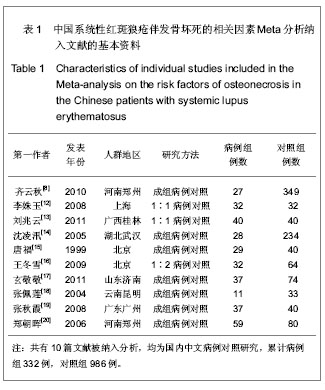
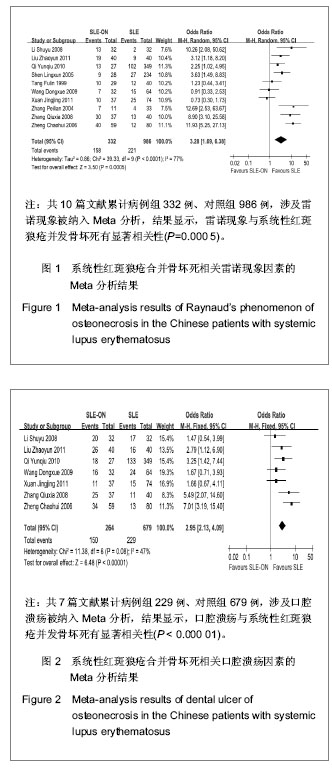
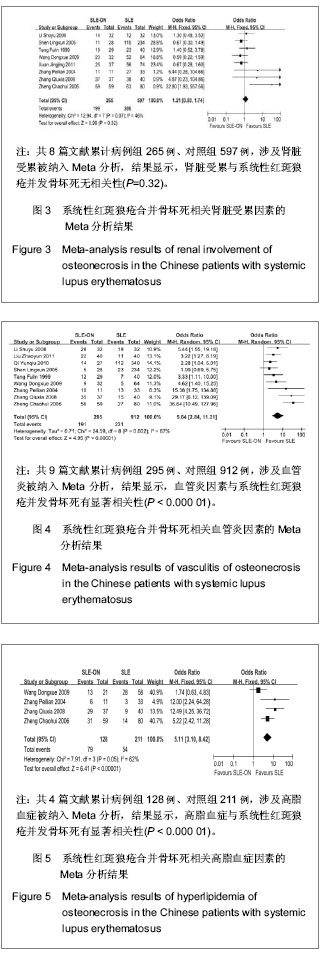
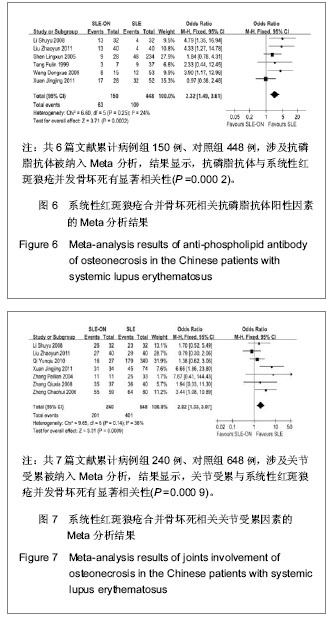
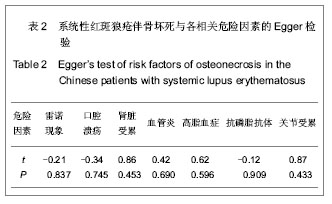
| [1] Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(22): 2110-2121.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22129255[2] Pickering MC, Botto M, Taylor PR, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus, complement deficiency, and apoptosis. Adv Immunol. 2001;76: 227-324.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11079100[3] Gordon C. Long‐term complications of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41(10): 1095-1100.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12364626[4] D'Cruz DP, 张卓莉. 系统性红斑狼疮[J]. 英国医学杂志: 中文版, 2006, 9(4): 236-241.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=12&CurRec=8&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=YGYX200604022&urlid=&yx=[5] Jones LC, Hungerford DS. The pathogenesis of osteonecrosis. Instr Course Lect. 2007;56:179-196.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Jones+L+C%2C+Hungerford+D+S.+The+pathogenesis+of+osteonecrosis%5BJ%5D.+Instructional+course+lectures%2C+2007%2C+56%3A+179.[6] Zizic TM, Hungerford DS, Stevens MB. Ischemic bone necrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. II. The early diagnosis of ischemic necrosis of bone. Medicine. 1980;59(2): 134-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7360041[7] Abu-Shakra M, Buskila D, Shoenfeld Y. Osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2003;25(1): 13-24.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?cmd=HistorySearch&querykey=7[8] 齐云秋, 程敬亮, 潘芦翎, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮患者并发股骨头坏死危险因素研究[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2010, 27(12): 1937-1939.http://210.45.242.22/WFknowledgeServer_Mirror/D/Periodical_zhsywk201012060.aspx[9] Johnson AE, Gordon C, Palmer RG, et al. The prevalence and incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus in Birmingham, England. Relationship to ethnicity and country of birth. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(4): 551-558.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7718010[10] Hedges LV, Pigott TD. The power of statistical tests in meta-analysis. Psychol Methods. 2001;6(3):203-217.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=(%22Psychological%20methods%22%5BJournal%5D)%20AND%20Fixed-and%20random-effects%20models%20in%20meta-analysis[11] Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109): 629-634.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Egger+M%2C+Smith+G+D%2C+Schneider+M%2C+et+al.+Bias+in+meta-analysis+detected+by+a+simple%2C+graphical+test%5BJ%5D.+Bmj%2C+1997%2C+315(7109)%3A+629-634.[12] 李姝玉, 胡大伟. 系统性红斑狼疮并发无菌性股骨头坏死的相关因素分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2008, 14(5): 324-327.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=3&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=ZGZS200805007&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdkF0Rk4yakozWGhobUVseDZVRTNVOXZhQ3NFTGFsWU1YK0NlbU1RTzM1eUxpdSs0PQ==[13] 刘兆云, 赵铖, 米存东, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头缺血性坏死相关因素分析[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2011, 27(7): 1226-1228.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=9&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD1112&filename=SYYZ201107041&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdkF0Rk4yakozWGhobUVseDZVRTNVOXZhQ3NFTGFsWU1YK0NlbU1RTzM1eUxpdSs0PQ==[14]沈凌汛, 夏菲, 余立凯, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮患者并发无菌性骨坏死的调查分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2005, 9(1):20-23.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=3&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0305&filename=FSBZ200501007&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhcEFjU3VlY3FPeExNZlpyYVNGRWFZM0FKd2kwbEJhc2RRNGhwV2ttOTFMRTMvLzk4PQ==[15] 唐福林, 金聂, 吴敏, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发无菌性骨坏死的危险因素分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 1999, 3(3):166-168.