6219.
[29]Dontu G, Al-Hajj M, Abdallah WM,et al. Stem cells in normal breast development and breast cancer.Cell Prolif. 2003;36 Suppl 1:59-72.
[30]Kruger JA, Kaplan CD, Luo Y,et al. Characterization of stem cell-like cancer cells in immune-competent mice.Blood. 2006;108(12):3906-3912.
[31]Roarty K, Rosen JM.Wnt and mammary stem cells: hormones cannot fly wingless. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010;10(6): 643-649.
[32]Arce L, Pate KT, Waterman ML. Groucho binds two conserved regions of LEF-1 for HDAC-dependent repression. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:159.
[33]Kruger JA, Kaplan CD, Luo Y,et al. Characterization of stem cell-like cancer cells in immune-competent mice. Blood. 2006; 108(12):3906-3912.
[34]Stingl J, Eirew P, Ricketson I,et al. Purification and unique properties of mammary epithelial stem cells.Nature. 2006; 439(7079):993-997.
[35]Leong ML, Maiyar AC, Kim B, et al. Expression of the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase, Sgk, is a cell survival response to multiple types of environmental stress stimuli in mammary epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2003;278(8): 5871-5882.
[36]Lang F, Böhmer C, Palmada M,et al. (Patho)physiological significance of the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase isoforms.Physiol Rev. 2006;86(4):1151-1178.
[37]Brickley DR, Mikosz CA, Hagan CR,et al. Ubiquitin modification of serum and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase-1 (SGK-1).J Biol Chem. 2002;277(45):43064-43070.
[38]Klaus F, Palmada M, Lindner R,et al. Up-regulation of hypertonicity-activated myo-inositol transporter SMIT1 by the cell volume-sensitive protein kinase SGK1. J Physiol. 2008; 586(6):1539-1547.
[39]Mauro TM, McCormick JA, Wang J, et al. Akt2 and SGK3 are both determinants of postnatal hair follicle development. FASEB J. 2009;23(9):3193-3202.
[40]Campagna DR, Custodio AO, Antiochos BB, et al. Mutations in the serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 3 (Sgk3) are responsible for the mouse fuzzy (fz) hair phenotype. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128(3):730-732.
[41]Mauro TM, McCormick JA, Wang J,et al. Akt2 and SGK3 are both determinants of postnatal hair follicle development. FASEB J. 2009;23(9):3193-3202.
[42]Maier G, Palmada M, Rajamanickam J,et al. Upregulation of HERG channels by the serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase isoform SGK3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2006;18(4-5): 177-186.
[43]Wang Y, Zhou D, Phung S,et al. SGK3 is an estrogen-inducible kinase promoting estrogen-mediated survival of breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25(1): 72-82.
[44]Xu J, Liao L, Qin J, et al. Identification of Flightless-I as a substrate of the cytokine-independent survival kinase CISK.J Biol Chem. 2009;284(21):14377-14385.
[45]Jin Q, Esteva FJ. Cross-talk between the ErbB/HER family and the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008;13(4):485-498.
[46]Fagan DH, Yee D. Crosstalk between IGF1R and estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008;13(4):423-429. |
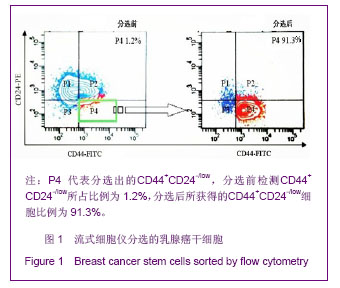

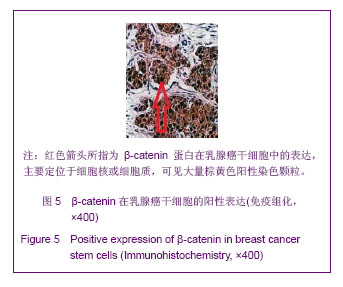
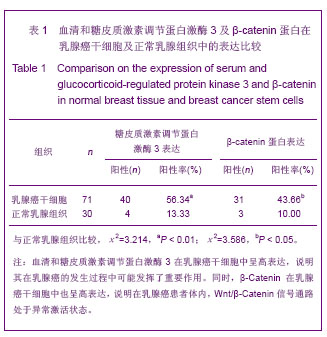
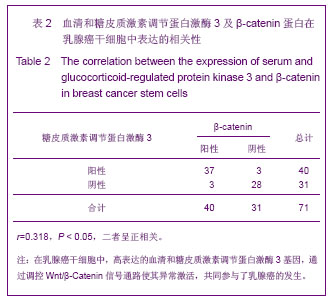
.jpg)