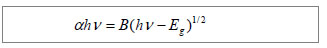X-ray diffraction characteristics, ultrastructure and ζ potential of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites
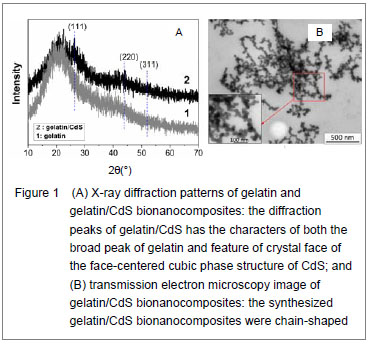
X-ray diffraction patterns of gelatin and the prepared gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites are presented in Figure 1A. Comparing with the broad peak of gelatin, the diffraction peaks of gelatin/CdS were broad and weak, and three main peaks at 2θ of 26.30°, 43.95°, and 52.03° were characteristics to the (111), (220) and (311) directions of the face-centered cubic phase structure of CdS, respectively. It could be well matched with the standard values (JCPDS Card No. 10-454). The positions of the peaks were in good agreement with literature values
[8]. This result confirmed the existence of CdS nanoparticle as final product in gelatin. Microscopic observation showed that the size of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites was uniform with average diameters around 25 nm, and they were chain-shaped (Figure 1B). The same conclusions have been found by Sreekumari
et al [9] and Oluwafemi
et al [10] for preparation of the polyacrylamide-PbS nanocomposites, and gelatin capped Ag nanoparticles, respectively.
When the concentrations of gelatin and S
2- ion were 4.0×10
-5 and 2.0×10
-3 mol/L, respectively, the ζpotentials of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites were estimated to be circa -19.9, -19.4, -18.9 and -17.6 mV corresponding to the 0.0, 1.0×10
-4, 4.0×10
-4, and 1.4×10
-3 mol/L of Cd
2+. In another word, the ζ potentials of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites were decrease with the increasing concentration of CdS.
 Optical properties of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites
Optical properties of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites
Figure 2A shows the optical transmission spectra of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites for different concentrations of Cd
2+. The optical transmittances of all the samples could reach to above 90% beyond the wavelength of 500 nm. It was observed that a shift toward longer wavelength with the increasing concentration of Cd
2+. According to the related theories of semiconductor materials, the relation connecting the absorption coefficient
α, the incident photon energy
hv and optical band gap
Eg obey Tauc’s formula
[11]:
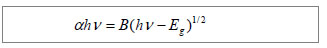
Where B was a constant. The band gaps have been calculated by extrapolating the linear region of the plots (
αhν)
2 vs.
hν on the energy axis, as shown in Figure 2B, which were higher than that of the bulk CdS (2.42 eV at 27
℃)[12]. The decreasing of band gap with the increase in Cd2+ concentration at different temperatures was observed as shown in Figure 2C.
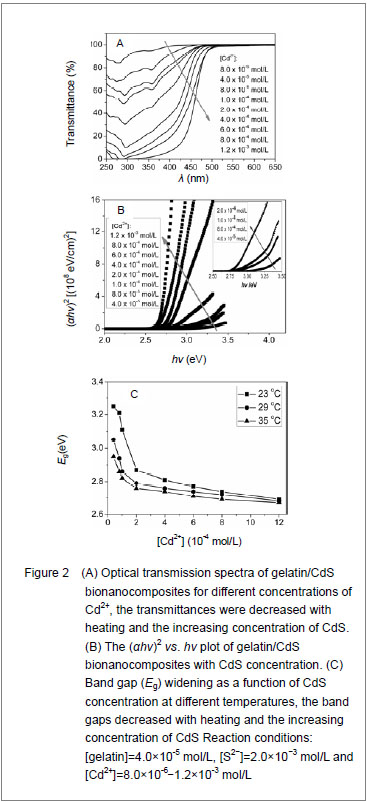
It was clear that the band gaps decreased due to an increasing of particle size with heating and the increasing concentration of Cd
2+, and this was known as the quantum size effect
[13-14]. The lower
Eg value corresponded to the higher temperature, which indicated that the increasing temperature was favorable to the increasing of particle size, as predicted by the kinetic and the thermodynamic behavior of growth of CdS nanoparticles
[15]. The similar phenomenon was observed for the synthesis of the mercaptoacetic acid modified CdSe quantum dots and the gelatin-PbS nanocomposites by Mi
et al [16], and Wang
et al [17], respectively.