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=3&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD9902&filename=FSBZ199903010&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[16]王冬雪, 李桂叶, 马丽, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发无菌性股骨头坏死的临床研究[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2009, 48(11):926-929.http://210.45.242.22/WFknowledgeServer_Mirror/D/Periodical_zhnk200911009.aspx[17]玄敬敬, 张源潮, 杨清锐. 系统性红斑狼疮合并无菌性股骨头坏死的危险因素分析[J]. 山东大学学报: 医学版, 2011, 49(3):109-114.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=23&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD1112&filename=SDYB201103027&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[18]张佩莲, 冒长峙, 李学平, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死11例[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2004, 37(6):366.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=28&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0305&filename=ZHPF200406026&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[19]张秋霞, 陈镇秋. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头缺血性坏死的相关性临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2008, 40(8):27-28.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=34&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=REND200808018&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[20]郑朝晖, 赵占正, 刘章锁. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头坏死相关因素分析[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2006, 6(17):3311-3312.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=38&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=ZWZX200617024&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[21] Asherson RA, Liote F, Page B, et al. Avascular necrosis of bone and antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(2): 284-288.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8474066[22] Gladman DD, Chaudhry-Ahluwalia V, Ibañez D, et al. Outcomes of symptomatic osteonecrosis in 95 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(10): 2226-2229.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Gladman+DD%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+Outcomes+of+symptomatic+osteonecrosis+in+95+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus[23] Sayarlioglu M, Yuzbasioglu N, Inanc M, et al. Risk factors for avascular bone necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(1): 177-182.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Sayarlioglu+M%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+Risk+factors+for+avascular+bone+necrosis+in+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus[24] Weinstein RS. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis. Endocrine. 2012;41(2): 183-190.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22169965[25] Assouline-Dayan Y, Chang C, Greenspan A, et al. Pathogenesis and natural history of osteonecrosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002;32(2): 94-124.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=(Assouline-Dayan%20Y%5BAuthor%5D)%20AND%20(Pathogenesis%20and%20natural%20history%20of%20osteonecrosis)[26] Jones JP Jr. Intravascular coagulation and osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;277: 41-53.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1532547[27] Oinuma K, Harada Y, Nawata Y, et al. Osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus develops very early after starting high dose corticosteroid treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(12): 1145-1148.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11709458[28] Colwell CW Jr, Robinson CA, Stevenson DD, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients with inflammatory arthritis or asthma receiving corticosteroid therapy. Orthopedics. 1996;19(11): 941-946.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8936529[29] Mok CC, Lau CS, Wong RW. Risk factors for avascular bone necrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol.1998;37(8): 895-900.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9734682[30] Leventhal GH, Dorfman HD. Aseptic necrosis of bone in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1974;4(1): 73-93.