中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (37): 6587-6593.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.37.008
• 神经组织构建 nerve tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
长期置入骶神经根刺激电极的兔组织学变化及其安全性
闫 鹏1,郑伟东1,张季凯1,谭云冰1,李高峰1,李光淳1,宋 成1,杨小玉2
- 1吉林省人民医院脊柱外科,吉林省长春市 130021
2吉林大学中日联谊医院骨科,吉林省长春市 130021
Histological changes and safety of long-term acral nerve root stimulation electrode placement in rabbits
Yan Peng1, Zheng Wei-dong1, Zhang Ji-kai1, Tan Yun-bing1, Li Gao-feng1, Li Guang-chun1, Song Cheng1, Yang Xiao-yu2
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, Jilin Province People's Hospital, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
2Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
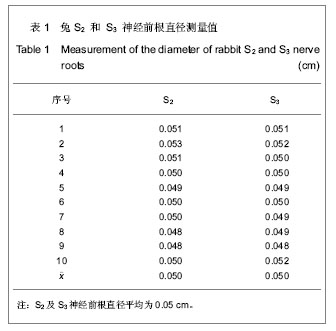
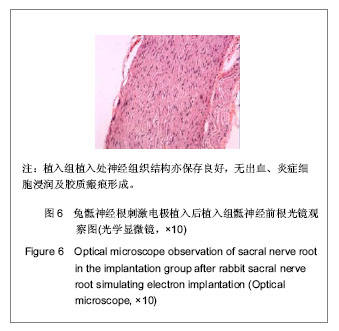
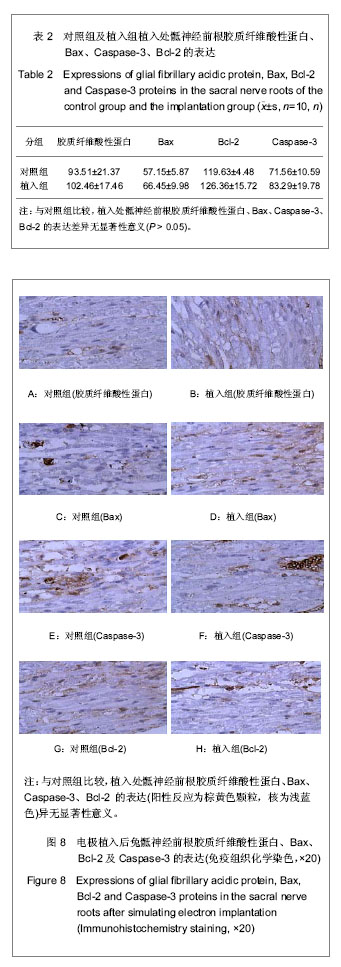
背景:有研究表明基于阳极阻滞技术的骶神经根刺激器能有效重建脊髓损伤兔的膀胱排尿功能,但符合此技术的刺激电极至今未见报道。 目的:设计并研制既与兔骶神经根匹配又符合阳极阻滞技术的刺激电极,观察长期植入刺激电极的兔骶神经根超微结构及病理形态学变化,评估刺激电极安全性。 方法:纳入新西兰兔30只,随机抽取10只兔切取双侧S2及S3神经前根,光镜下测量其直径后,制成与其直径相匹配的套筒型刺激电极。将剩余20只兔随机分为对照组及植入组,每组10只。植入组麻醉后将刺激电极植入S2及S3神经根前处,饲养半年后处死取材,观察植入处骶神经根超微结构变化。 结果与结论:长期植入该刺激电极后,光学显微镜下见植入组植入处骶神经根神经细胞结构保存良好,轴突无明显变性,无炎症细胞浸润及胶质瘢痕形成;透射电镜下观察,植入组髓鞘排列紧密,无脱髓鞘现象,神经元无核萎缩、核凹陷和异染色质增多等现象。免疫组织化学染色显示,与对照组相比,植入组植入处神经根中胶质纤维酸性蛋白、Bax,Bcl-2和Caspase-3蛋白表达差异无显著性意义。结果说明实验成功研制了兔骶神经根刺激电极,长期植入骶神经根未出现组织病理学改变及无细胞凋亡现象,安全性好。
中图分类号:


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)