Conformational change of gelatin
The binding of protein to nanoparticles often induced significant changes in secondary structure, which made it essential to understand the effect of nanoparticles on fundamental biological process
[18]. The amideⅠband (1 600-1 700 cm
-1) has been widely used for conformational studies
[19]. To visualize the spectral changes more clearly, deconvolution of the amideⅠband was used for further analysis of the actual deformation on gelatin structure. The component peaks, their location and percentage of areas are showed in Figure 3 and Table 1. It was clear from the significantly differing band shapes and the shift of the peak maxima that the conformations of gelatin have changed due to its interaction with the Cd
2+ and CdS.
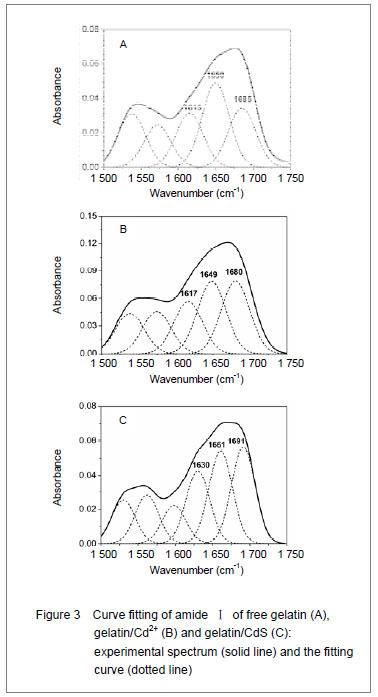
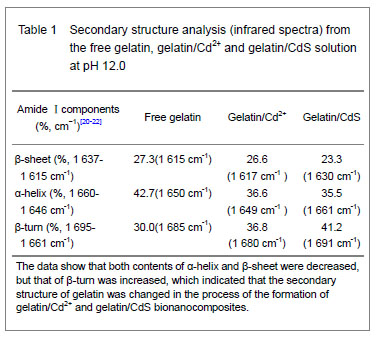
Curve fitting analysis of component bands showed that gelatin lose a large percentage of its α-helix and β-sheet characters
[23], showed by a decreasing in the percentage of area of the component band centered at 1 650 and
1 615 cm-1, respectively. In contrast, the fraction of β-turn was 30.0% in pure gelatin but increased up to 36.8% in gelatin/Cd2+ solution, and increased to 41.2% in gelatin/CdS solution (Table 1), respectively. These findings indicated that Cd2+ and CdS combined with gelatin, could weaken or break the hydrogen bond, respectively. In other words, the formations of gelatin/Cd2+ complex and gelatin/CdS nanocomposites resulted in that the secondary structures of gelatin were changed from α-helix and β-sheet to β-turn, and the peptide chains of gelatin macromolecules were stretched. This changed conformation of the gelatin formed a configuration, which was well suitable for the formation of gelatin/Cd2+, and also the growth of CdS nanoparticles in gelatin matrix[24]. Similar feature that has been previously reported for the formation of CdS nanocrystals in pepsin solution by Yang et al [25]. The conformational changes may affect the biological function of gelatin protein[26-27].
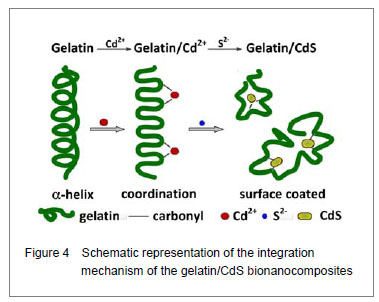
Integration mechanism of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites
Based on the results of discussion above, the schematic representation of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites formation is illustrated in Figure 4. It was speculated that the synthesis reaction of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites consisted of two steps as follows: First, there was a coordination interaction between the Cd
2+ and carbonyl group (C=O) in gelatin macromolecular peptide chain to form initial precursor complexes (gelatin/Cd
2+), and gelatin played the roles as oxygen source and structure-directing reagents
[5]. At the same time, the interaction caused the gelatin conformation change from α-helix to β-turn, and the β-turn secondary structure formed a suitable conformation for the oriented growth of CdS nanoparticles. Second, when the S
2− was added to gelatin/Cd
2+ solution, the gelatin/Cd
2+ interacted with S
2− to form gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites, and the excess S
2− could be adsorbed on the surface of CdS nanoparticles
[18, 28]. In this reaction process, gelatin macromolecular conformation was changed from α-helix and β-sheets to β-turns, and coated on the surface of CdS nanoparticles, which may foreshow the biological functional change of protein.