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4846262[31] Fialho SCMS, Bonfa E, Vitule LF, et al. Disease activity as a major risk factor for osteonecrosis in early systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2007;16(4): 239-244.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Fialho+SCMS%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+(Disease+activity+as+a+major+risk+factor+for+osteonecrosis+in+early+systemic+lupus+erythematosus)[32] Sari RA, Polat MF, Taysi S, et al. Serum lipoprotein (a) level and its clinical significance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2002;21(6): 520-524.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Sar%C4%B1+RA%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+(Serum+lipoprotein+(a)+level+and+its+clinical+significance+in+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus)[33] Houssiau FA, Toukap ANZ, Depresseux G, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-detected avascular osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: lack of correlation with antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37(4): 448-453.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Magnetic+resonance+imaging-detected+avascular+osteonecrosis+in+systemic+lupus+erythematosus%3A+lack+of+correlation+with+antiphospholipid+antibodies[34] Mok MY, Farewell VT, Isenberg DA. Risk factors for avascular necrosis of bone in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Is there a role for antiphospholipid antibodies? Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(6): 462-467.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Risk+factors+for+avascular+necrosis+of+bone+in+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus%3A+Is+there+a+role+for+antiphospholipid+antibodies[35] Tektonidou MG, Malagari K, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, et al. Asymptomatic avascular necrosis in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome in the absence of corticosteroid use: a prospective study by magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(3): 732-736.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Asymptomatic+avascular+necrosis+in+patients+with+primary+antiphospholipid+syndrome+in+the+absence+of+corticosteroid+use%3A+a+prospective+study+by+magnetic+resonance+imaging[36] Nagasawa K, Ishii Y, Mayumi T, et al. Avascular necrosis of bone in systemic lupus erythematosus: possible role of haemostatic abnormalities. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989;48(8): 672-676.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2506841[37] Nagasawa K, Tada Y, Koarada S, et al. Prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus by anti-coagulant. Lupus. 2006;15(6): 354-357.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16830881[38] Smith FE, Sweet DE, Brunner CM, et al. Avascular necrosis in SLE. An apparent predilection for young patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976;35(3): 227-232.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Avascular+necrosis+in+SLE.+An+apparent+predilection+for+young+patients[39] Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Chaudhry-Ahluwalia V, et al. Predictive factors for symptomatic osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(4): 761-765.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11327247[40] Calvo-Alén J, McGwin G, Toloza S, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA): XXIV. Cytotoxic treatment is an additional risk factor for the development of symptomatic osteonecrosis in lupus patients: results of a nested matched case–control study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(6): 785-790.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Systemic+lupus+erythematosus+in+a+multiethnic+US+cohort+(LUMINA)%3A+XXIV.+Cytotoxic+treatment+is+an+additional+risk+factor+for+the+development+of+symptomatic+osteonecrosis+in+lupus+patients%3A+results+of+a+nested+matched+case%E2%80%93control+study[41] DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3): 177-188.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed |